Key Takeaways
- Standard operating procedures (SOPs) help ensure equipment is used safely and correctly.
- By being proactive with their maintenance efforts, companies unlock better equipment reliability and longevity.
- Without an inventory of spare parts, equipment managers risk unplanned downtime and increased repair costs.
The quality of your equipment management directly impacts every aspect of your operations, from efficiency to profitability and safety.
So, how can you improve this process?
In this article, we answer this very question and share seven game-changing tips for smarter, more effective equipment management.
Some of these may be familiar, while others could be entirely new to you.
Either way, they’re sure to help you unlock the full potential of your valuable machinery.
Let’s get right into it.
In this article...
1. Standardize Equipment Procedures
At the core of any successful equipment management process are clear, easy-to-follow standard operating procedures (SOPs) for handling, storage, operation, and safety protocols.
They aren’t just a formality, but the key to ensuring machinery is actually used correctly.
When followed, they lead to safer, more efficient, and cost-effective operations, preventing damage that shortens equipment life cycle.
So, in short, SOPs are designed to protect the workforce, the assets, as well as your business as a whole.
Unfortunately, there are many real-world examples that show what can happen when operating procedures aren’t standardized.
For instance, in July 2024, a crawler dozer operator tragically lost his life after failing to engage the safety lever while exiting the machine.

Similarly, back in 2010, a 19-year-old worker lost an arm when a hydraulic excavator crushed it—all because the operator didn’t switch off the ignition before leaving the seat.
These are painful reminders of how human error, often stemming from a lack of knowledge or focus, can lead to serious consequences.
That’s where SOPs come in.
Their role is to prevent these mistakes by providing detailed instructions for using assets safely and effectively.
They should clearly lay out who’s qualified to use the equipment, which safety standards apply, and what PPE is required.
Just like in the example below, which illustrates what to wear when using welding equipment.
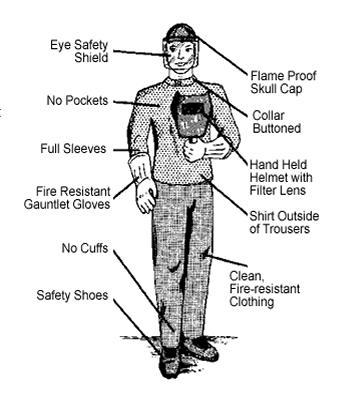
The main goal here is, essentially, to create a document that provides detailed instructions, while still being user-friendly.
Here’s a quick breakdown of which elements are commonly incorporated into SOPs:
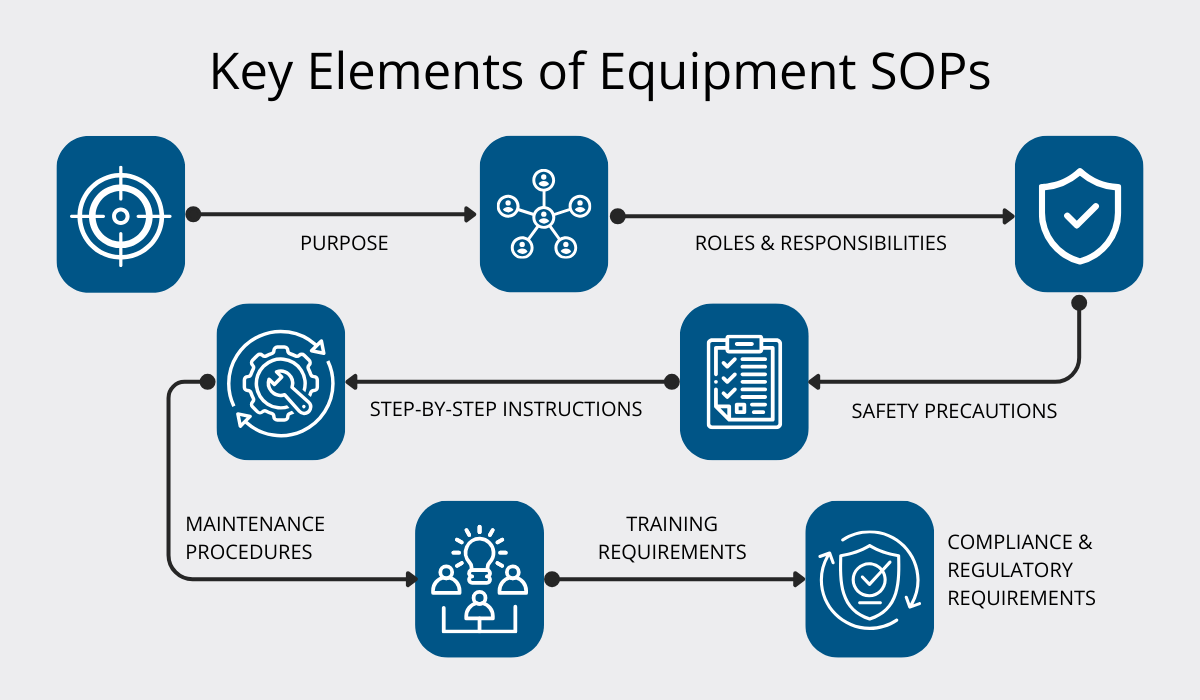
The “step-by-step instructions” part is the most important one, so ensure it’s detailed enough.
