Equipment failure is one of the worst things that can happen in the field. One minute, you’re all set to start your construction project, and the next, you’re left without valuable machinery.
Such breakdowns cause delays, downtime, and monetary losses. What’s more, equipment issues negatively impact your reputation as a construction specialist.
Thankfully, machinery usually gives warning signs before malfunctioning. Do you want to learn how to recognize the early warning signs of equipment failure?
Some signs, like the dashboard light warnings and alarms, are glaringly evident, while others are a bit trickier to spot.
This article will cover those slightly less obvious signals, so you don’t miss them when they occur.
Let’s figure out how to notice signs and prevent machinery malfunctions!
In this article...
Low Fluid Levels
The first thing to look at when you’re trying to determine if your equipment needs servicing is the level of fluid.
When your machinery is running low on fluids, you’re risking serious malfunctions and severe damage. Without sufficient lubrication, equipment parts grind against each other, leading to excessive wear and tear and, eventually, engine failure.
At the same time, if you keep your fluid levels at an adequate point, you prolong the equipment’s useful life. The moving components can perform smoothly without damaging other parts.
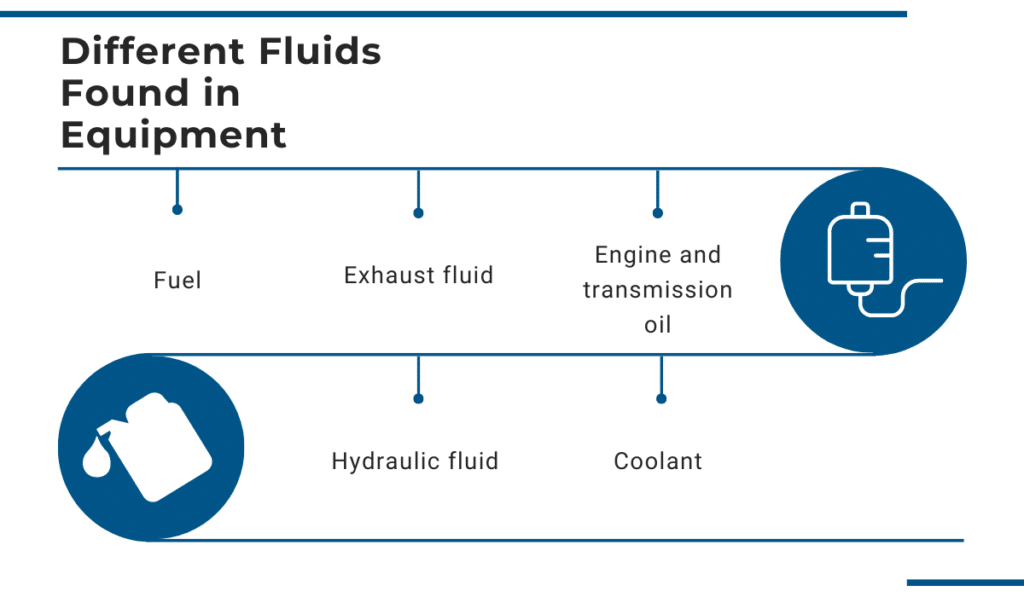
Therefore, you should always keep an eye on the levels of the following equipment fluids:
- fuel
- exhaust fluid
- engine and transmission oil
- hydraulic fluid
- coolant
Let’s take the hydraulic fluid as an example and see what could cause problems with it.
First, hot temperatures can thin the fluid, leading to pump leaks and fluid loss. The more fluid your machinery loses, the more prone it will be to damage.
Temperature changes can also cause condensation of the hydraulic fluid and, consequently, water contamination. You will know this has occurred if your equipment’s hydraulic fluid turns milky.
Air can also contaminate your hydraulic fluid. In fact, air and water contamination are the causes of 80-90% of the cases of hydraulic failure.
Luckily, these problems can be solved by frequent hydraulic fluid checks and occasional water draining.
The easiest way to maintain fluid levels is to check the dashboard: it should show you when the amount of liquid diminishes too much. In that case, you should immediately fill the equipment up before using it. That way, you’re minimizing the risk of damage.
Nevertheless, sometimes, technology can be unreliable, so nothing beats a manual inspection. Teach your team to inspect fluid levels before every use, despite the dashboard signals.
