Asset management is vital for any business.
Knowing where your assets are, how they’re used, and keeping track of their operational status can make the difference between a smoothly run office or job site and a hectic one.
This is where technologies like QR codes and RFID step in, helping streamline the entire process.
Sure, both QR Codes and RFID each have their own impressive set of features, but they aren’t without drawbacks.
So, before you invest your budget into adopting one of these systems, we’re going to make sure you’re fully informed.
In this article, we’ll explore these two stellar asset management technologies, shedding light on their strengths, weaknesses, and everything in between.
Without further ado, let’s start!
In this article...
What Is a QR Code
If you take a closer look at websites, event tickets, packaging, bills, and even restaurant menus, you’ll likely spot these small, square, pixelated patterns on various items.
Despite their unassuming appearance, these QR codes hold a mighty punch when it comes to data storage and retrieval.
Conceived in the Japanese automotive industry back in the mid-’90s, QR codes were essentially born out of necessity.
It became increasingly evident that traditional barcodes fell short in one significant area—data storage.
Hindered by their linear design, barcodes could only hold up to 25 alphanumeric characters.

Filling this data gap, two-dimensional QR codes came onto the scene with starkly superior data storage abilities.
These pattern squares can hold up to 3 kilobytes of data, translating to up to 7,089 numeric or 4,296 alphanumeric characters.

In terms of practical, day-to-day operations, this means that where a barcode might give you basic item identification, the QR code can encompass website URLs, text, media, and email addresses, to name just a few.
All this information lies under the surface of a QR code and can be easily unlocked with a quick scan using a smartphone or a scanning device.
Given their versatile nature, it’s no wonder that they’re being used extensively across various industries and have found their place in asset management as well.
Advantages of QR Codes for Asset Management
When it comes to detailing the benefits of QR codes, it’s best to start with the most obvious one: they offer a practical, reliable means of digitizing assets while simplifying asset-tracking processes.
In other words, instead of manually logging every piece of equipment and updating spreadsheets, you can generate a unique, two-dimensional QR code for each item.
Every time you need to check the status or history of an asset, you simply scan the QR code with the relevant app on your smartphone.
Just like that, every piece of information you need will be right there in your hands.
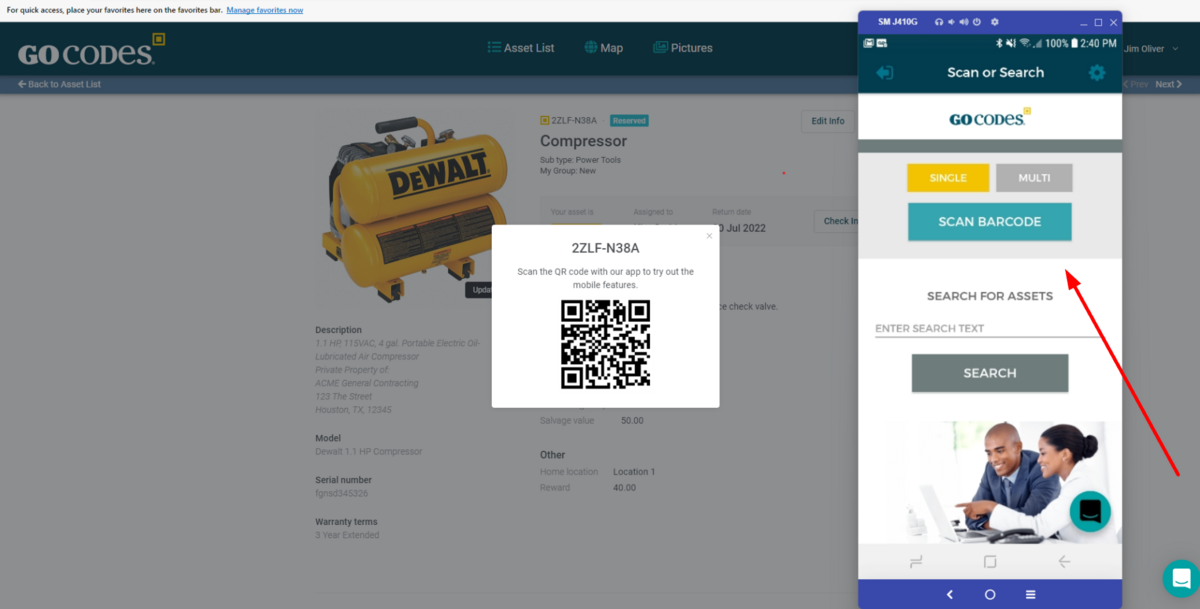
Additionally, despite their small size and relatively simple appearance, QR codes can contain all of the important information about an asset—its purchase date, maintenance records, usage history, and even the person responsible for it.