This is what’s usually included:
- Pre-check inspection
- Start-up procedure
- Operating instructions
- Shutdown procedure
Once your SOP is ready, the real work begins.
Make sure your heavy machine operators are fully trained on the procedures and can demonstrate competency before they even touch the machinery.
Then, and only then, can you move on to the next step: implementing a centralized asset tracking system.
2. Implement a Centralized Tracking System
A centralized tracking system shows where your machines are, who’s using them, and what project they’re assigned to, all from a single dashboard you can access wherever you are.
On fast-paced, chaotic construction sites, this is incredibly valuable, especially if you’re managing multiple projects simultaneously.
Matthew Jackson, Senior Director of Marketing at Hilti North America, a company that develops and manufactures products for construction, explains why.

Ultimately, this enables you to minimize downtime due to asset loss and boost overall productivity—something that’s nearly impossible to do in a decentralized environment.
To build such a system, you’ll need equipment management software, like our very own GoCodes Asset Tracking.
This solution allows you to automatically update your asset records, instead of having to manually input and search data across scattered systems.
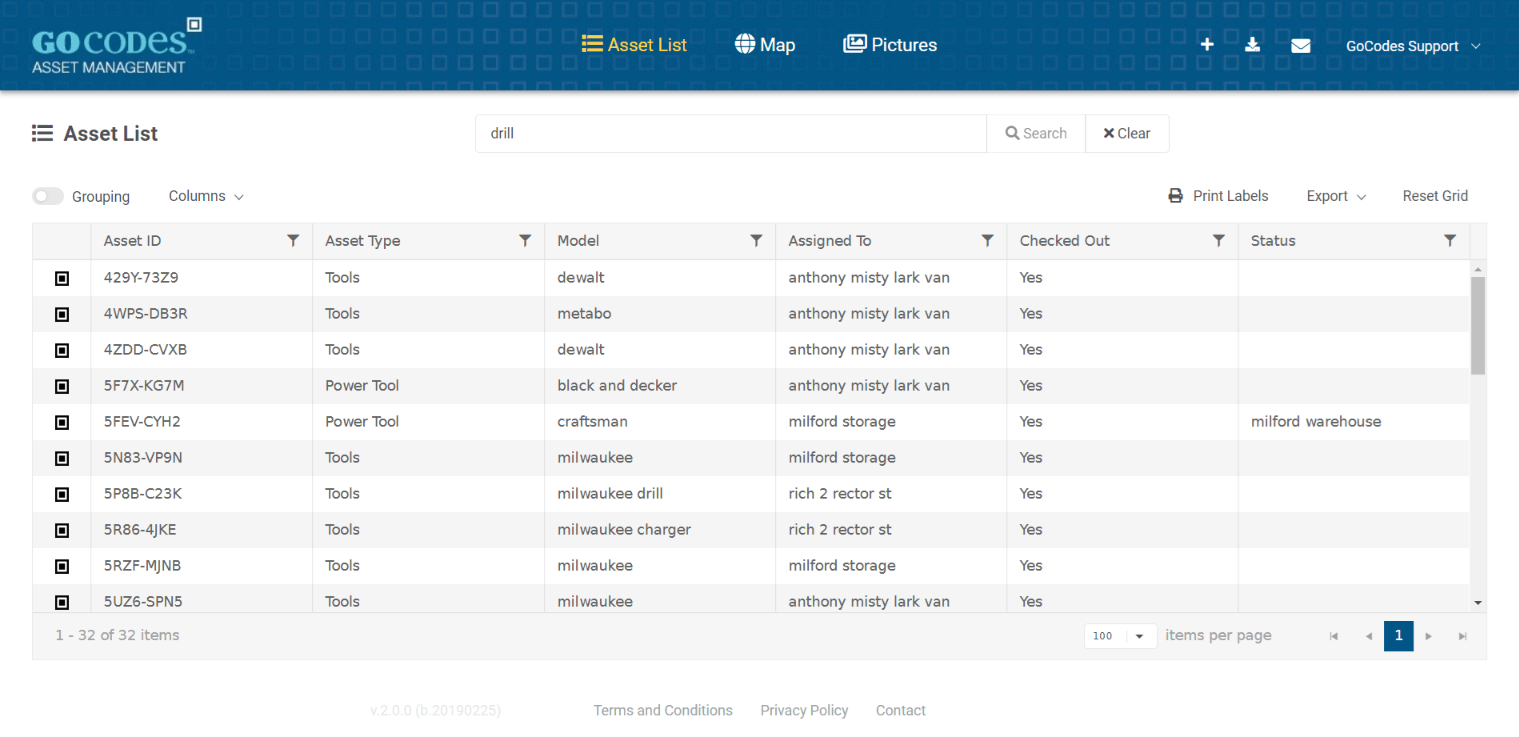
That way, you’ll ensure the information you work with is always accurate, up-to-date, and complete.
So, how does it work exactly?
It’s all very simple.
First, you attach GoCodes Asset Tracking’ durable QR code asset labels to your equipment, and then, using our intuitive mobile app, just scan the labels to instantly view or update asset details.
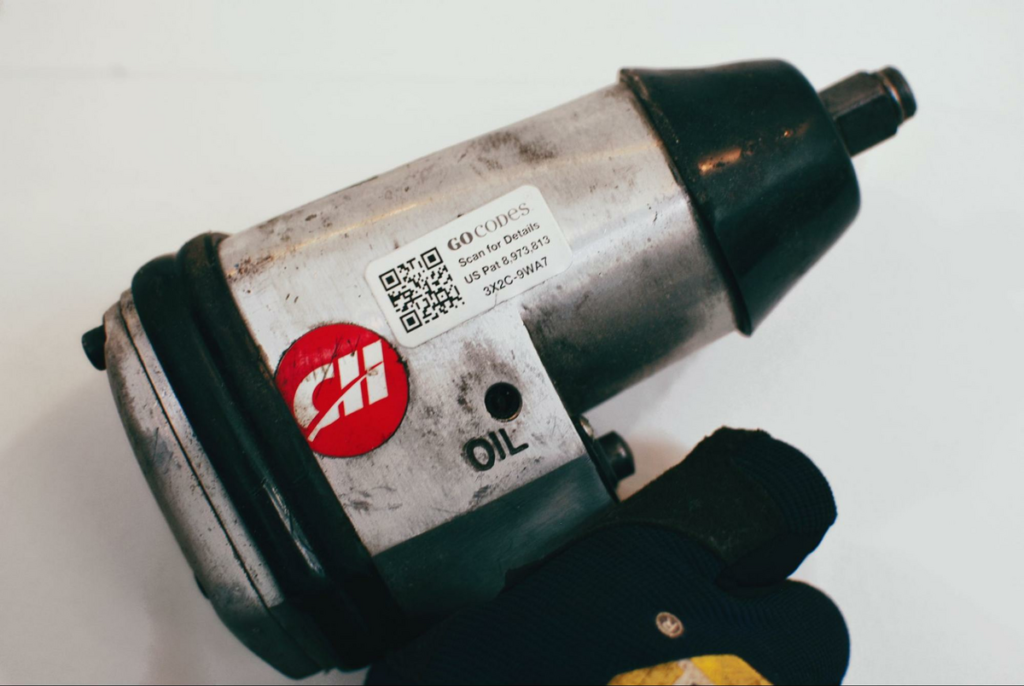

Every time you do this, the GPS location updates too, so you’ve always got the latest information about your machines’ whereabouts.
