In the dynamic world of construction, technology is rapidly reshaping the way projects are planned, executed, and managed.
From the simplicity of QR codes and mobile technology to the complexity of artificial intelligence and building information modeling, innovation lies at the heart of improving construction operations.
In this article, we’ll explore six key technologies and how they can help your construction company streamline operations, enhancing productivity and safety across your jobsites.
In this article...
QR Codes
We’ll start with the simplest and most affordable technology that can help you improve construction workflows in various ways—quick response (QR) codes.
These advanced barcodes were created nearly 30 years ago, and since then have found numerous applications in many different industries, including construction.
You can think of QR codes as gateways into the world of digital information.
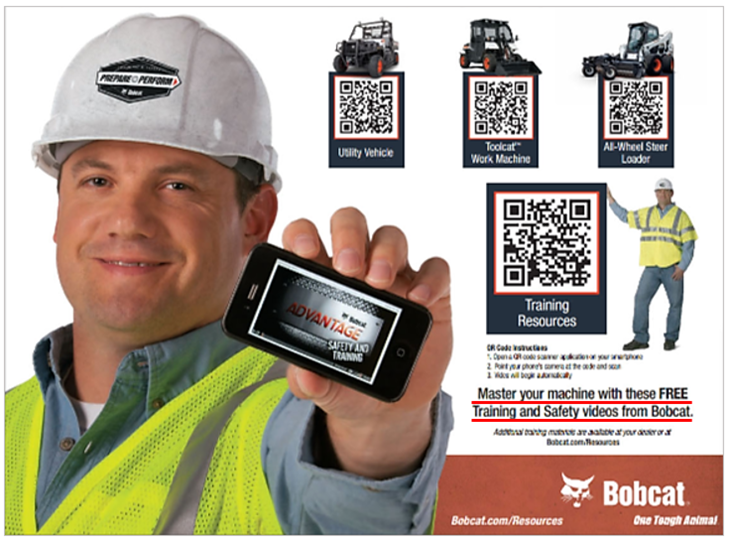
When you scan a QR code, you’re instantly taken to a particular online destination, whether it’s a website, an interactive map, or a video tutorial, like in this example.

Additionally, when QR codes are paired with a dedicated software app, a simple scan can allow you to view and update relevant equipment info, such as its purchase date, maintenance and usage history, and other relevant data.
This functionality opens up a multitude of opportunities to improve your construction operations, such as:
- tracking users of your equipment, tools, and other assets (check-in/check-out system)
- tracking their locations (automatic, scan-based GPS tracking)
- scheduling maintenance and assigning work orders
- performing asset audits
For instance, our QR code-based asset-tracking software, GoCodes Asset Tracking, allows you to do all the above and more, as shown here.
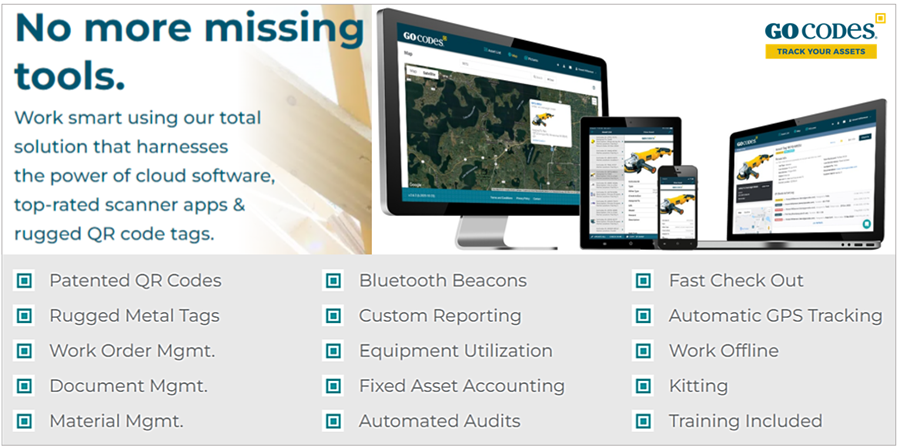
As you can see, GoCodes Asset Tracking utilizes cloud software, patented QR codes, and an in-app scanner that enable construction companies to use multiple, software-generated features and take advantage of the benefits they bring.