In other words, QR codes serve as a miniature, self-contained database for each of your assets, as shown in the image below.
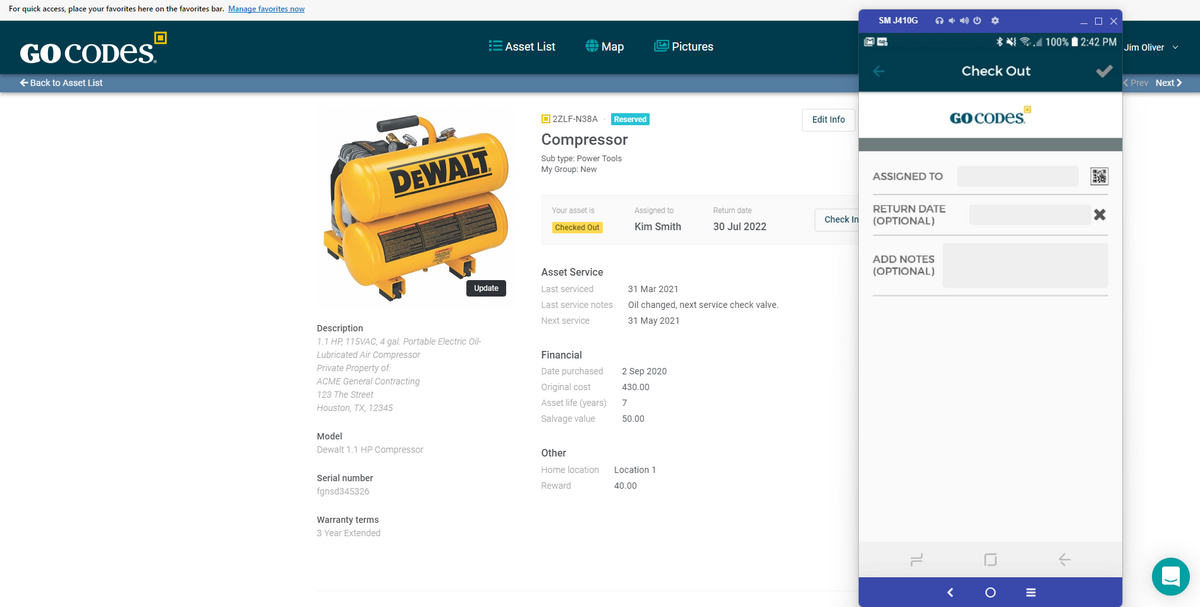
They also offer an advanced level of accuracy. Human error is a constant battle in asset management, and let’s face it, we’ve all had those fat-fingered moments.
However, by scanning a QR code, the risk of manual entry errors pretty much disappears, leading to highly accurate record-keeping.
QR codes are also highly durable and can withstand harsh environmental conditions.
Whether it’s scorching heat on a construction site or chilly climatic conditions in a storage facility, QR codes stand tall.
And lastly but equally important, you don’t need a degree in software engineering to create and start using QR codes.
Reliable software with a user-friendly app and a couple of taps on your screen is all it takes.
Disadvantages of QR Codes for Asset Management
Now that we’ve elaborated on the benefits QR codes can bring to the table, let’s inspect what it says in the fine print. QR codes also come with their own set of drawbacks.
First off, technology is always a two-edged sword. On one hand, the smartphones needed to scan QR codes are widespread and accessible.
But on the other hand, you need to consider the consequences if those devices are unavailable, or have an inconsistent internet connection.
If you don’t use asset tracking software that allows offline mode (shown in the image below), and most of them don’t, and the internet’s down, or there’s a power outage, your QR code system can come screeching to a halt.