Want even more control?
GoCodes Asset Tracking also allows you to assign equipment to specific employees, set due dates, and enable notifications for overdue assets, ensuring your tools are in the right hands at the right time.
But the best part about such solutions?
Whether you’re in the office, on-site, or on the go, you and your team can access this data from anywhere and from any device, as long as there’s an internet connection.
That’s the beauty of centralized tracking: you get all this flexibility and advanced equipment management capabilities from one system, but without sacrificing ease of use.
Even less tech-savvy workers can get on board with it.
3. Streamline Equipment Transportation
Streamlining your equipment transportation not only boosts operational efficiency but also slashes those hefty transportation costs.
As you know, moving large, heavy machinery—especially over long distances or even overseas—can be incredibly expensive.
Just take a look at the estimated shipping costs from Elevation Transport Services below.
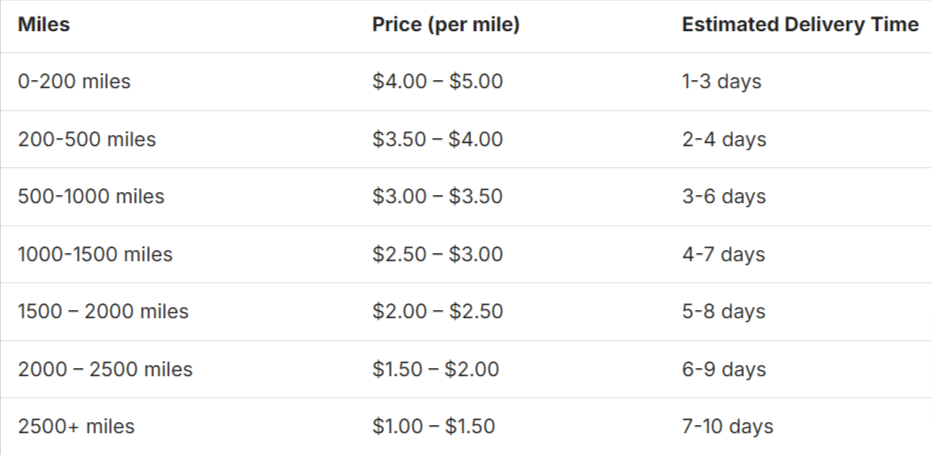
But here’s the thing: several factors can push that price even higher, like the size and weight of the machines, permits, or insurance.
Luckily, with the right strategy, you can reduce these costs while still ensuring your equipment is exactly where it needs to be when you need it to be.
One thing you could do is consolidate your shipments.
So, instead of frequently shipping smaller loads, you can group your assets based on:
- size
- necessary permits
- final destination proximity
- the project it’s needed for
- stackability (e.g., smaller items or components that can be safely stacked) and
- compatibility (e.g., don’t mix fragile assets with equipment that might shift and cause damage).
This way, everything arrives together—faster and at a lower cost.
Planning out the best route helps in this context as well, because it can significantly reduce transit time.
But remember, just because you’re looking to shorten the time on the road, that doesn’t mean the shortest route is always the best option.
Seems a bit counter-intuitive, right?
Still, it’s true: there’s a myriad of other factors to take into account, such as road and bridge weight limits, terrain, road conditions, tolls, and even rest stops for drivers.
If you want to avoid analyzing all these variables manually, consider using route optimization software.
Just make sure it’s specifically designed for commercial vehicles, like the one you see below.