When QR codes are attached to assets, and the software’s database is filled with initial data, workers can simply scan a QR code label or tag with their smartphone or tablet to access individual equipment data and the central inventory of assets.
You can see this process in action here.
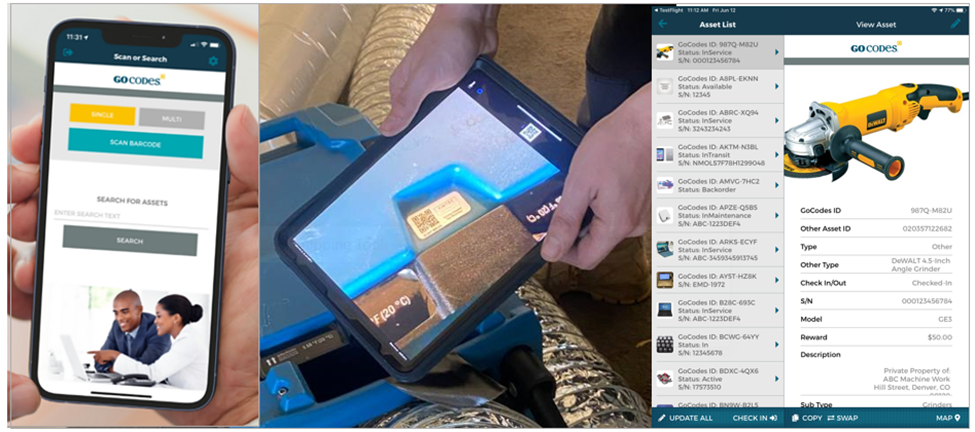
Moreover, every time an asset tag is scanned, the software will use the scanning device’s GPS locator to automatically record the asset’s location.
When these automatic location updates are coupled with an automated check-in/check-out system (that tracks asset users), this maximizes worker accountability and productivity and minimizes asset loss and theft.
Given the exceptional versatility, simplicity, and affordability of QR codes (and accompanying software), this technology is increasingly used by construction companies to streamline the way workers access information and perform various construction tasks.
Artificial Intelligence
Despite the current craze about ChatGPT and other artificial intelligence (AI) assistants, this technology has been present in the construction industry for a long time.
For example, some companies use AI-driven systems to analyze vast amounts of data from construction projects, identifying patterns and trends that might go unnoticed by human analysts.
This helps construction companies achieve improvements like more accurate project cost estimations, optimal resource allocation, and comprehensive risk assessment.
Of course, AI is an evolving, fast-developing technology, meaning that its potential uses in the construction industry are still largely untapped.
Below you can see some construction domains where AI applications can streamline operations, courtesy of Science Direct.
