Key Takeaways:
- Poor asset management leads to downtime, waste, and security risks.
- Unplanned downtime costs manufacturers up to $695M annually.
- 27% of construction asset thefts are insider jobs.
- Cloud-based asset management software improves tracking, maintenance, and real-time visibility.
Think about all the physical assets that keep a business running—equipment, vehicles, IT hardware, and even entire facilities.
Without a structured approach to managing them, costs spiral, downtime increases, and businesses waste money on inefficient operations.
That’s where asset management comes in.
Whether you run a construction company, a manufacturing facility, or even a healthcare organization, managing assets effectively ensures they provide maximum value over their lifecycle.
In this article, we’ll break down what asset management is, why it matters, and how modern digital tools are transforming the way businesses handle their assets.
In this article...
What is Asset Management?
Assets are everything a business owns that contributes to its operations—whether it’s machinery, vehicles, IT equipment, or infrastructure.
These assets fall into different categories:
- Fixed assets (e.g., buildings, heavy machinery)
- IT assets (e.g., servers, laptops, software)
- Infrastructure assets (e.g., roads, bridges, utilities)
- Enterprise assets (e.g., fleet vehicles, production equipment)
Asset management is, therefore, the structured process of tracking, maintaining, and optimizing these assets throughout their lifecycle.
Done well, it ensures businesses get the most value from their investments while reducing waste and unexpected costs.
In numbers, the global asset management market is expanding rapidly.
Valued at $927.61 billion in 2025, it’s projected to skyrocket to $12.74 trillion by 2034, growing at an impressive CAGR of 33.95%.
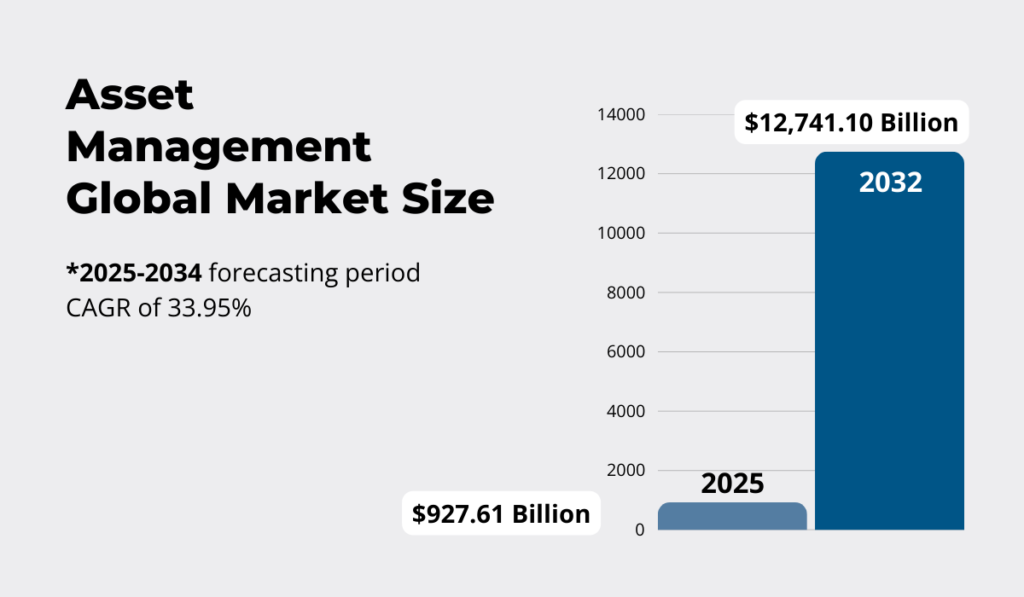
Illustration: GoCodes Asset Tracking / Data: Precedence Research
This surge is driven by industries adopting digital solutions to improve efficiency and reduce costs.
Key Challenges in Asset Management
Even as businesses adopt digital tools, asset management remains a struggle for many.
Some companies still rely on spreadsheets or paper logs, while others lack a structured system to track asset performance, costs, and maintenance needs.
And even those using modern software face challenges—poor data entry, lack of system integration, and insufficient real-time updates, all of which cause inefficiencies.
These gaps in asset management create three major challenges that cost businesses time and money.
Poor Asset Visibility
One of the biggest problems businesses face is not knowing where their assets are or how they are performing.