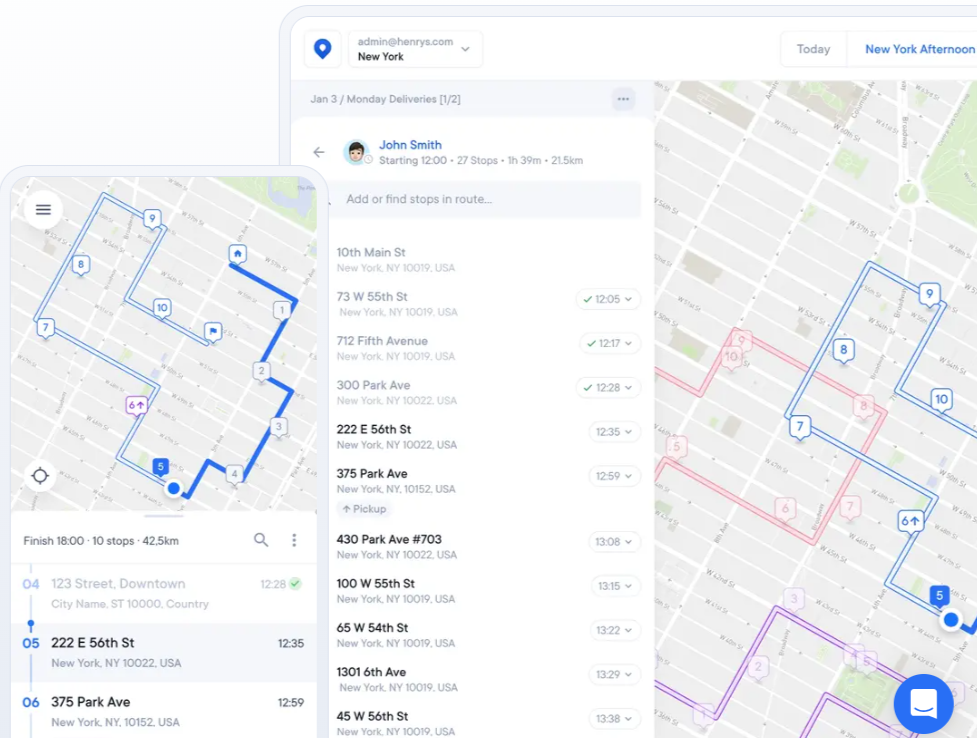
These solutions let you enter all the relevant details and quickly calculate the most efficient route according to the vehicle or load type, as well as necessary rest stops.
Many also have in-cab features that offer dynamic routing.
In other words, they provide real-time updates and alternative routes based on changing road conditions and driver needs.
All in all, with the right tools and some thoughtful planning, you can make your equipment transportation smarter, faster, and far more cost-effective.
Your bottom line will certainly thank you for it.
4. Monitor Equipment Utilization Rates
Besides tracking where your machines are and who’s using them, it’s also important to monitor their utilization.
By keeping track of this metric, you can easily identify which assets are over- or underutilized, and reallocate them accordingly.
No more hoarding, no more overworking equipment to the point of damage, and certainly no more valuable machinery sitting unused.
Jon Shapiro, Senior Telematics Sales and Business Development Consultant at LightMetrics, sums it up perfectly:
Utilization data is key for getting that complete picture of your assets.

Put simply: utilization data directly translates to better equipment management.
Now, utilization can be measured using various KPIs.
For vehicles and mobile equipment, mileage is frequently used, while for static machinery that doesn’t move often, operating hours work better.
Productivity output is another useful metric, although it’s more commonly used in manufacturing.
You could still apply it to certain construction equipment, too—like measuring cubic meters pumped per hour for concrete pumps, for instance.
But how do you capture this data?
For the most accurate results, it’s best to integrate your equipment management software with GPS trackers, like the ones made by GoCodes Asset Tracking you can see below.
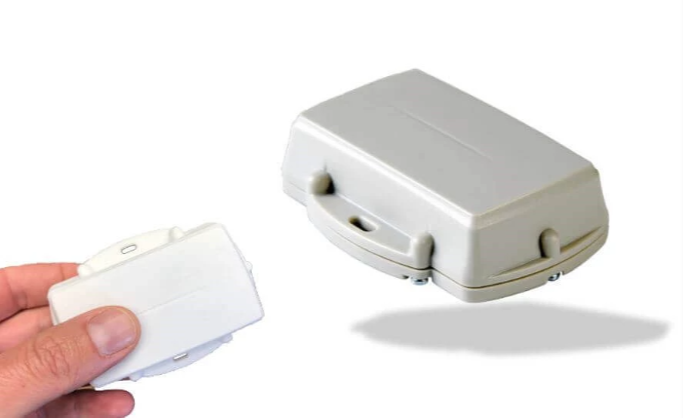

These small, yet powerful devices show an asset’s engine hours, along with other useful insights like location, speed, acceleration, harsh braking, and more—all in real time.