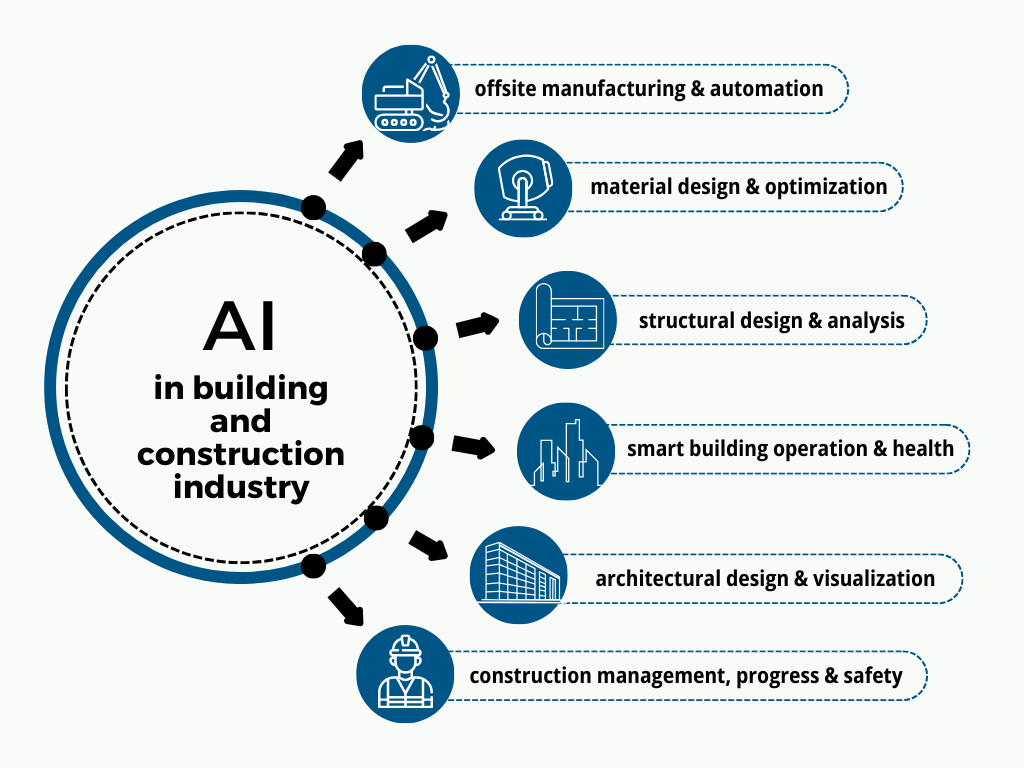
As you can see, there is almost no aspect of construction that can’t be improved with the help of AI-powered tools.
Moreover, remote-controlled and still emerging autonomous (self-driving) construction vehicles and equipment can, guided by AI algorithms, navigate complex jobsites with precision, enhancing both safety and productivity.
In summary, since AI can learn, make predictions, and streamline complex tasks, its integration into construction operations promises to make your projects safer, more efficient, and cost-effective.
Virtual Reality Technology
Virtual reality (VR) is a technology that creates immersive, computer-generated environments or simulations.
Users can interact with and experience these virtual worlds using specialized VR headsets and input devices.
Although VR applications in the construction industry are still evolving, companies are currently using them primarily for architectural visualization and training simulations.
For example, you can turn an architectural house design into a 3D digital environment, and your client can take a virtual tour of their future home using VR goggles.
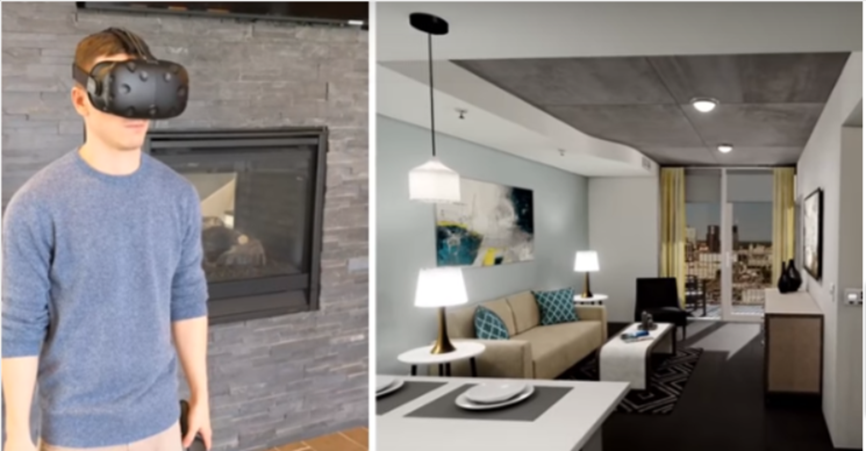

In the design phase (under design-build scenarios), this helps the client, designer, and contractor visualize the project and address any design issues before the client approves it.