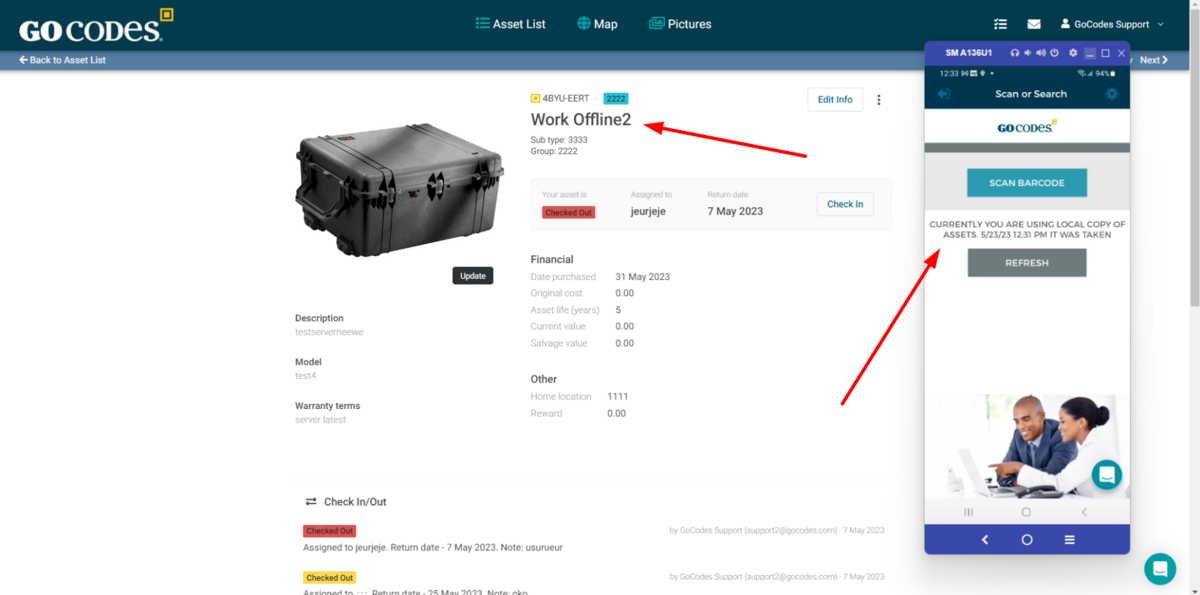
Suddenly, your efficient asset management strategy won’t be so efficient anymore.
Sometimes, QR codes might also be physically challenging to implement. You need to consider where you’ll place them so they’re both visible and protected from damage.
Also, if you’re dealing with heavy machinery or harsh environmental conditions, for example, your QR codes may be subject to wear and tear.
And a worn-out QR code is as good as no code at all, so you’ll need to choose a reliable QR code supplier that’ll provide you with high-quality labels and tags that can withstand various conditions.
Then there’s the issue of user-friendliness. While scanning a QR code is simple, ensuring everyone on your team, regardless of their tech savvy or education, can use them effectively might prove to be a challenging task.
Some might struggle with downloading the relevant apps or using them to scan codes correctly.
So, you either have a steep learning curve ahead or the potential for significant hurdles.
And here, again, you’ll have to be careful to choose the software that is intuitive enough that everyone on your team can master its features in no time.
To sum it up, QR codes, despite their obvious benefits, do have a few setbacks you should be aware of.
Therefore, balance the pros and cons sides of your asset management coin wisely.
What Is RFID
Have you ever wondered how those security gates in retail stores instantly know when an item hasn’t been properly checked out? Or how toll booths can charge your account as you fly by without stopping?
This is possible because of the use of Radio Frequency Identification, known as RFID.
In its most straightforward sense, RFID is a technology that uses radio waves to identify and track assets.
Let’s break it down a bit. An RFID system typically has three main parts: an RFID reader, RFID tags, and RFID software.
The heart of this system is the RFID tag, a tiny device made of an antenna and a chip.
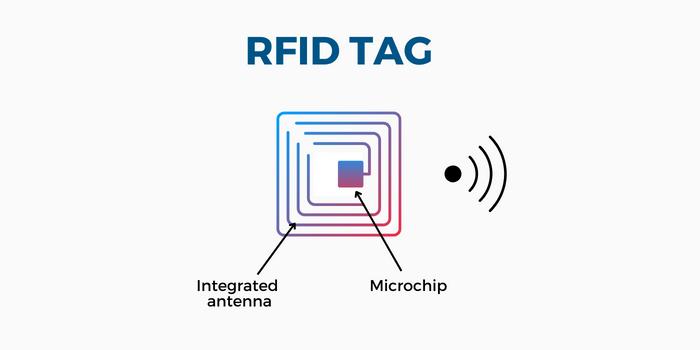
The antenna transmits signals while the chip holds data about the tagged asset.
