Understanding depreciation is crucial for safeguarding your fixed assets as well as the financial well-being of your company.
Neglecting it, on the other hand, can spell trouble.
Fear not, though, because this article is your guide to mastering the art of managing and calculating depreciation.
Packed with clear insights and practical tips, we’ll take you step-by-step through the process, empowering you to navigate the intricate landscape of fixed asset valuation with confidence and ease.
Let’s start with the basics.
In this article...
Identify Your Fixed Assets
The very first step is to make sure you’re keeping track of all your fixed assets.
This includes the heavy machinery, vehicles, tools, safety equipment, and all other property you use to make a profit, and that has a life span of more than a year.
Such assets can be found on the company’s balance sheet under the Property, Plant, and Equipment classification.
Consumable items you don’t use for long-term production, like fuel, lubricants, or office supplies, are, therefore, not considered fixed assets.
Knowing what equipment you have, how much of it there is, and where it is is obviously a must for any successful business, but not many realize just how important keeping accurate records is when it comes to managing property throughout its lifecycle, including tracking depreciation.
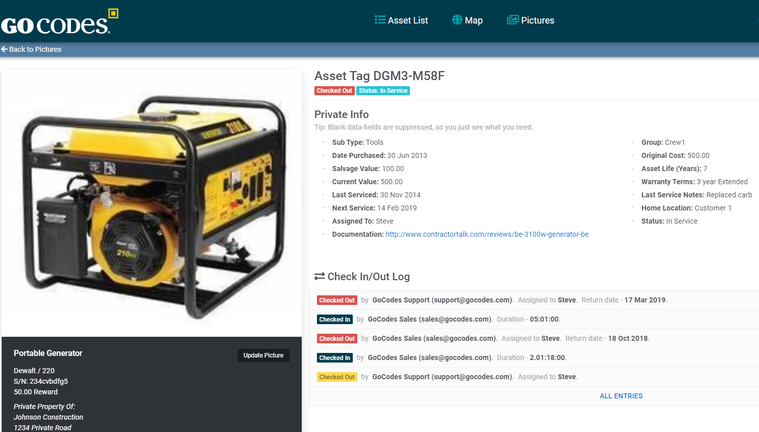
A robust and up-to-date database that keeps a record of all the vital data, such as the original price, salvage value, and date of purchase, is invaluable for your accounting team since it serves as the foundation for precise depreciation calculations.
In simpler terms, incorrect data results in miscalculated depreciation.
So, how do you ensure that the information you have is accurate?
You use a reliable asset tracking method.
Manual methods like spreadsheets and paper forms are highly inefficient and prone to human error.
In fact, one quick Google search, and you’ll find numerous stories about Excel mistakes turning out to be quite costly.
Instead, consider automating the whole process and using asset management software like GoCodes Asset Tracking.
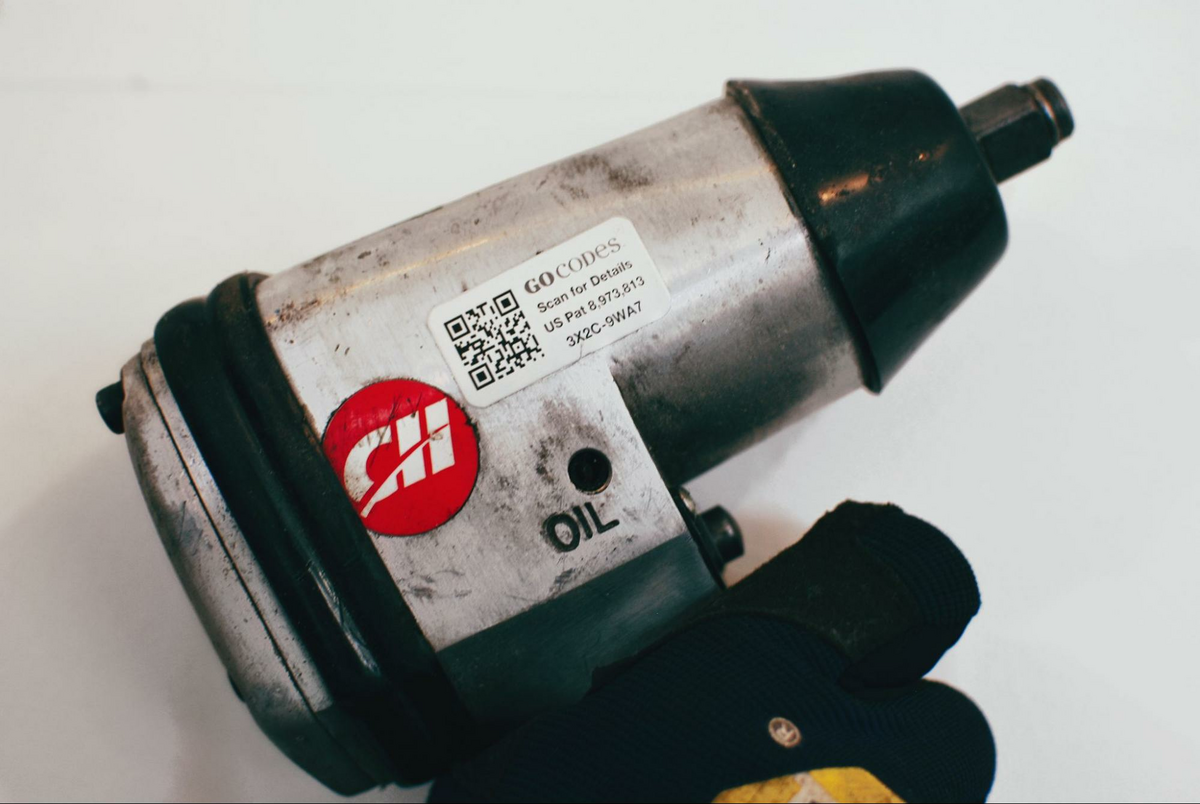

Our system consists of only two components: QR code labels or tags and a scanner app.