Naturally, VR can also be used for turning engineering drawings (water and sewage pipes, electric and heating installations, etc.) into 3D representations, as discussed in the section on building information modeling (BIM).
This allows the construction team to catch any structural overlaps or other problems that would otherwise lead to costly project changes and delays.
Another often-used VR application in construction refers to training simulations that mimic real-world scenarios, allowing workers to experience potential hazards and learn how to respond without the risk of actual harm.
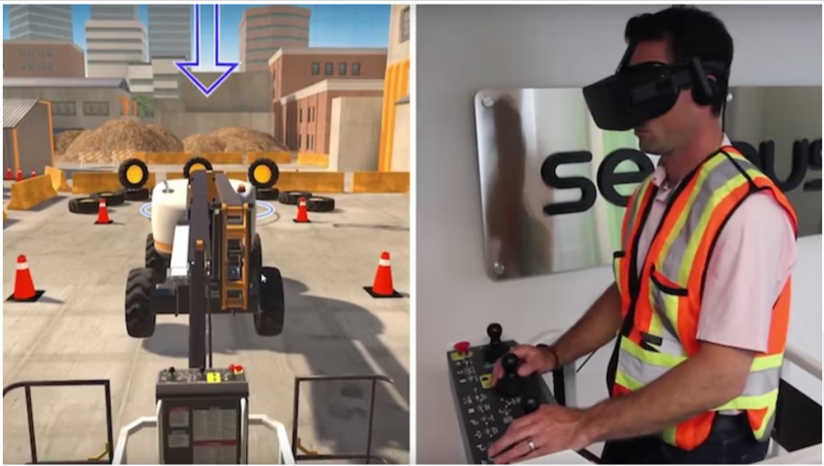

When you approach training in such a practical way, equipment operators learn better and are better prepared for any situation that’s out of the ordinary.
As a result, when the operators are more proficient, the construction sites themselves are safer and usually boast higher productivity.
Whether VR is used for design visualization or worker training, it can be used together with AI in certain applications, such as AI-driven simulations within VR environments.
To recap, VR helps construction companies in design visualization, clash detection, and realistic training simulations, enhancing safety and efficiency across their projects.
Mobile Technology
Nowadays, we take mobile devices like smartphones and tablets and ever-present internet connectivity for granted.
To illustrate this, we can cite JBKnowledge’s 2018 survey of general contractors, where over 90% of respondents said they use smartphones, and over 65% said they use tablets on their construction sites.
The benefits of workers using mobile technology on-site are immense, ranging from increased worker mobility and efficiency to better collaboration and fewer errors.
For example, workers can easily access cloud-based applications on their devices to access project plans and documents in real time, communicate with team members instantly, submit digital reports, and attach photos or videos.
Additionally, they can problem-solve on the spot, by accessing the equipment’s info page to review instruction manuals, report an equipment-related issue, or find where a specific piece of equipment is located.
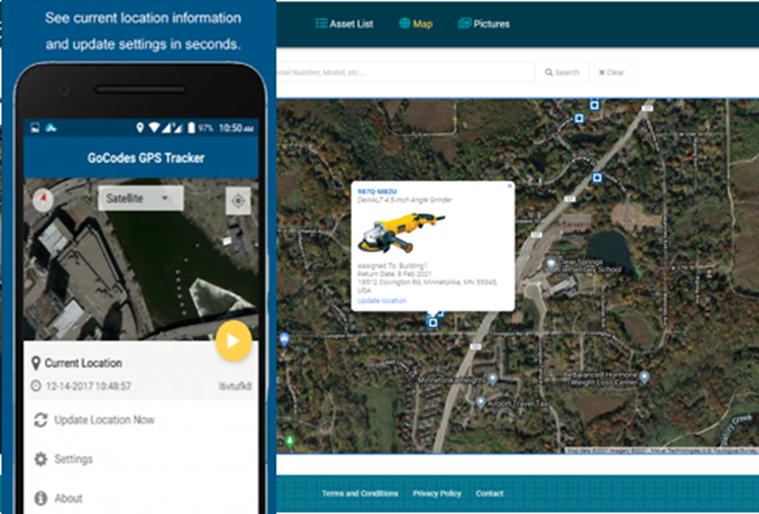
In other words, mobile technology enables both workers and managers to easily find what they’re looking for instead of rummaging through piles of papers, which saves time and increases overall productivity.