So, what happens when an RFID reader comes into play?
The tag and the reader exchange information.
The antenna in the tag sends out a signal, sharing the information stored on the chip with the reader.
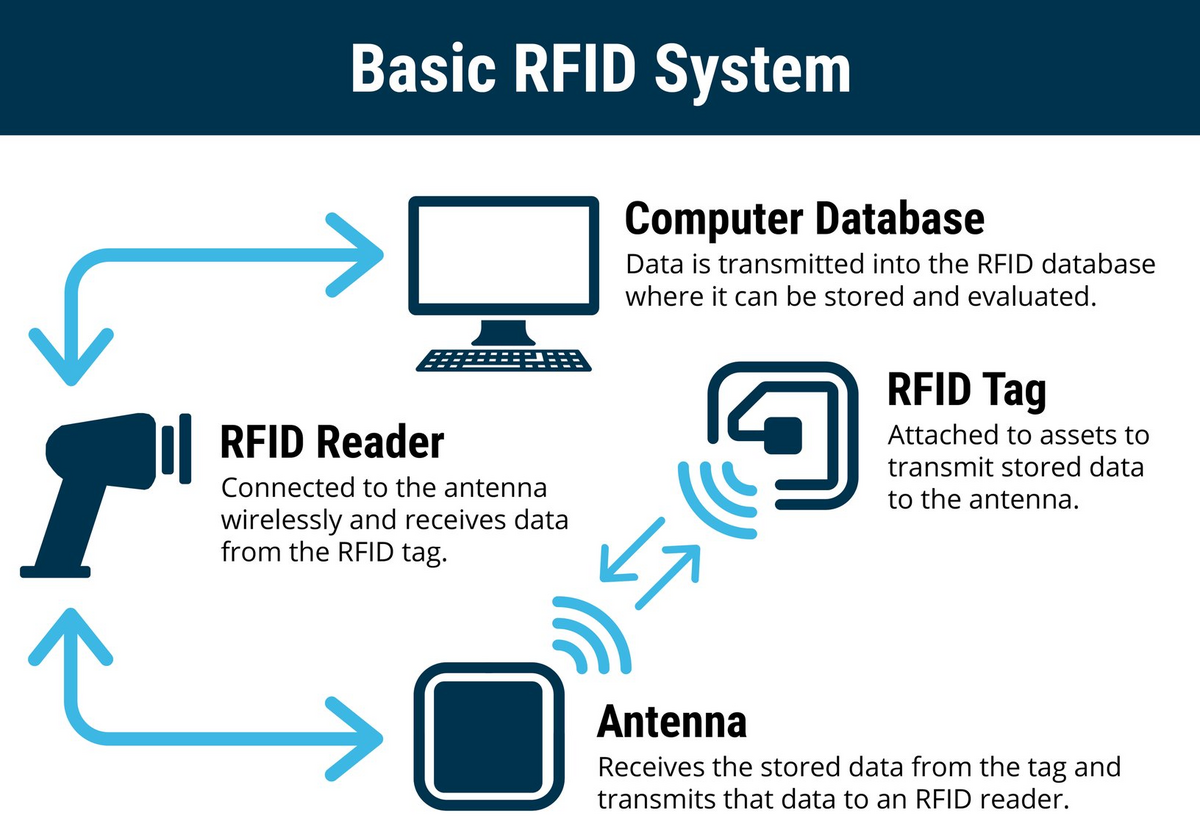
All the chat logs from this communication are reported and managed using RFID software.
As a result, the location of the assets, inventory levels, and even alerts for an asset are all at your disposal.
The capacity to transmit data without making any contact is very convenient, not just for the streamlined retail experience or toll booth encounters, but for many other industries like healthcare, education, logistics, manufacturing, and construction.
In fact, the potential of RFID spans across a multitude of sectors, creating seamless asset management processes wherever it’s employed.