Labels are attached to the machines and tools you want to monitor and then scanned via the app to update asset data in real time.
So, every time a worker scans the label to, say, check a machine in or out, the location of the update will be automatically recorded, safely stored in the cloud, and readily available on any internet-connected device.
The result?
Easily searchable, thorough, and up-to-date database of all your fixed assets.
Determine Which Fixed Assets to Depreciate
Once all the machinery, tools, and equipment are accounted for and identified, it’s time to move on to the next step.
Since it wouldn’t be the smartest move to try to depreciate each and every one of your fixed assets, it’s necessary to determine which ones are eligible for depreciation.
First, let’s take a look at the criteria a property must meet to be considered depreciable. It must be:
- It must be a property you own
- It must be used to generate income for your business
- It must have a useful life that can be determined
- Its expected useful life must be more than one year
Generally, businesses depreciate high-value equipment that will be used to turn a profit for much longer.
On the other hand, low-cost, short-term-use items are typically excluded from the depreciation process.
After you make the decision, the next step will be to fill out and submit the IRS form 4562, outlining all the details about the purchased machine, including how much you paid for it, and the period over which you’ll depreciate it.
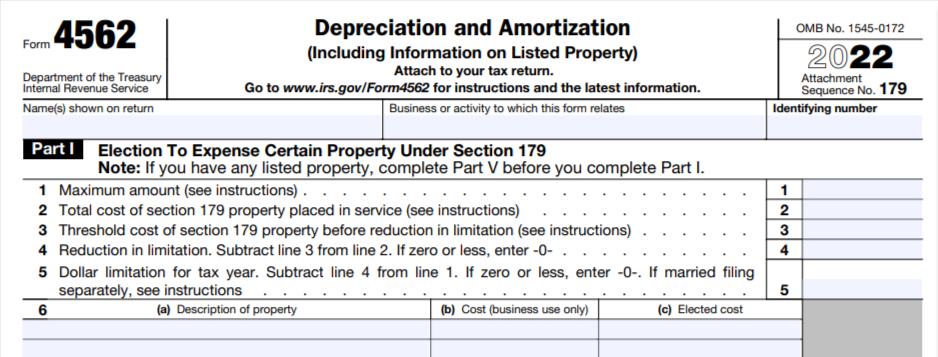
This form will be used to claim deductions for the depreciation or amortization of an asset.
Bear in mind that the IRS has predefined depreciation periods for various asset types, such as, for example, a five-year period for vehicles and computers, and a 27 ½ year period for residential rental property.
Overall, understanding and adhering to the IRS guidelines can help you optimize the timing and amount of depreciation deductions, potentially reducing your taxable income and lowering tax liability.
Define Your Depreciation Factors
So, what are the key factors in depreciation tracking?
What information do you need in order to calculate the rate at which your assets will depreciate?
There are several important elements to consider, the first one being the original cost of a machine.