If you do that, your equipment will always be well-lubricated and function correctly. You will also be able to notice if specific machinery is losing fluid too quickly, which isn’t a good sign.
Some possible causes of such fluid loss are:
- leakage
- faulty valves
- change of temperatures
None of these are good for your equipment, so your maintenance team should immediately inspect any machinery that loses fluid quickly.
Also, train your operators to understand the effect temperature can have on fluids.
That way, you can be entirely sure that your equipment won’t need servicing due to fluid-related issues.
Exhaust Problems
Here’s a word of advice: never take exhaust problems lightly. If your equipment is showing signs of exhaust problems, it’s time for an urgent repair!
Diesel engine exhaust emissions (DEEE) exposure can have grave consequences for the employees who spend time around such equipment.
According to the Health and Safety Executive, the exposure:
- can lead to lung cancer due to cancerogenic substances in the emissions
- causes eye and respiratory tract irritation
- leads to coughing and breathlessness
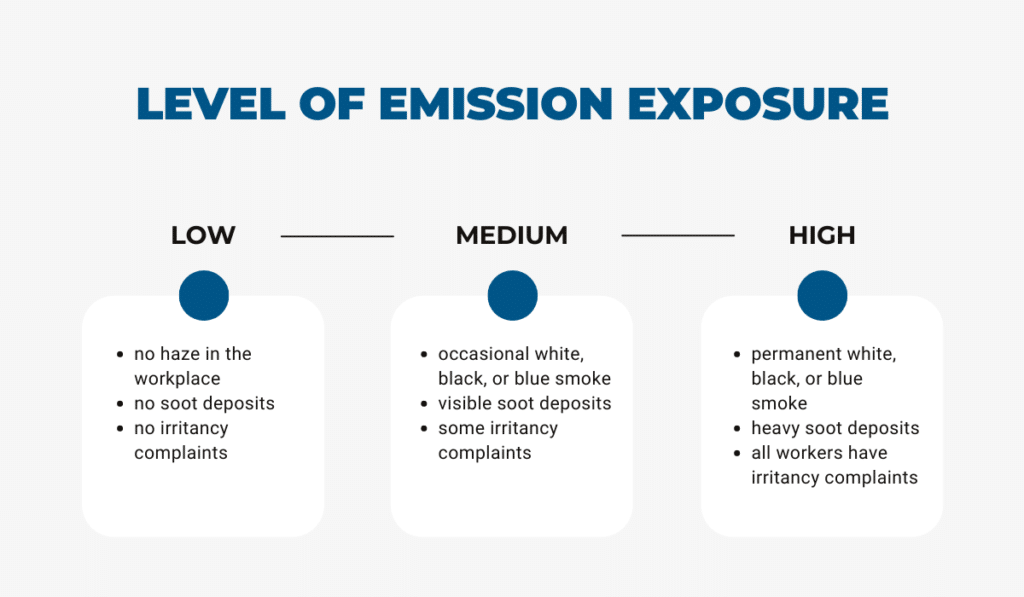
When determining whether you have an emission problem, consider three factors: haze, soot, and irritancy complaints.
First, check for haze or smoke coming from the exhaust system. Do you notice it here and there, or is smoke present at all times? Permanent smoke is a clear warning sign of exhaust problems and critical emission exposure.
Then, you can look for soot around the suspicious piece of equipment. Do you see it everywhere, only in a couple of places, or nowhere at all? If there are heavy deposits, your exhaust system isn’t functioning properly.
Last but certainly not least, think of the complaints you’re getting from workers. If they all report eye and/or respiratory tract irritation, there’s an emission issue. Look into it immediately, and avoid using the machinery until the issue is resolved.
The point is, exhaust fumes are dangerous in their own right, even without any additional damage.
To make your workplace safe, you should also keep an eye out for sudden changes in the color or smell of exhaust fumes. These warning signs require immediate attention.
So, how can you prevent exhaust issues?
The most common exhaust problems come from air filters or ventilation failures, so add regular air filters checks and replacements to your maintenance plan.
Whenever you suspect exhaust system damage, perform a vacuum gauge test to see if your exhaust pipe is plugged or restricted, i.e., whether something is blocking the air from getting out.