Advantages of RFID for Asset Management
One of the most significant advantages RFID offers is eliminating manual entry and reducing human error while streamlining the asset tracking process.
Manual checking of equipment in and out, trying to locate items, or assessing current inventory data can all be laborious and error-prone tasks.
With RFID, these processes are automated.
Each item tagged with an RFID is identifiable and trackable via radio waves, significantly reducing the time taken for inventory checks and locating specific items.
Unlike traditional barcodes that require a line of sight to scan, RFID tags can be read remotely, even through other materials.
Thanks to radio waves, you can get accurate, real-time information about your assets’ whereabouts, whether they’re behind a wall, under a pile of boxes, or in another room completely.
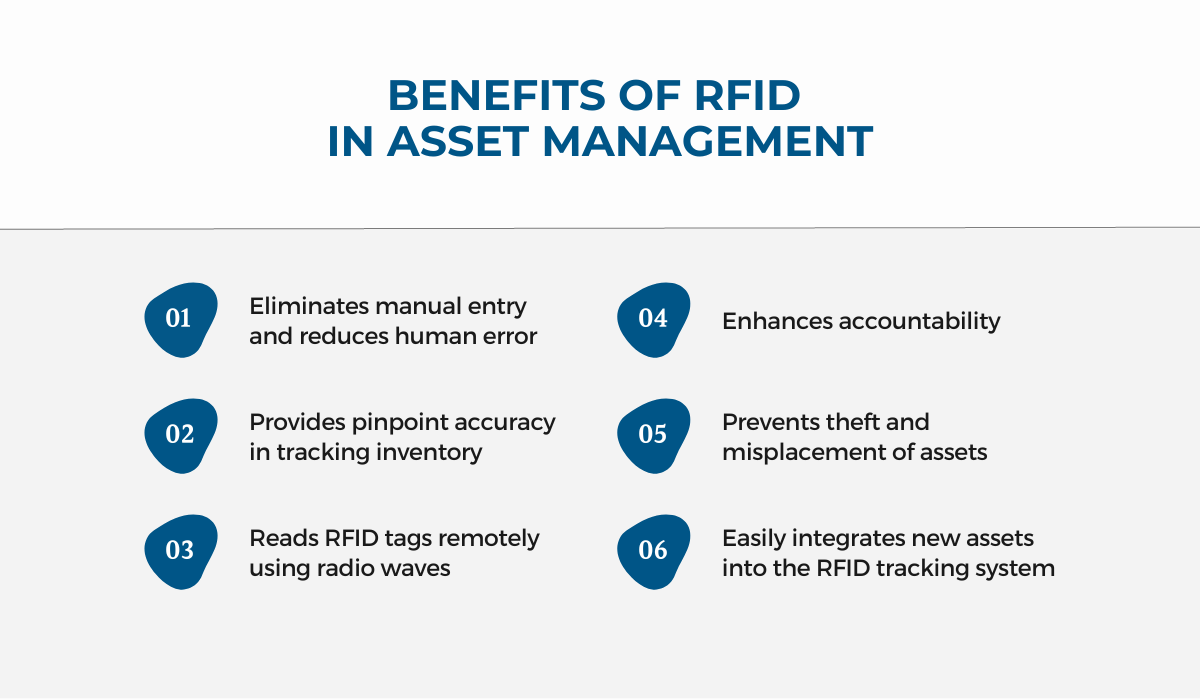
RFID also introduces a higher level of accountability.
Once you’ve tagged your tools and equipment with RFID, it becomes transparent who is responsible for what.
This clarity contributes not only to preventing theft and misplacement but also to instilling a sense of responsibility among team members.
They’ll know that their care of your assets isn’t just expected, but monitored.
Growing businesses need agile solutions, and RFID can be of great help here, too.
Regardless of the scale of your operations, this technology expands with your asset base. There’s no stress typically associated with growth here.
Just add new tags to your expanding set of tools and equipment and make them a part of your RFID tracking system.
Hence, if you seek efficiency, precision, and accountability, RFID could prove to be an outstanding solution for your asset management procedures.
Disadvantages of RFID for Asset Management
As mentioned previously, there are a lot of benefits to implementing RFID for managing assets in your business.
But like any technology, RFID isn’t without its complications. Let’s dive into some potential drawbacks that you should be aware of.