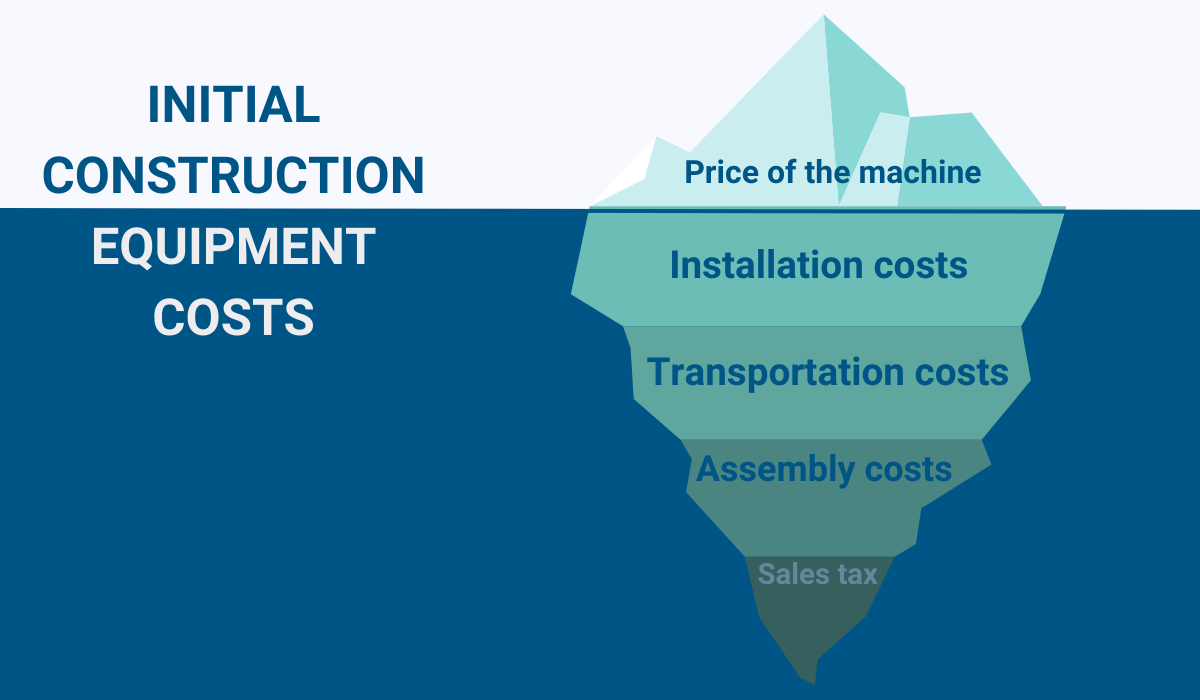
Extending beyond just the purchase price to include expenses such as installation, assembly, or transportation costs, as well as the sales tax, this factor reflects how much money in total was invested to make that piece of equipment operational.
Another key factor is the salvage value, representing the anticipated monetary return from selling the machine at the conclusion of its useful life.
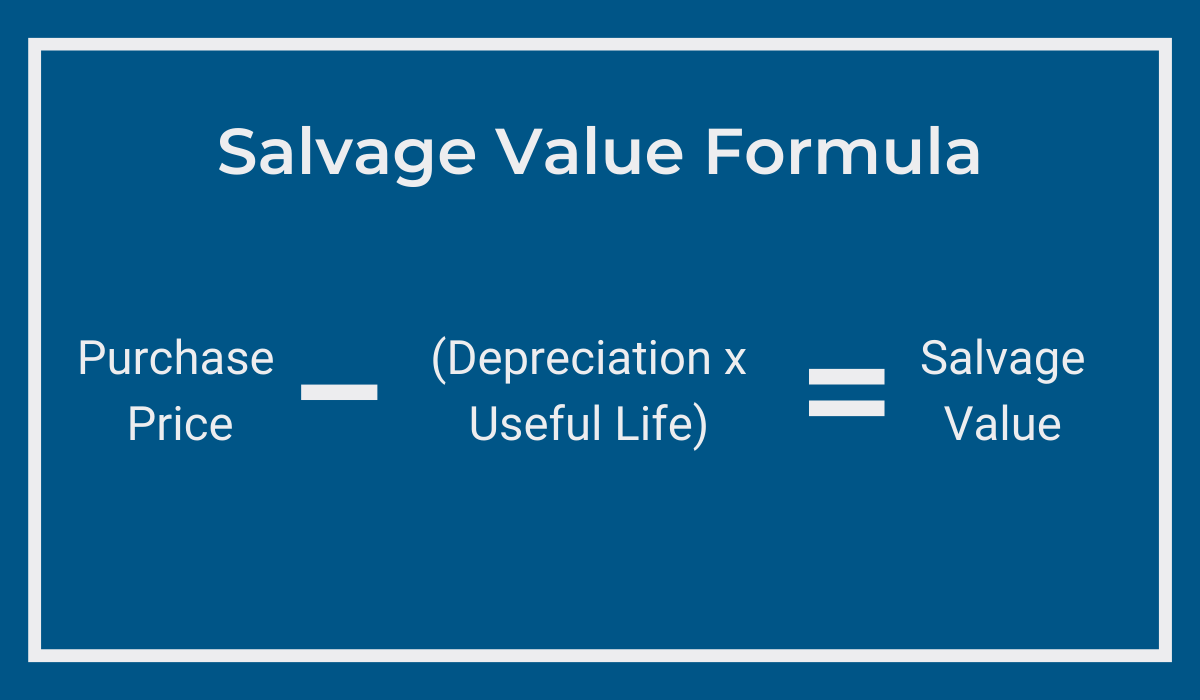
Calculating this element involves multiplying the annual depreciation by the expected useful life and subtracting this resulting number from the original cost.