This can happen for several reasons:
| Manual tracking is inefficient | Spreadsheets and handwritten logs are prone to errors, missing entries, and outdated information. |
| Lack of real-time data | Even businesses using asset management software may not have real-time updates if their systems don’t integrate well or if employees don’t log asset movements properly. |
| Frequent asset movement | Industries like construction and field services often move equipment between job sites, making it harder to track where assets are and whether they’re being used effectively. |
The consequences?
Wasted time, wasted money, and even security risks.
Take St. Charles Parish, Louisiana, for example.
Their public works team managed over 60,000 assets but lacked clear visibility into costs and maintenance histories.
Meme Fortier, an Automation Control Technician, explained:

Illustration: GoCodes Asset Tracking / Quote: Asset Works
Without a clear view of asset conditions and costs, they held onto outdated equipment longer than they should have, missing opportunities to replace or reallocate resources efficiently.
And poor asset visibility isn’t just an operational problem—it’s also a security risk.
According to BauWatch, 27% of asset thefts are insider jobs.
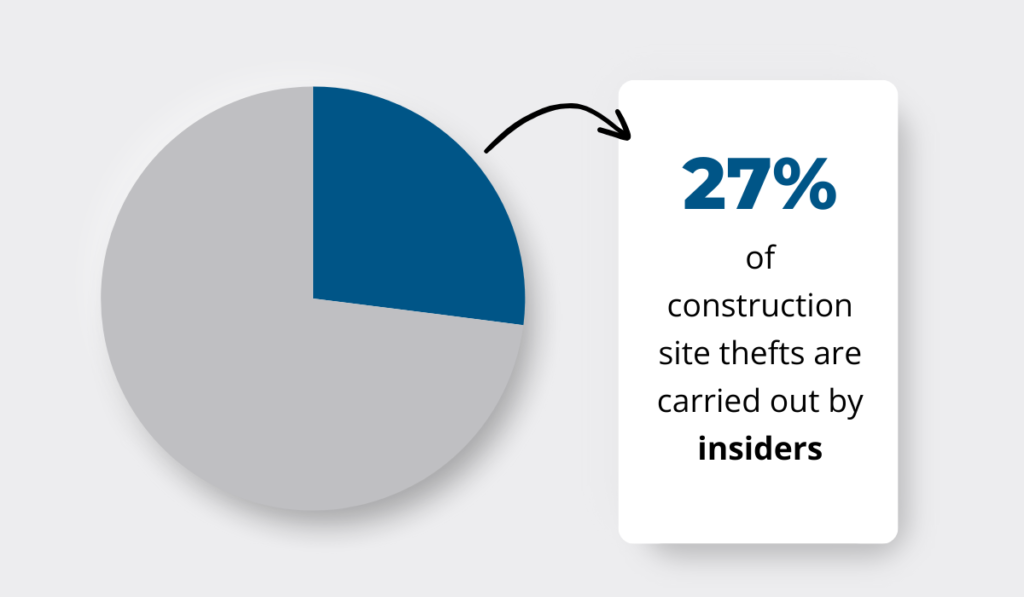
Illustration: GoCodes Asset Tracking / Data: BauWatch
If employees know their company doesn’t have proper visibility into its assets, they might be more likely to steal equipment, knowing it won’t be immediately noticed.
Maintaining Asset Uptime
Another challenge is keeping assets running efficiently.
Whether it’s a construction excavator, a factory assembly line, or an IT server, every asset needs regular maintenance to avoid breakdowns.
That’s why unplanned downtime is one of the most expensive consequences of poor asset management.
Without regular maintenance tracking, businesses miss critical service intervals, leading to breakdowns, costly repairs, and unexpected disruptions.
And the financial impact is staggering.