In general, you can avoid safety hazards by adhering to the manufacturer’s manuals and performing regular maintenance. Using your equipment as intended helps keep it functional for longer. If you top that off with an excellent servicing plan, your machinery should operate smoothly for a long time.
To sum it up, you should invest in regular equipment inspections and keep an eye for changes in the color or smell of the exhaust fumes.
Engine Stalls
Another telltale sign that your machinery is in need of servicing is if the engine starts stalling.
Engines shouldn’t stop for no reason. You also shouldn’t have a hard time getting them to run. If either of these happens, something is not right with your equipment.
Luckily, engine stalls are easy to notice, and any operator who comes across one will be able to recognize and report the issue immediately.
Of course, the first thing you should check after such a report is whether the operator knows what they’re doing.
When someone inexperienced is running the machinery, there’s a chance that the cause is something minor, like the operator taking their foot off the clutch too quickly or forgetting to change to neutral before stopping.
Both options cause the engine to stall. So, before deciding there’s an engine problem, look into the operator’s expertise.
However, inexperience isn’t the only cause of engine stalls.
Some of the most common causes are:
- powertrain issues
- hydraulic system problems
- low fuel pressure
- improper ignition
Thankfully, investing in regular maintenance and inspections will help you notice any damage to the engine on time. That way, you’ll get to ensure that your employees are safe when using your equipment.
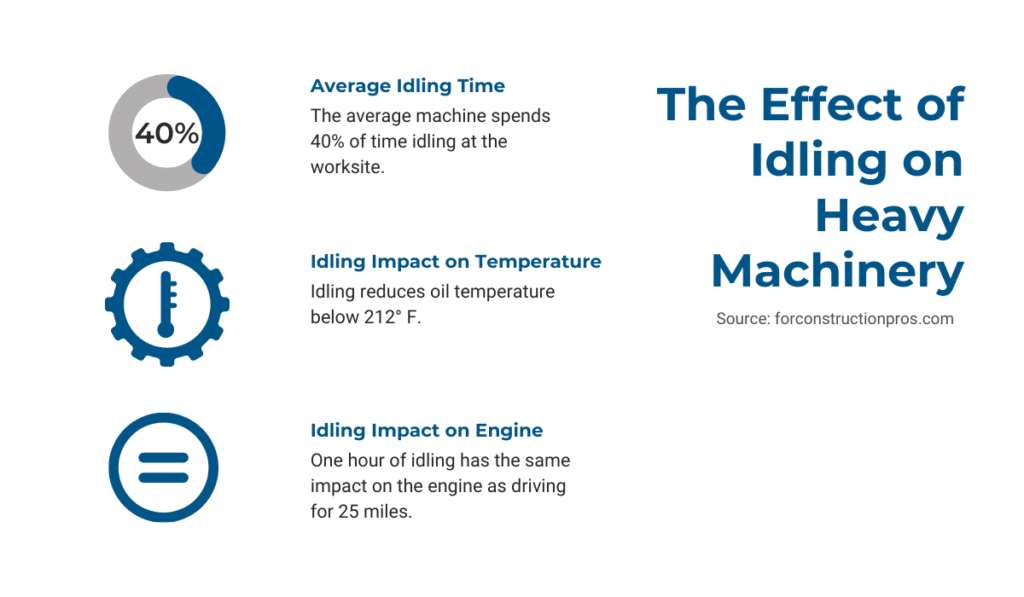
One more thing you can do to prevent engine problems is to avoid idling. Of course, machinery will never be in use 100% of its running time, but if you know that you won’t need it for longer than another 30 seconds, you should turn it off.
You may think it’s easier for the engine to idle rather than restart, but that’s not true.
While frequent restarting causes circa $10 worth of wear and tear yearly, idling costs you more, as it can mean burning through as much as a gallon of fuel per hour.
There are other downsides to idling, too.
First, leaving the engine running lowers the engine temperature. When the temperature is far from ideal, the fuel doesn’t combust as it should. Instead, it leaves behind a residue that can damage the engine.
To be more precise, idling can reduce the oil temperature below 212° F, which increases the stress on your engine and leads to more wear and tear.
Additionally, studies have shown that one hour of idling has the same effect on the engine as a 25-mile drive. If you consider that heavy machinery spends 40% of its run time idling, the number of miles goes up significantly.