In short, salvage value provides insights into the residual worth of the asset.
Book value, primarily used for tax purposes, refers to the value of an asset as recorded on a company’s financial statements, specifically on the balance sheet.
Lastly, the expected equipment lifetime is a forward-looking estimate, projecting the duration during which the asset is anticipated to generate revenue before reaching full depreciation.
Here, we’re not talking about how many years, months, or hours a piece of equipment will exist, but instead, this estimate shows how long the machine will be able to remain functional and productive in its intended capacity.
All in all, these factors collectively form the foundation for a comprehensive understanding of depreciation and are, therefore, indispensable in effective asset management.
Decide on the Depreciation Method
When it comes to recording fixed asset depreciation, the choice of method is a crucial decision that carries long-term implications.
Once a strategy is selected, changing it requires the approval of the IRS, underscoring the importance of careful consideration beforehand.
Seeking advice from your accounting department is paramount during the decision-making process.
Now, let’s take a look at the most common depreciation methods.
The most popular, as well as the simplest one, is called the straight-line method, which evenly distributes depreciation expenses annually until the asset reaches its salvage value.
Here’s how it’s calculated.
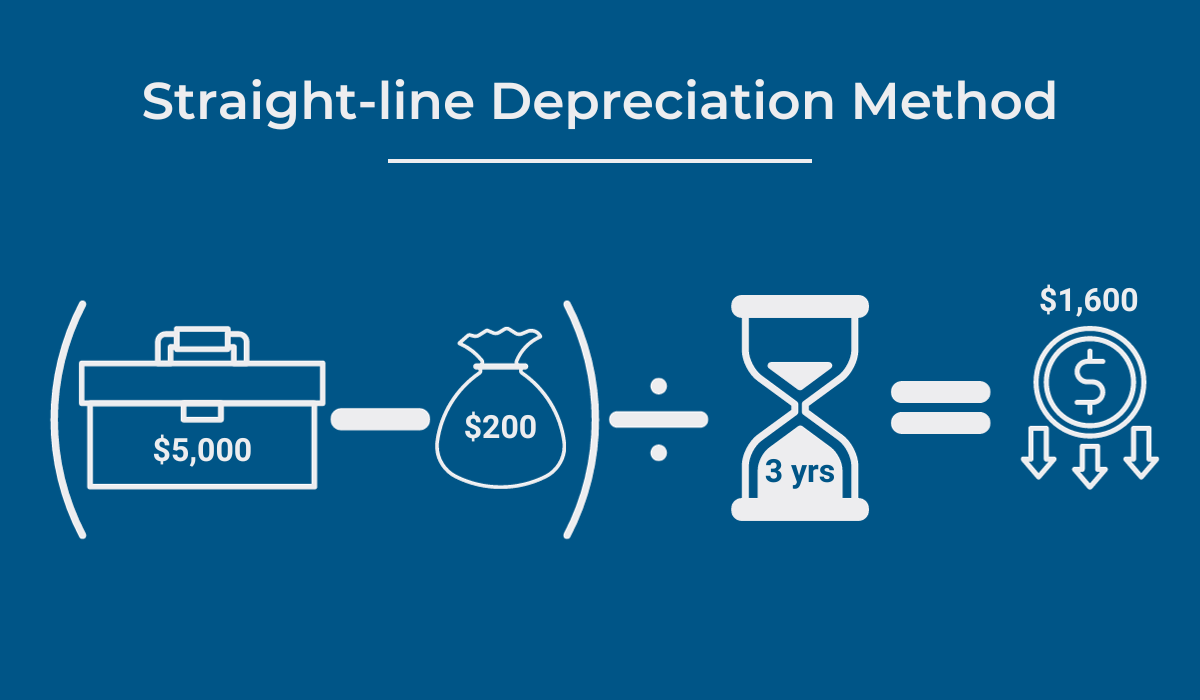
To illustrate, if a piece of equipment is acquired for $5,000, with a salvage value of $200 and a useful life of 3 years, the annual depreciation using this approach would be $1,600.