And while the trackers monitor the data, the software displays it all in an intuitive dashboard like this:
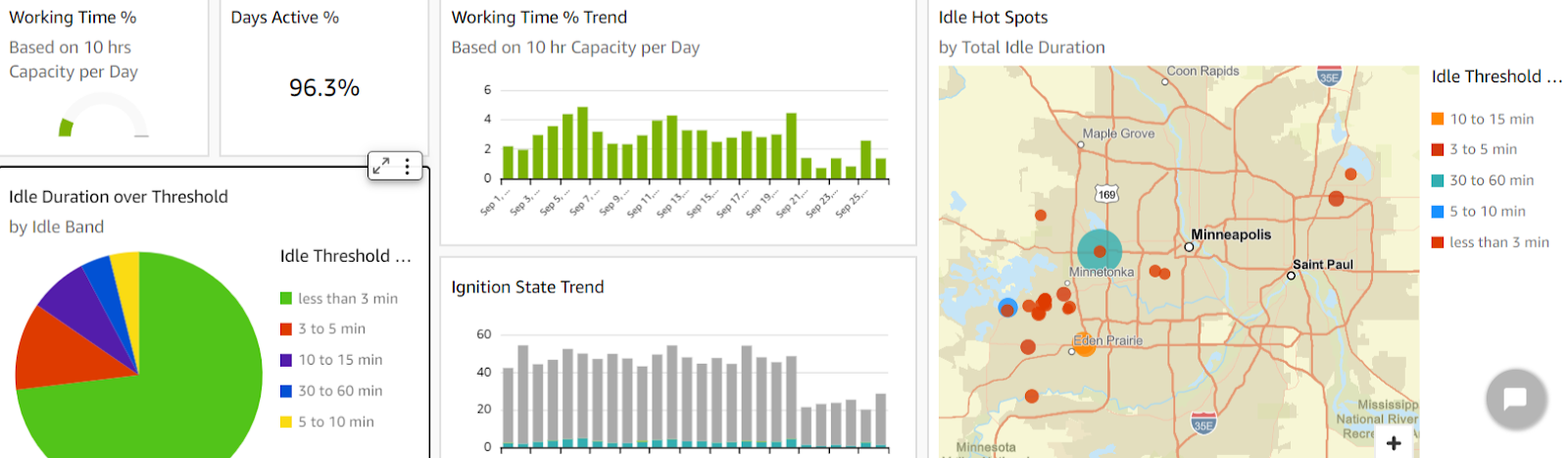
That way, you get an accurate, up-to-date snapshot of how your equipment is being used across multiple projects and job sites.
5. Establish a Preventive Maintenance Schedule
Taking care of your machinery proactively, with regular checkups and minor repairs is a smart way to ensure your assets stay reliable and your operations run smoothly, free from unplanned downtime.
As Terri Ghio, former President of the manufacturing optimization solution FactoryEye North America notes, this approach is also far more cost-effective down the line:
“As a typical example, a blown motor can cost tens of thousands of dollars to repair but keeping that motor in good condition through regular maintenance is usually inexpensive. It is akin to regular oil changes for your car or driving until the engine seizes up.”
That’s because preventive maintenance enables you to spot potential issues early and address them before they escalate into serious, more expensive disruptions.
But, did you know that you can approach preventive maintenance scheduling in different ways?
Time-based or usage-based upkeep, for instance, entails scheduling based on regular intervals.
This simply means that you plan service based on either specific time elapsed or utilization metrics, such as operating hours.
If you choose this method, Tyler Smith, Product Manager at Volvo Construction Equipment, recommends following OEM service plans.

However, it’s important to note that this type of maintenance isn’t one-size-fits-all.
Why?
Because it overlooks a very crucial factor: the actual condition of the asset, which can significantly impact how often upkeep is needed.
Ryan Anderson, Product Manager at the equipment, technology, and services company CNH Industrial, provides an example in the context of backhoes.

In such cases, condition-based scheduling is far more effective.