Let’s start with the elephant in the room: cost. Setting up an RFID system can be quite a blow to your finances.
Tags, readers, software, and integration into your existing systems—it all adds up, especially if you’re managing a vast amount of assets.
It has to be noted that RFID tags could be either passive or active.
The passive doesn’t have a power source, drawing power from the RFID reader to transmit their signal.
Hence, they’re more cost-effective and require less maintenance than their active counterparts.
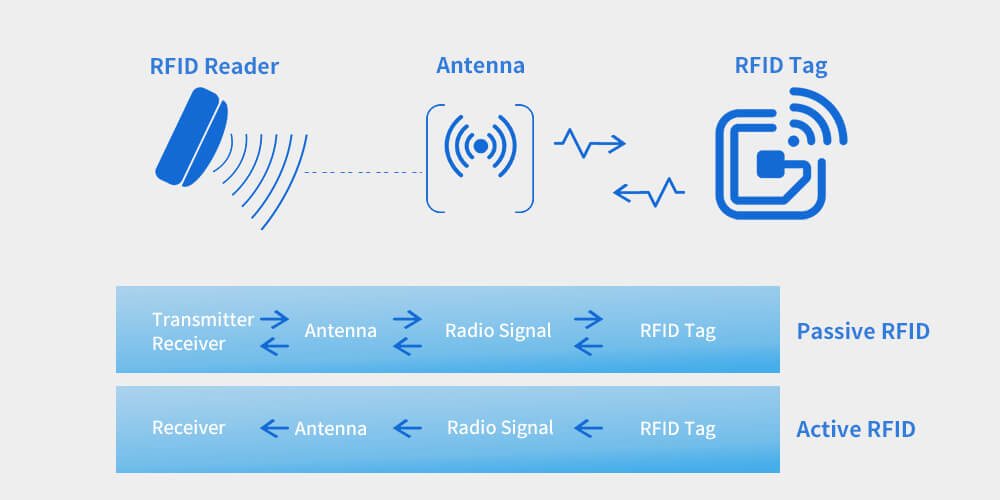
Active RFID tags, on the contrary, are equipped with their own power source to transmit their signal over more considerable distances. They’re also more expensive.
However, regardless of the type of tags you’re using, RFID is still one of the most costly technologies around.
Also, RFID systems, while amazing when functioning correctly, do run the risk of interference.
For instance, materials commonly found on a construction site—metals and liquids—can disrupt the radio signals, leading to glitches in tag readability.
Just imagine getting scrambled readings from your new RFID system because your equipment is near a water source or a large metal structure.
Here’s another thing to think about: data security.
While RFID tags can store a wealth of data on each asset, which is quite a handy feature, the lack of stout encryption or protection may expose sensitive information to potential threats.
So, if you’re dealing with high-value assets, this becomes a major concern.
Therefore, if you’re considering an RFID approach for asset management, ensure you’re treating it as a full package—benefits and disadvantages inclusive.
QR Codes vs. RFID: The Main Differences
Although both QR code and RFID technology offer their own advantages and disadvantages, knowing the nuances between them will assist you in picking the right one for your needs.