The declining balance is an accelerated method of calculating depreciation and it’s particularly advantageous for smaller businesses since it allows them to deduct larger amounts at the beginning of a machine’s useful life, reducing tax liabilities and strengthening cash reserves.
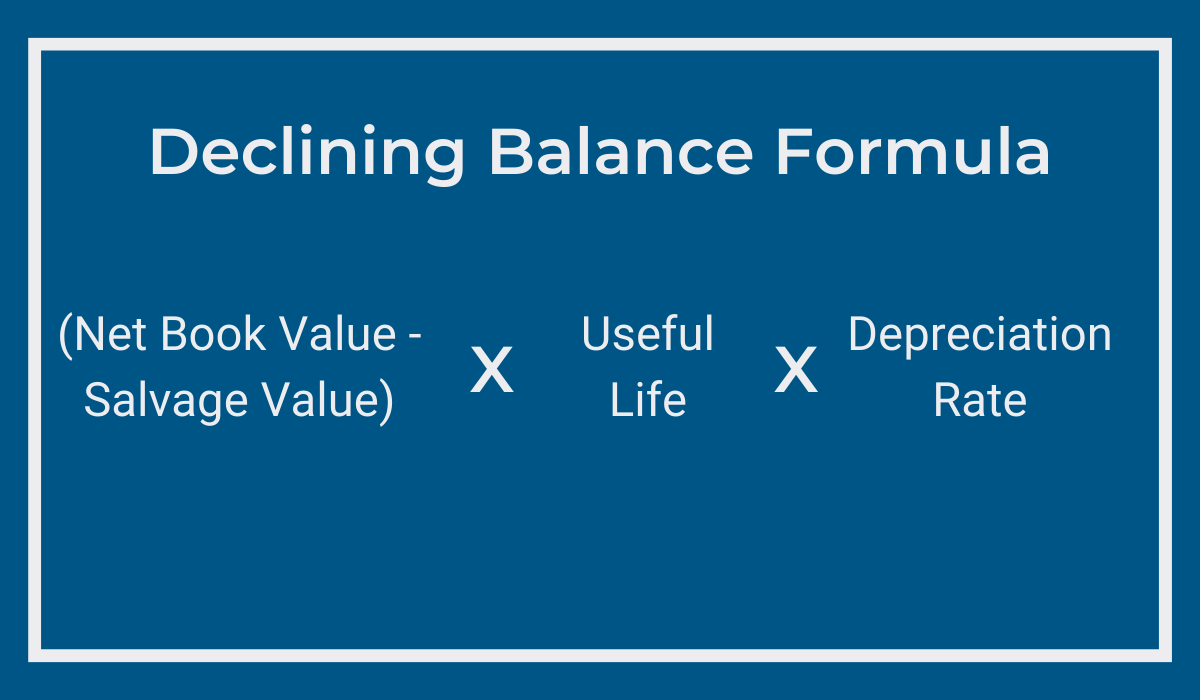
In this method, assets depreciate by the same amount as with the straight-line approach, but expenses are higher in the initial years and decrease over time, with a higher depreciation rate during the asset’s early, higher-value period.
Taking acceleration a step further, the double-declining balance method essentially doubles the useful life value, making it twice as fast as the straight-line rate.