This approach relies on diagnostic data from OBD systems, GPS trackers, and sensors to monitor the health of your equipment in real time and inform decisions about when to schedule upkeep.
This prevents the risk of over-maintaining assets—as can happen with time/usage-based schedules—by ensuring maintenance is performed only when truly necessary.
Ultimately, both types have their strengths and can be quite effective if implemented correctly.
Time- or usage-based scheduling definitely works well for non-critical assets or those with predictable wear patterns.
In contrast, condition-based maintenance is better suited for critical assets, where failure could pose a significant risk to safety and efficiency.
In short, it all depends on your assets, business needs, and, of course, budget.
6. Adopt Digital Inspections
Frequent inspections are the foundation for any preventive maintenance program, but imagine how much more effective they can be when performed through a mobile app.
By digitizing audits and inspections, you can view asset data instantly and report issues on the spot, which allows you to address them more quickly.
Just take Superior Paving Corp., a paving and asphalt mix supply company from the north of Virginia, as an example.
Around ten years ago, they set out to digitize their operations as much as possible, all with the goal of driving more efficiency and reliability.
Tyler Mitchell, the company’s equipment manager, explains how this has affected their inspections:
“One of my favorite parts about our audits is if a piece of equipment isn’t up to standards, the app immediately generates a service request. The service request goes directly to our planning and scheduler within a minute of the audit being submitted. This allows a quick response to any items that are found to be defective before they cause a breakdown.”
Essentially, the whole process is far more efficient.
Their checkups take only about 20 minutes to complete and it’s so much easier to keep the entire team in the loop about each asset’s condition.
Now, the good news is that you don’t need some sort of specialized maintenance software to unlock these benefits.
Many general equipment management systems come packed with features that make inspections a breeze.
For instance, they usually feature task management capabilities, which allow you to assign upkeep activities to specific workers.
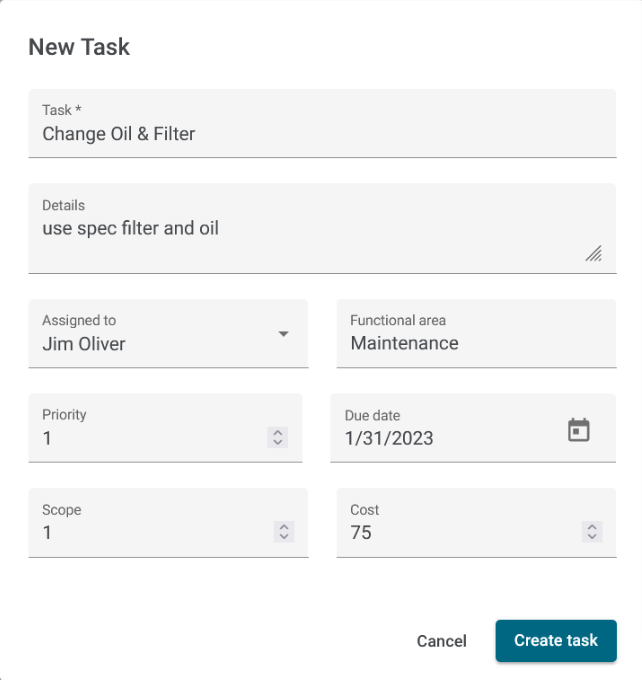
You can even set due dates, track progress, and add notes to ensure everything gets done properly and on time.
Similarly, if workers spot an issue in the field, they can quickly request service through the app.
The system automatically logs all these activities, so you can easily pull up details on when the equipment was last serviced, who did the work, and exactly what was done—ideal for strategic maintenance planning.
7. Maintain a Spare Parts Inventory
To support your preventive maintenance efforts and keep your equipment in optimal condition, ensure you always have a stock of essential replacement parts on hand.
That way, you don’t have to worry about running out of key components just when you need them, along with unnecessary downtime that usually follows.
But, how do you make sure you have just enough inventory without risking overordering?
The answer, yet again, lies in automation.
And if you’re wondering why couldn’t you simply use spreadsheets for this task, just take a look at Formula 1.
Although not exactly construction-related, this example perfectly illustrates the challenges of (im)proper spare parts management.