That would mean that in an eight-hour workday, your machinery idles for more than three hours, the equivalent of taking a 75-mile drive. That’s 375 miles per week!
Because of these additional miles that your machinery didn’t even make, you’ll have to invest in more frequent maintenance, including filling the equipment up with oil and fuel more often.
On top of that, these 375 miles a week age your machinery faster than if you’d turned the machine off when not using it.
Clearly, it’s a lot better for the equipment to restart the engine often than to leave it running idle for over half a minute at a time.
Unusual Noises and Other Noise-Related Issues
Your equipment will often let you know there’s an issue by creating different sounds than usual.
Because of this, noticing the difference between the regular sound of running equipment and noises that represent a cause for concern should be a priority.
Chances are, the average employee won’t be good at this, especially at first, but your experienced operators will likely develop this skill after a while.
Since they use the machinery daily, operators get used to the sounds it usually makes. They understand how the machine behaves when the engine starts, when it runs, or is idling.
If something goes wrong with the equipment and a strange noise appears, your operator should quickly notice it.
Instead of continuing to use the machinery, the employee should report the issue to the maintenance staff immediately.
Let’s look into the possible causes of unusual noises made by the equipment.
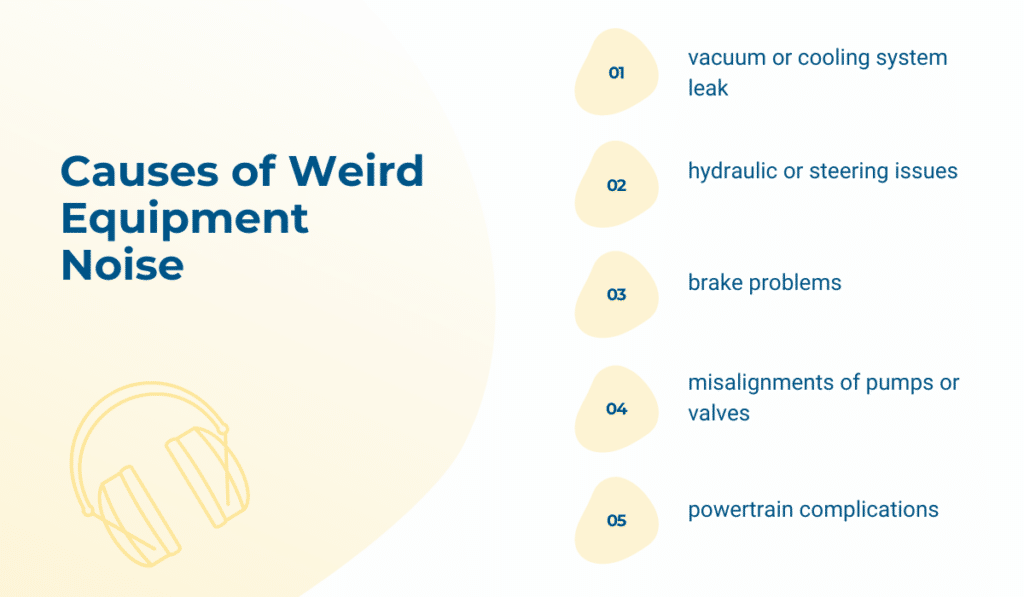
If your vacuum or cooling systems have leaks, you’ll probably hear hissing sounds coming from the equipment. Since hissing isn’t exactly a typical sound for machinery, it should raise the alarm for your operators.
On the other hand, hydraulic, steering, or braking system issues can cause a clunking noise. If you hear it, your equipment needs immediate servicing.
When there are some pump or valve misalignments on your machinery, you’ll hear a grinding noise.
However, if the noises are high-pitched and sound like whining, your machinery could be experiencing powertrain issues. The noise caused by powertrain complications can also sound like gurgling or grinding.
As always, when you notice something unusual with the machinery, it’s best to let your service team inspect it right away. A professional will know what to check to determine the root cause of the issue. After the analysis, your team will be able to offer solutions.
If your equipment sounds strange, it’s trying to tell you something’s off, so have it serviced!
Moreover, even when it doesn’t indicate a particular issue, noise is a big problem on the construction site. Prolonged exposure to it can lead to hearing loss.