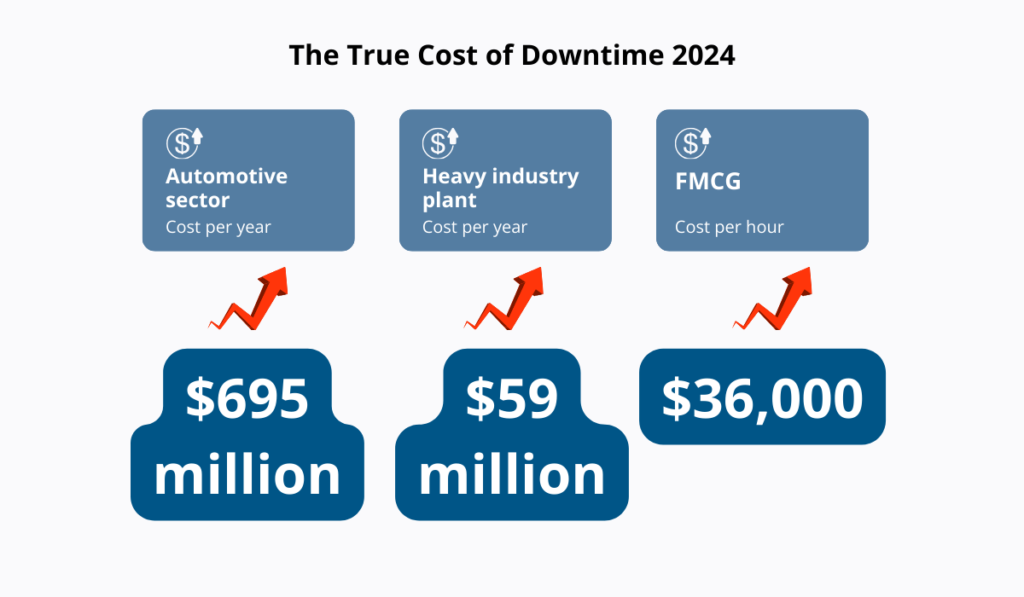
Illustration: GoCodes Asset Tracking / Data: Siemens
In automotive manufacturing, an idle production line costs $695 million annually—1.5 times higher than just five years ago.
In heavy industry, downtime costs have jumped 1.6 times since 2019, reaching $59 million per year.
For fast-moving consumer goods (FMCG), a single lost hour costs $36,000.
IT downtime isn’t any cheaper—a survey by Information Technology Intelligence Consulting (ITIC) found that even one minute of IT downtime costs a minimum of $5,000.
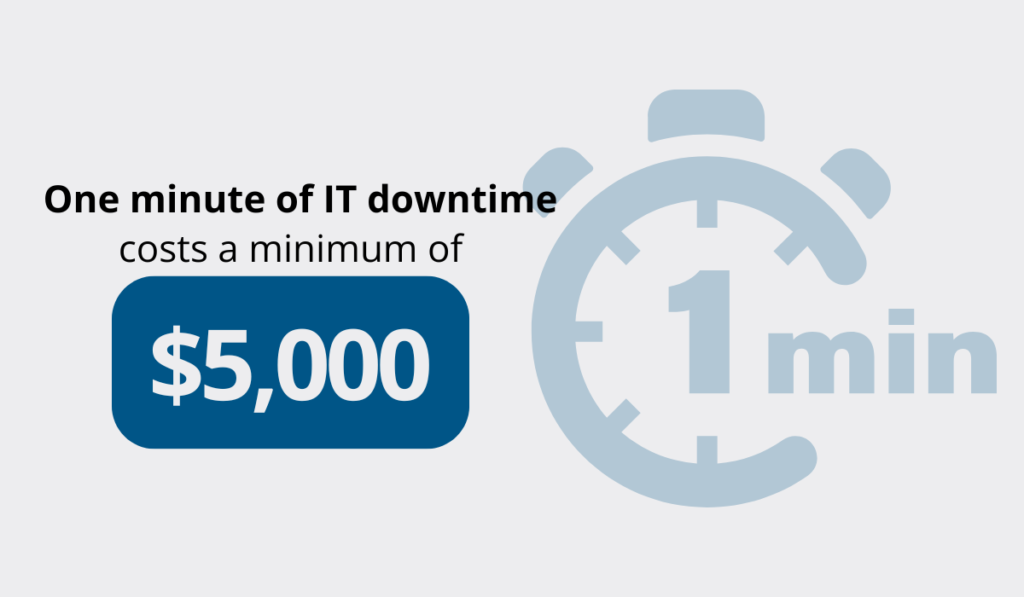
Illustration: GoCodes Asset Tracking / Data: ITIC
But financial loss is just one part of the problem.
When assets fail, employees can’t work, projects stall, and customers get frustrated.
Industries like construction and manufacturing feel this impact the most.
If a key piece of equipment goes down, the ripple effect can delay entire projects.
An excavator sitting idle means workers waiting around, deadlines getting pushed back, and costs piling up.
The best way to prevent this?
Proactive asset management—tracking maintenance schedules, ensuring timely servicing, and preventing costly breakdowns before they happen.
Not Understanding Asset TCO
One of the reasons why businesses struggle to manage their assets comes from not fully understanding the total cost of ownership (TCO).