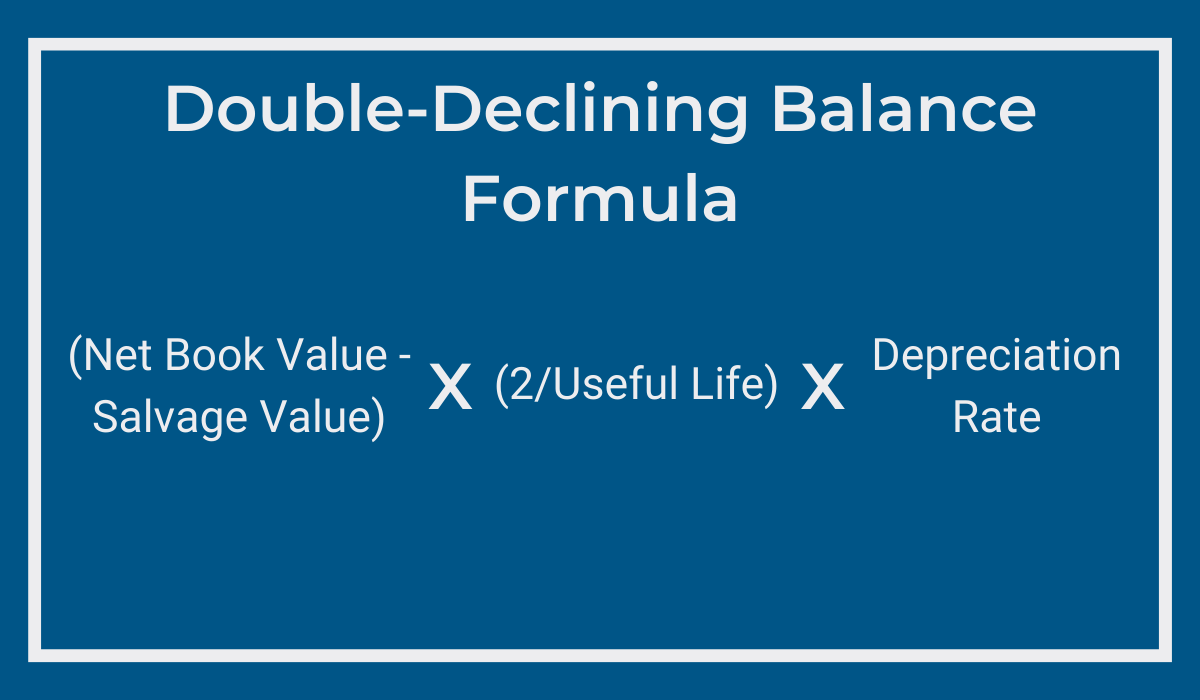
This accelerated approach is well-suited for those looking to front-load depreciation costs.
While some alternative strategies, such as the sum-of-the-year’s digits or units of production, exist, the straight-line and declining balance methods remain the most commonly embraced approaches.
These other techniques are generally used less frequently, but ultimately, the choice of the depreciation method depends on various factors.
You have to consider what kind of asset you’re dealing with, which financial requirements and tax considerations you have to take into account when doing so, as well as which financial goals the company is striving towards, and how.
Use Software to Calculate Fixed Asset Depreciation
Navigating through a sea of numbers and intricate formulas may initially seem overwhelming, but understanding and managing depreciation offers a multitude of benefits for a company’s financial well-being.
From bringing stability to your finances and enabling accurate asset value estimates, to helping with equipment replacement and maintenance planning, tracking assets’ decrease in value is important for many different facets of business operations.
Luckily, the once daunting task of calculating depreciation has been simplified with equipment management solutions like GoCodes Asset Tracking.
Our system, along with providing a complete and accurate asset list, streamlines the entire depreciation process, providing user-friendly calculations tailored to the most prevalent fixed asset scenarios, and employing widely recognized IRS MACRS schemes.
Input the necessary data, like the cost value or estimated useful life, and the software seamlessly generates reports in a Microsoft Excel-compatible .csv file format.
These reports provide a comprehensive list of your machinery and tools, accompanied by essential depreciation data, such as:
- The prior year’s depreciation
- The current year’s depreciation
- The total depreciation across all years
- The remaining balance to be depreciated
Notably, these calculations adhere to the conventions outlined in the US IRS publication 946, making them suitable for financial statement filings and tax returns.
GoCodes Asset Tracking ensures that its users can confidently tackle common asset depreciation scenarios with ease, all while conforming to the IRS-mandated half-year (HY) convention.
Conclusion
Hopefully, this article managed to demystify the fixed asset depreciation process.
As illustrated, it involves a systematic approach, starting with diligent equipment tracking and management.
Remember, accurate data is key.
So, update your records regularly, make sure your team is aware of their role in compiling asset information, work in tandem with the accounting department, and consider relying on modern tools that can automate the process.
As a result, your depreciation game will be taken to a whole new level.