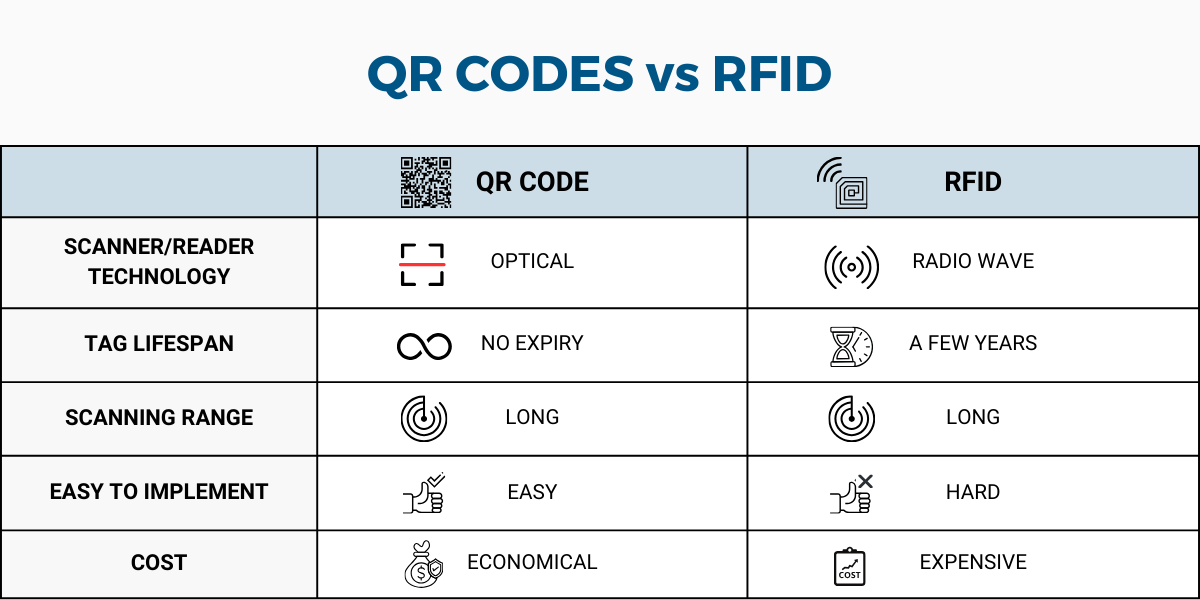
The way these two technologies interact with their scanners or readers plays a crucial role in their suitability for asset management.
When using QR codes, you’ll need to get close to your assets to scan them with either your smartphone camera or a dedicated scanner.
For the QR code to be decoded correctly, it must be clearly visible within the scanner’s viewfinder. This close-up requirement results in a manual and potentially more time-consuming scanning process compared to RFID readers.
On the other side, RFID tags boast a non-contact approach to data transmission, relying on radio waves to pass along information to RFID readers.
These tags can be read from quite a distance—anywhere from a few centimeters up to several meters—depending only on the frequency and power of the reader.
Thanks to this feature, RFID tags don’t need any direct line of sight; they just need to be within the reader’s range to be scanned automatically.
If budget constraints have you pondering your asset management options, QR codes might just come out on top.
They’re relatively cheap to create and versatile enough to be printed on various surfaces, like tags, labels, and even packaging materials.
This effectiveness makes QR codes a suitable option for businesses that require scalable solutions without breaking the bank.
However, don’t discount RFID technology just yet. Though specialized RFID tags and readers can be pricier than QR codes, the cost of your RFID system will depend on factors such as the system type, tag functionality, and scanning range.
If your business would benefit significantly from RFID’s automated tracking, the investment may well be worth it.
When deciding between two asset management systems, give some thought to their lifespan.
QR codes are virtually timeless, having no expiry date. RFID tags, though still enduring, can last for several years.
Having said that, now it’s up to you to decide which of these two technologies is more suitable for your asset management needs and, more importantly, which one you should pick. But more about this in the next section.
QR Codes or RFID: Which Is Better for Asset Management
So, the question now is: which one of these technologies should you choose? Like many things in business, it’s a matter of weighing your needs and resources.
While RFID touts impressive functionality, it does suffer from a few notable limitations compared to QR codes.
Primarily, it lacks the ability to provide geographical data of moving items–a crucial feature for many businesses.
RFID usage is typically confined to controlled indoor environments, where tags are comfortably detected and localized.
However, as we already mentioned, the RFID’s Achilles heel perhaps lies in its hefty cost, which might be prohibitive for smaller or mid-sized enterprises.
With even a single reader costing hundreds of dollars, implementing an RFID technology setup to track all your assets could drain resources.
This technology hurdle is usually more surmountable for larger organizations with greater financial resources, especially when managing expansive warehouses.
So, while RFID tags have a significant effect when it comes to instantaneous, multiple-asset detection, they may not be the most feasible choice for every business.
Now, let’s switch gears and look at QR codes.
They’re commonly seen attached to assets to aid identification and location tracking.

Perfectly suited for stationary equipment, QR codes provide a solution for assets with known locations.
In other words, they, too, lack inherent GPS tracking capabilities.
But when coupled with GPS-enabled QR code scanners, like, say, a typical smartphone, this restriction is eliminated.
Take our own tool, GoCodes Asset Tracking, as an example.
The integration between QR and GPS turned on on a smartphone equips your tracking system with near real-time visibility into tagged assets’ geospatial data.
The practical application? If an asset changes its position, with every new scan you can quickly pinpoint its new location.