Sany, a heavy equipment manufacturing company, has seen that firsthand in some of their customers’ choices.
Samuel Zhang, General Manager of Sany Southern Africa, says that although Sany’s larger customers mostly understand the importance of TCO, many businesses still need education on what it really means for their bottom line.

Illustration: GoCodes Asset Tracking / Quote: Capital Equipment News
TCO goes beyond the initial purchase price—it includes operational costs, maintenance, depreciation, and even disposal expenses.
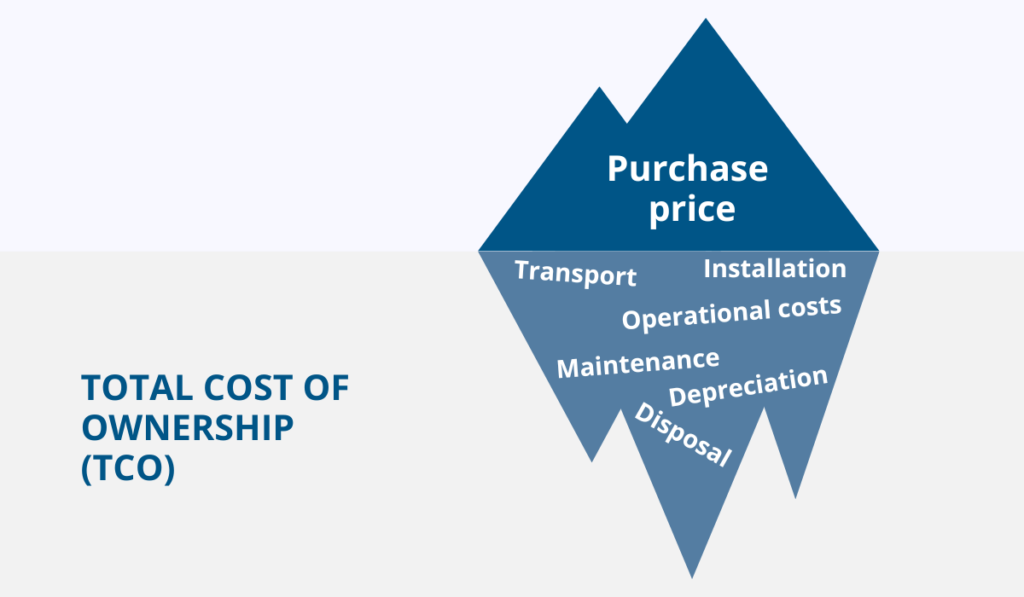
Source: GoCodes Asset Tracking
Yet, many companies fail to account for these hidden costs, leading to financial strain in the long run.
For example, a company may choose to buy an excavator instead of renting one, assuming ownership is the cheaper option.
However, without considering maintenance expenses, fuel costs, and long-term depreciation, they might end up spending far more than they anticipated.
Similarly, businesses often overlook employee training costs or compliance fees, which can add up quickly, especially for highly specialized equipment.
Without a clear understanding of TCO, companies risk making decisions that seem cost-effective upfront but hurt profitability in the long run.
The challenge isn’t just about adding up numbers—it’s about shifting mindsets toward long-term financial planning and asset optimization.
Key Benefits of Effective Asset Management
By tackling these common challenges, businesses can unlock significant financial, operational, and security benefits.
Here’s how asset management drives real results.
Cost Savings
One of the most immediate and measurable benefits of effective asset management is cost savings.
When companies take control of their assets, they:
- Prevent unnecessary expenses
- Optimize maintenance
- Reduce theft
All this leads to cost savings.
Let’s start with theft, one of the biggest sources of financial loss in asset-heavy industries like construction.
A survey by BauWatch we cited earlier found that the UK construction industry alone loses £800 million per year due to stolen equipment.

Illustration: GoCodes Asset Tracking / Data: BauWatch
The problem is often made worse by poor tracking systems—many businesses don’t even realize when assets go missing.
But when companies use real-time tracking tools, such as GPS monitoring and geofencing, theft drops dramatically.