Until recently, the Formula 1 team was using Excel to manage over 20,000 parts—a system that, according to their new team principal James Vowles, was “useless” and difficult to navigate:
“You need to know where each of those independent components is, how long it will take before it’s complete, how long it will take before it goes to inspection. If there have been any problems with inspections, whether it has to go back again. Once you start putting that level of complexity in, which is where modern Formula 1 is, the Excel spreadsheet falls over, and humans fall over.”
The main problem was that this system made it nearly impossible to keep track of vital information, such as spare part locations, lead times, costs, and stock levels.
This data complexity is simply beyond what manual solutions like Excel can handle effectively, especially when monitoring such a large inventory.
In contrast, this is where CMMS (Computerized Maintenance Management Systems) really shine.
They not only maintain a detailed catalog of all critical parts and vendors, which they automatically update, but they also offer some other, more advanced features.
For instance, CMMS can be programmed to trigger reorder notifications when parts reach predefined stock levels, ensuring you always restock on time.
Plus, the software can pull data directly from work orders, linking spare parts to specific equipment.
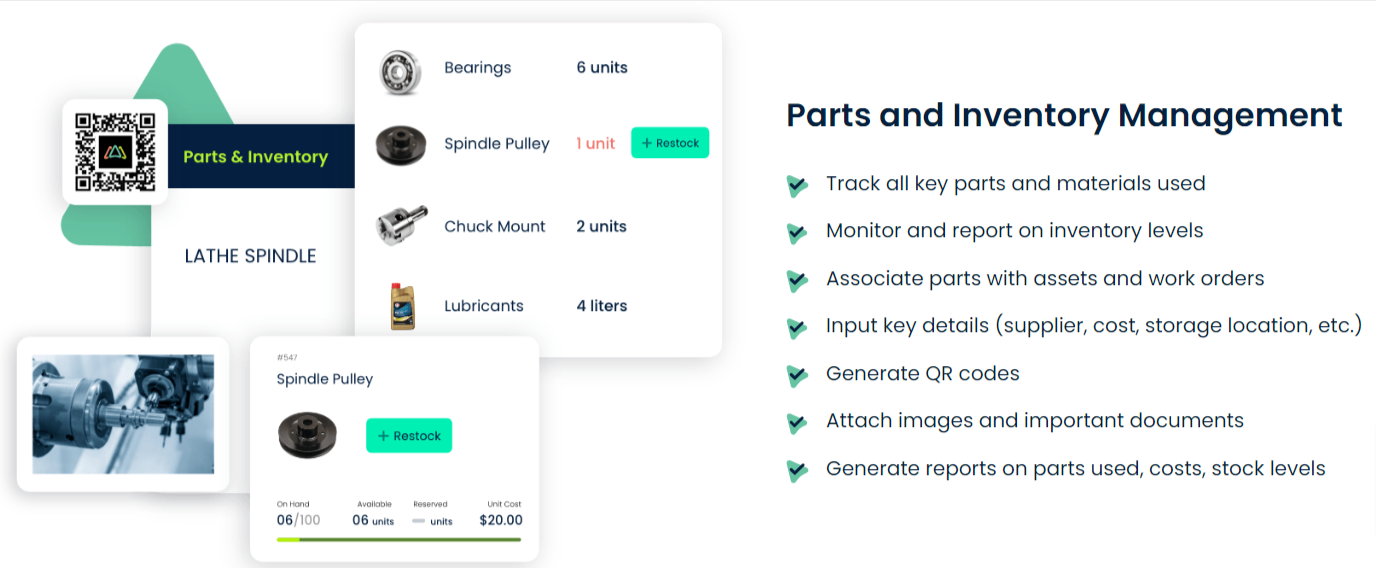
This allows you to easily identify needed parts during maintenance, as well as those that fail the most frequently.
So, in short, from inventory planning and forecasting to procurement itself, CMMS really takes your decision-making to a new level.
Excel, and other similar tools, simply pale in comparison.
Conclusion
Overall, the path towards better equipment management starts by streamlining operations as much as possible.
This entails eliminating unnecessary processes and fine-tuning those that truly matter.
Remember: when tasks are clearly defined and easy to execute, the likelihood of them being done correctly skyrockets.
And, as a result, employees use equipment in a much safer, more efficient, and cost-effective way.