Likewise, they can coordinate their activities in real-time since there is no time lapse between, for instance, filing an equipment failure report and the maintenance team receiving it.
Lastly, when construction-related cloud software solutions are simple and easy to use, even less tech-savvy construction workers can easily use them.
Overall, mobile devices, internet connectivity, and cloud-based apps provide construction teams with improved flexibility and mobility, easy information access and sharing, and strong data security, all of which enable companies to streamline their operations.
Drones
After mobile devices, drones are probably the most widely adopted “new” technology used on construction sites.
The reason behind this is their ability to collect real-time data (i.e., perform aerial surveys and jobsite inspections) while reducing risks some surveyors and inspectors would otherwise be exposed to.
The simplest example is measuring/inspecting high-rise buildings and bridges, as well as other elevated construction elements in hard-to-reach places.
According to the Florida Drone Supply, drones can generate the following improvements in construction site operations:
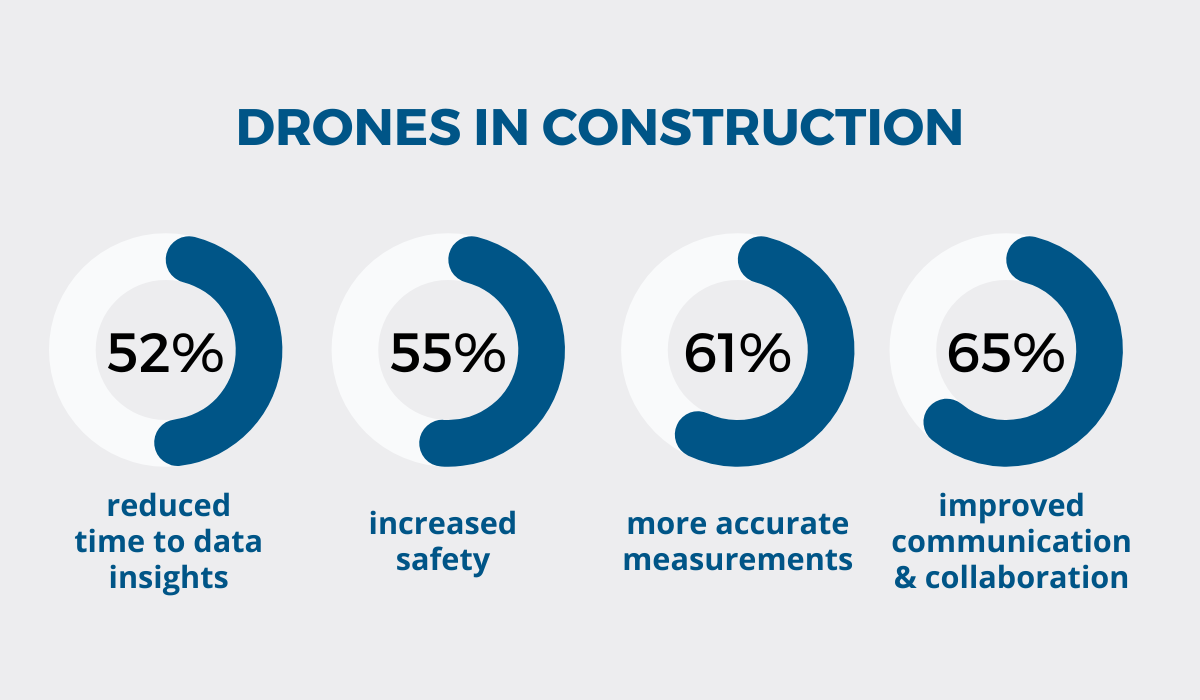
As you can see, drones don’t just significantly enhance jobsite safety but also reduce the time needed for gaining crucial data insights before, during, and after a construction project.