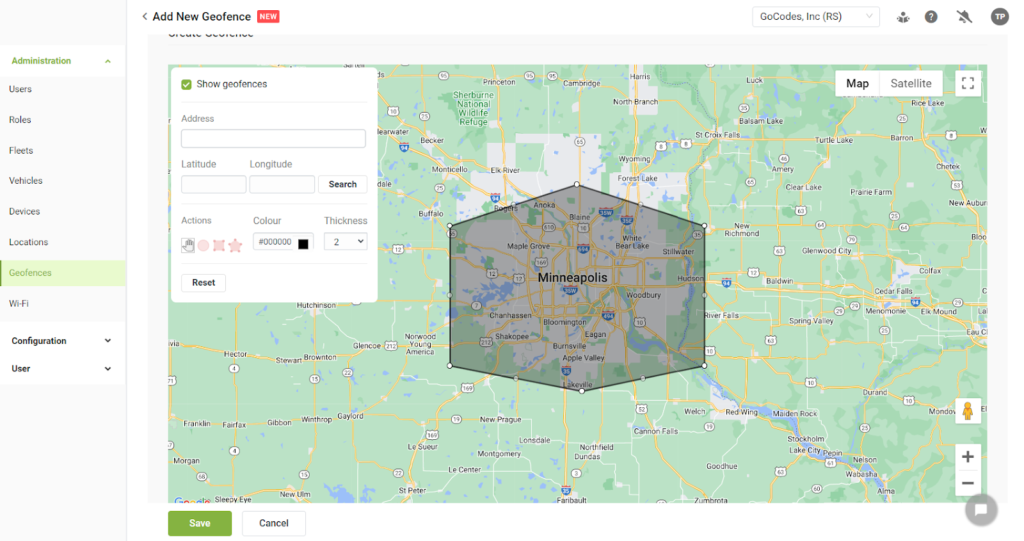
Source: GoCodes Asset Tracking
Stolen equipment is recovered faster, and just the presence of tracking technology discourages individuals from attempting theft in the first place.
Another way businesses save money is by avoiding unnecessary purchases.
Without proper visibility into their assets, companies often lose track of what they already own, leading them to buy duplicate equipment or stockpile unnecessary spare parts.
That is exactly where asset management systems come in.
They provide a clear picture of what’s available, ensuring businesses only invest in what’s truly necessary.
Source: GoCodes Asset Tracking
Maintenance costs are another area where businesses see significant savings.
As we saw earlier, equipment breakdowns can be expensive, not just in terms of repair costs but also in lost productivity.
When asset maintenance is managed proactively, businesses can avoid these surprise expenses and extend the asset’s lifespan.
Instead of reacting to problems after they occur, asset management ensures maintenance happens on time, reducing the risk of costly failures.
Improved Efficiency
Beyond saving money, proper asset management transforms how businesses operate.
When companies know exactly where their assets are, how they’re being used, and when they require maintenance, efficiency naturally improves across the board.
This is especially important in industries where workers rely on tools and equipment throughout the day.
Construction workers, for example, often waste valuable time searching for misplaced tools or waiting for equipment to be delivered to the job site.
One study showed that bricklayers lose 45 minutes per day due to inventory-related delays, while electricians waste up to 80 minutes and plumbers 83 minutes.
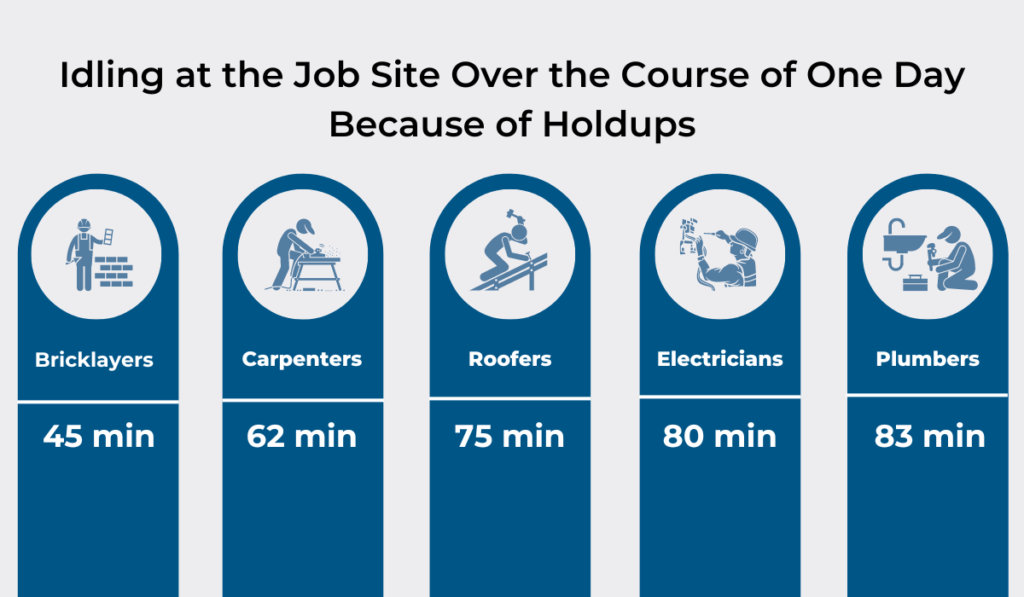
Illustration: GoCodes Asset Tracking / Data: Trekker Group
When assets are properly managed, businesses eliminate these inefficiencies, ensuring that workers can focus on their jobs instead of looking for missing equipment.