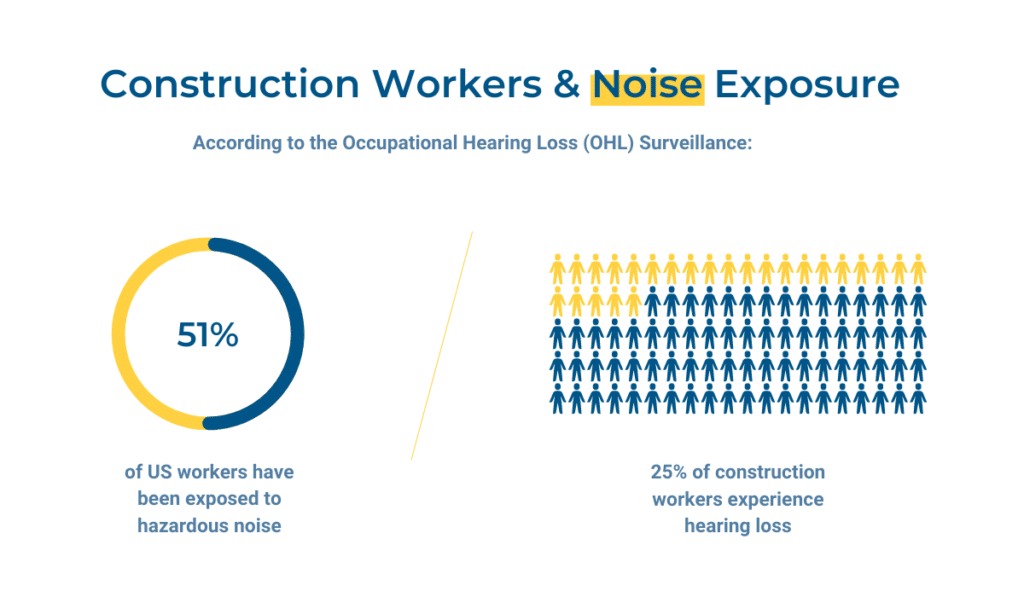
Even though the construction industry is aware of this threat, more than half of US construction workers have been subjected to hazardous noise at the worksite. What’s even worse is that a quarter of them have hearing loss which impacts their day-to-day life.
Because this is a prevalent issue in this business, you’re probably already taking precautions to protect your employees, like making hearing PPE obligatory.
There’s a catch, though.
Unmaintained equipment actually increases the risk of hazardous sounds.
Machinery, especially when starting to malfunction, sometimes creates a lot more noise than usual, endangering the health of your employees.
The noise is a lot louder and more piercing than you’d expect when there’s an underlying issue, which renders your current hearing protection measures useless.
OSHA’s recommendations include limiting noise exposure to 90 dBA over 8 hours. If the level of noise goes up by five dBA, you should cut the hours in half to prevent hearing damage.
However, if you aren’t aware that your equipment is making much more noise than it’s supposed to, you unknowingly subject your workers to the risk of hearing loss.
So, if you want to avoid damage to your equipment and the safety risks, invest in regular maintenance. During such inspections, your team should identify the causes of unnecessary noise and eliminate them before you can use the equipment again.
Therefore, if you don’t invest in servicing, you’re putting your workers at risk of noise exposure, as well as malfunctions.
How to Protect Your Construction Equipment From Further Damage
Now that you know how to recognize signs of equipment damage, let’s look into ways of preventing that damage in the first place.
The easiest way of doing that is by investing in preventive maintenance (PM).
This type of servicing happens more often than others, but it allows you to catch potential issues before they cause any significant damage or equipment problems. When you implement PM, the staff regularly inspects the machinery, making it easier for them to notice any changes.
That’s why it’s no wonder that preventive maintenance is favored by 80% of maintenance personnel.
You may be on the fence about this type of maintenance because of its cost. After all, you need to have enough employees to stay consistent and create a schedule that includes all the vital equipment. On top of that, the number of planned downtime hours goes up, which incurs expenses as well.
However, don’t let these initial investment costs deter you from conducting preventive maintenance.
Here’s a good reason: this type of maintenance has a 545% return on investment (ROI) over 25 years.
Let’s explain that in more detail so you can understand the fundamental importance of PM.