Moreover, they can ensure that designed and as-built measurements are more accurate and that construction teams communicate and collaborate better.
In addition to monitoring project progress, drones can be used to create great marketing materials for advertising campaigns that show off your company’s previous or ongoing projects.
Given their versatility and increasing affordability, drones are quickly becoming a vital part of construction operations, leading to reduced on-site risks, easier area mapping and inspections, more frequent project updates, and better team collaboration.
Building Information Modeling
For starters, it should be noted that building information modeling (BIM) is a technology that can incorporate the advantages of all the other technologies covered here, such as AI, VR, mobile technology, drone-generated data, and even QR codes.
That said, what is BIM?
According to Ralph Bond, manager at Autodesk:
“BIM is an intelligent model-based process that helps make design, engineering, project, and operational information accurate, accessible, and actionable for buildings and infrastructure.”
In other words, architects, engineers, and contractors use BIM software to create collaborative 2D, 3D, and even 4D models of their projects, which allow all the stakeholders to add their work and expertise to the same digital model.
The benefits this generates are numerous, and the 2021 Dodge Data & Analytics report nicely sums up the top five advantages reported by construction stakeholders.
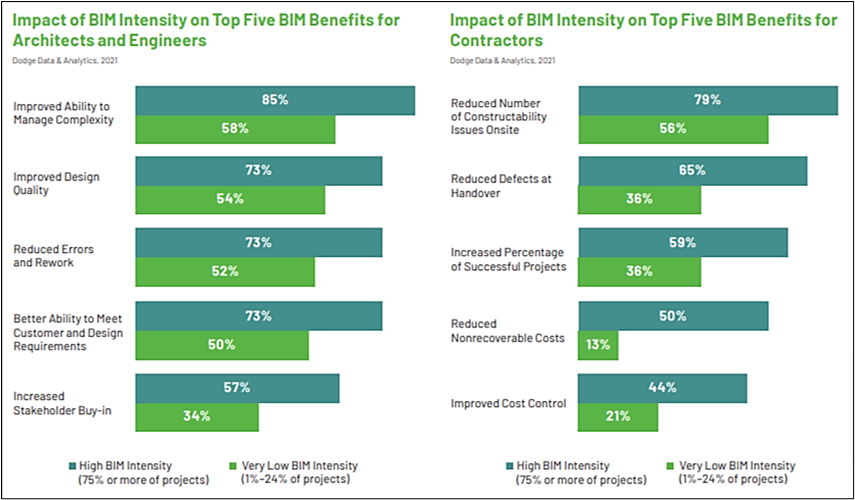
As you can see, designers report 54-73% improved design quality and 52-73% fewer errors and instances of rework.
Likewise, contractors report 56-79% less constructability issues and a 36-59% increased percentage of successfully completed projects.
Coupled with other reported advantages, it’s clear that BIM allows all stakeholders to visualize the design details and identify potential design errors or clashes, which helps address a multitude of issues caused by poorly coordinated, multi-sourced plans and drawings.
In fact, BIM is so useful that countries around the world have either mandated its use on large-scale projects or are about to.
All in all, BIM is specialized software that construction stakeholders use to create a single digital model of their project, enabling all involved to improve real-time collaboration and minimize project errors.
Conclusion
And there you have it.
These six technologies are quickly transforming the construction industry, enabling construction companies to realize enormous improvements in their construction operations.
From using simple and cost-effective QR codes, ever-present mobile technology, and drones to using more complex technologies like AI, VR, and BIM, each of these technologies (alone or, better yet, combined) can help your company save time and money.
In other words, their adoption will allow you to streamline construction processes, minimize errors and misunderstandings, reduce costs, and ultimately increase your company’s productivity and profitability.