Similarly, manufacturing plants and logistics operations benefit from improved asset tracking by ensuring that production lines and warehouse operations run smoothly.
With the right asset management strategy, businesses maximize productivity and ensure resources are always available when and where they’re needed.
Reduced Risks
A lack of asset oversight doesn’t just create inefficiencies, though.
It also introduces serious risks.
Untracked or poorly maintained assets can lead to unexpected failures, workplace safety hazards, and compliance issues.
One of the biggest risks comes from improper maintenance.
Equipment that isn’t serviced regularly is more likely to break down, causing delays and, in worst cases, workplace accidents.
A tragic example of this happened at the Simandou iron ore project in Guinea, where multiple workers lost their lives between 2023 and 2024 during the construction of a railway and port.

Source: Reuters
An investigation into one of the fatalities found that the subcontractor managing the site, Shaanxi Construction Engineering Group Corporation, had failed to assess forklift risks and neglected equipment maintenance.

Illustration: GoCodes Asset Tracking / Quote: Reuters
Failures like this highlight the critical role of asset management in workplace safety.
When businesses use a structured system, they can ensure maintenance schedules are followed, inspections are up to date, and equipment defects are detected before they lead to accidents.
Beyond avoiding breakdowns, asset management also plays a crucial role in ensuring workers can operate machinery safely.
Namely, in industries like construction and manufacturing, employees often rely on complex equipment that requires proper handling.
With the right asset management tools, companies can centralize safety documentation, maintenance logs, and operating manuals, making them easily accessible to employees.
For example, workers can scan a QR code on a machine to instantly check its condition, service history, and safety guidelines—helping to prevent misuse and accidents.
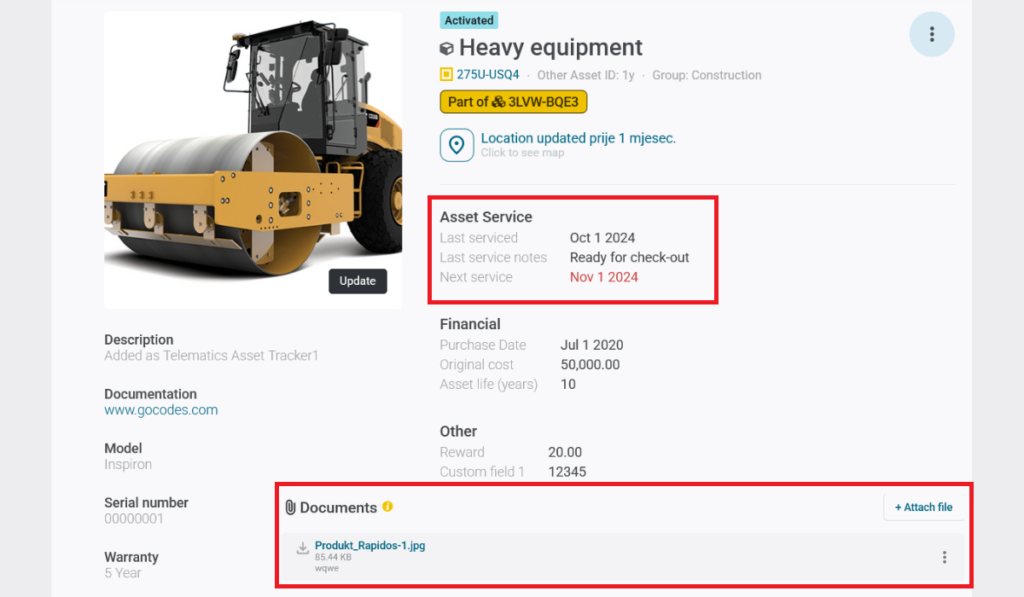
Source: GoCodes Asset Tracking
Compliance is another major concern.