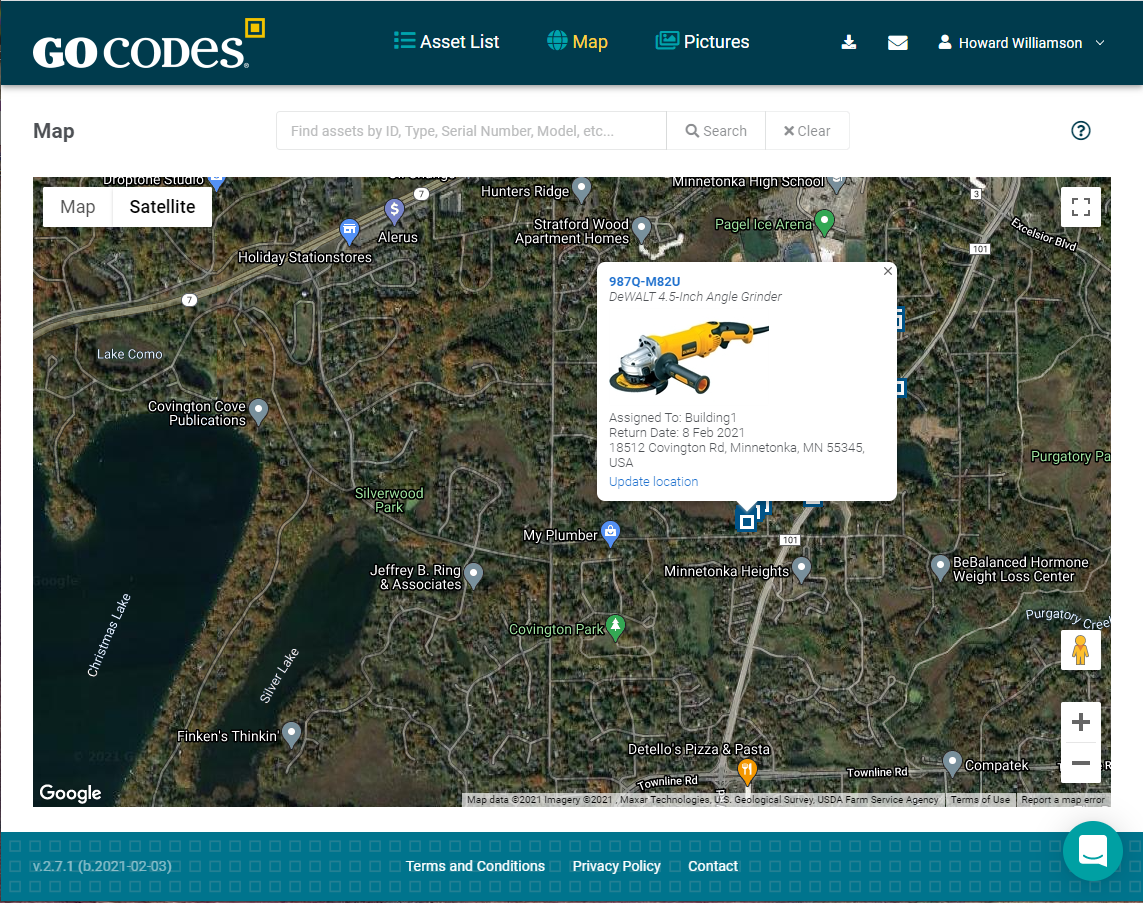
That means that you can also track the geographical position of moving equipment, tools, or other types of assets.
One of the biggest advantages of QR codes is their budget-friendliness, which RFID struggles to match.
This convenience opens up a wide array of asset management applications, including parts tracking for maintenance, monitoring work materials on-site and off, and consistently tracking items on the shop floor or in warehouses.
Therefore, when it comes to choosing between RFID and QR codes, let your specific use case guide you.
While RFID tags work wonders for bulk, rapid scans in controlled conditions, QR codes excel in cost-effective, simplified tracking in varying scenarios.
Conclusion
As you can see, both QR codes and RFID have their unique pros and cons.
At the end of the day, the best asset management solution should be custom-fitted to your individual business needs.
We strongly recommend that you analyze your requirements, outline your budget, and evaluate your technical capabilities before making a final call.