Many industries have strict regulations that require businesses to maintain records of inspections, certifications, and servicing.
Without a structured system, companies risk fines, legal issues, or even operational shutdowns.
An effective asset management solution ensures that compliance is always met by keeping accurate, up-to-date records of every asset’s condition and maintenance history.
How Technology Improves Asset Management
Modern asset management wouldn’t be possible without the right technology.
With smart asset management solutions, companies gain real-time visibility, automate maintenance, and secure their most valuable equipment.
So, what tools do we have in mind here?
One of the biggest headaches in asset management is not knowing where your equipment is or who last used it.
QR code-based asset management solves this issue.
With solutions like GoCodes Asset Tracking, our asset management software, each asset receives a unique QR-coded label linked to a centralized database.
Source: GoCodes Asset Tracking
Employees can scan the QR code with a smartphone to check the asset in or out instantly, update its status, or access important details like warranties, user manuals, and maintenance history.
Beyond QR codes, GoCodes Asset Tracking also supports GPS tracking, so businesses always know where their assets are—whether it’s construction equipment moving between job sites or IT hardware across multiple offices.
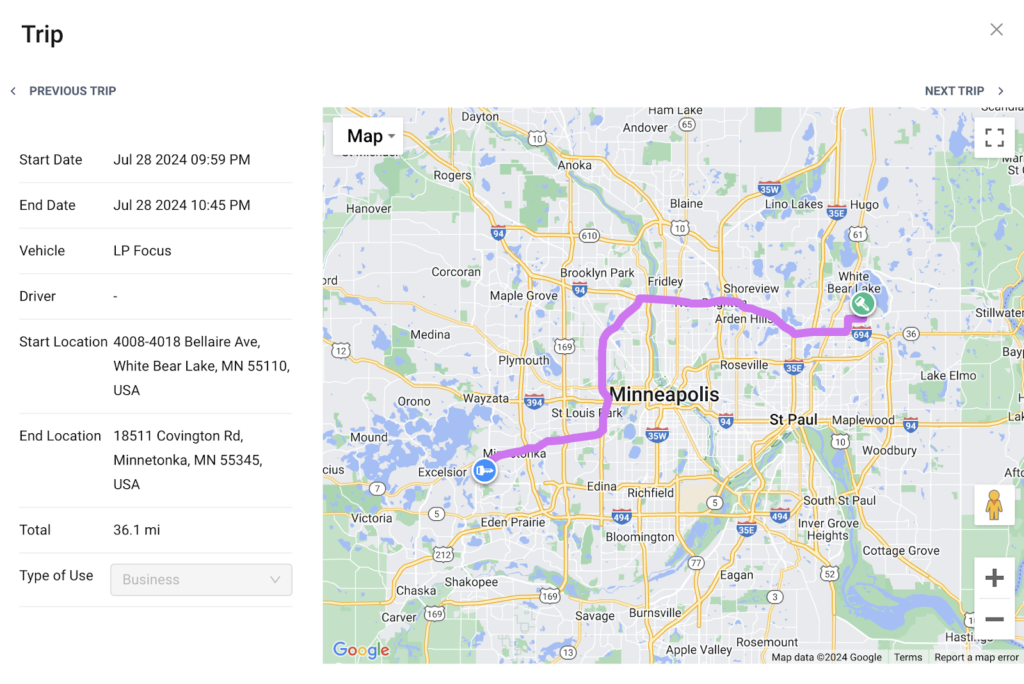
Source: GoCodes Asset Tracking
And with geofencing, managers get alerts if an asset moves outside a designated area, helping to prevent theft and unauthorized use.
With GoCodes Asset Tracking, businesses can also schedule maintenance tasks and assign them directly to employees.
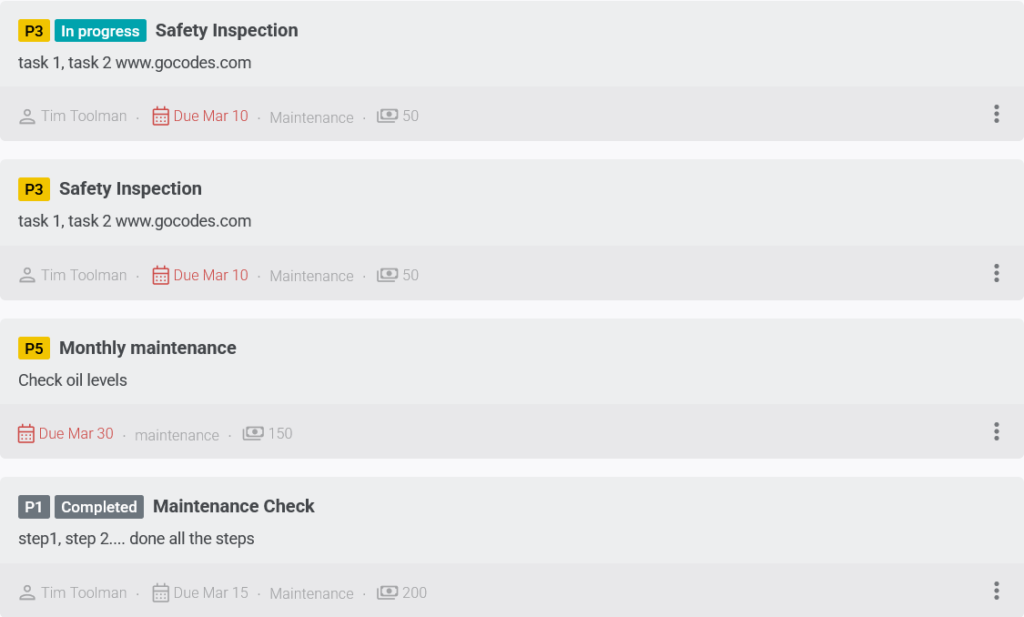
Source: GoCodes Asset Tracking
Instead of relying on memory or outdated spreadsheets, the system sends reminders when equipment is due for servicing.
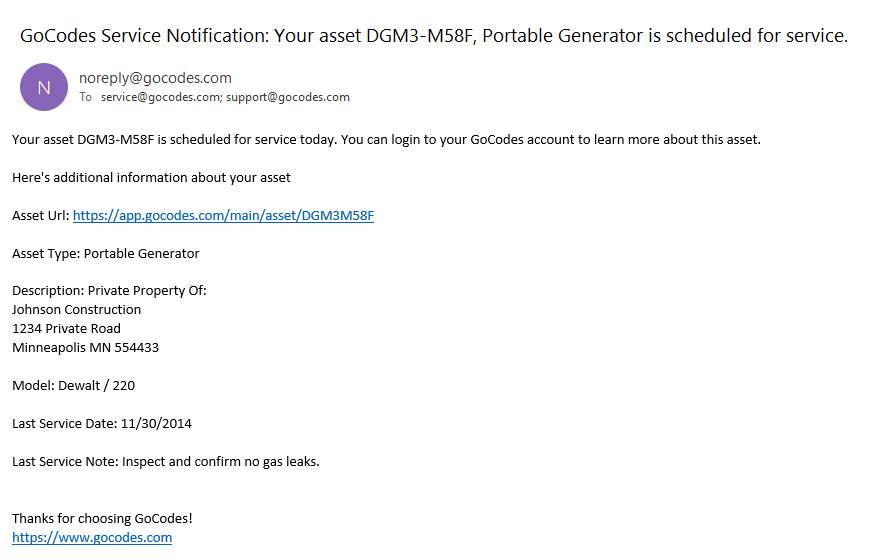
Source: GoCodes Asset Tracking
This reduces the risk of breakdowns and expensive repairs, but also extends asset lifespan.
For asset management to be truly effective, though, it needs to work with the systems businesses already use.
GoCodes Asset Tracking is well aware of this, which is why it has a complete REST/JSON-based API for easy integration with your other software solutions, allowing companies to manage assets within a unified system.
And because it’s web-based, teams can access asset data from anywhere—whether they’re in the office, on-site, or in transit.
By leveraging the right technology, businesses move beyond reactive asset management to a data-driven approach that saves time, money, and headaches.
Instead of scrambling to find misplaced equipment or dealing with unexpected failures, they have real-time visibility, automated processes, and complete control over their assets.
Simply put, with solutions like GoCodes Asset Tracking, asset management becomes simpler, smarter, and more efficient.
Conclusion
Effective asset management is the key to reducing costs, improving efficiency, and mitigating risks.
Without a structured system, businesses face unnecessary expenses, downtime, and security threats.
However, with the right technology—such as QR code tracking, GPS monitoring, and automated maintenance—companies can optimize asset performance and maximize their investments.
As industries continue to evolve, businesses that embrace smart asset management will gain a competitive edge.
Now is the time to take control of your assets and implement a system for long-term success.