ROI is a metric used to measure how much your initial investment pays off. If your ROI is 100%, it means that you gained the exact amount you paid for the investment in the first place. So, if you purchased a tool for $5,000, you got $5,000 back from the asset through its usage.
Of course, your goal is to have a higher ROI because it means you earned more than you initially paid.
The ROI for preventive maintenance is 545%, which means that paying $5,000 for maintenance costs would earn you $27,250. All it takes is patience and a good maintenance plan!
Teach Your Team About Equipment Maintenance
Investing in maintenance isn’t the only thing you can do to eliminate equipment breakdown. You can also invest in proper equipment maintenance training for your entire staff, and not just the maintenance team.
That way, anyone who comes in contact with a piece of machinery will know how to perform basic servicing tasks and notice when something is wrong. For example, you can teach your team to recognize the four signs mentioned in this article, so when they spot them, the operators will know to report them to the maintenance staff.
It’s also worth noting that equipment damage is often caused by operators who don’t know how to use it properly.
So, make sure to teach your staff to safely operate and inspect the machinery. That way, you’re lowering the chances of warning signs even appearing.
On top of all that, you can also invest in an equipment management tool if you want to prevent machinery damage.
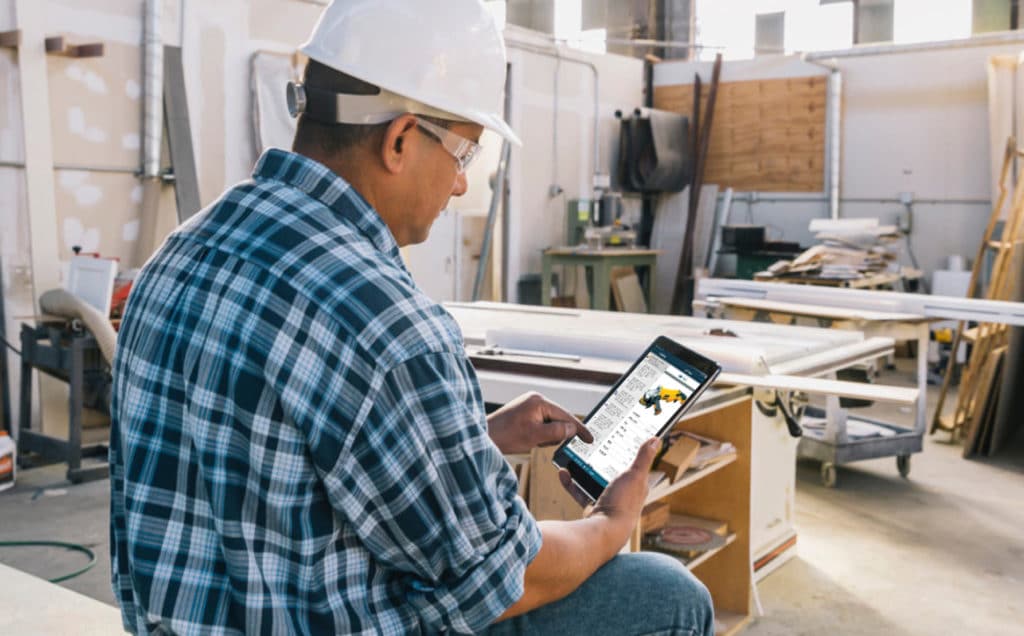

These tools let you track your equipment and its maintenance, allowing you to access past maintenance records and see the equipment’s current condition.
Based on this information, you can decide how often to schedule servicing and whether it even pays off to continue investing in the piece of machinery.
You can use this information to create a personalized servicing schedule that will help you prolong the equipment’s useful life and increase your ROI.

This type of equipment tracking isn’t exactly new in the construction industry: 53% of large general contractors use software to manage inspections, and another 42% plan to start tagging their machinery by 2022.
You have a choice: get on the trend and start using software to track your machinery or fall behind all the competitors who are already doing it.
Conclusion
Construction equipment usually lets you know that something is wrong before it breaks down.
So, if you want to react on time and save yourself time and money, teach your staff to recognize signs of potential issues.
The better trained your operators are, the easier it will be to notice when something is off. Your maintenance team will then be able to pinpoint the cause of this warning sign and fix the issue before the equipment malfunctions.
The easiest way to do all of this is to train your employees and invest in preventive maintenance.
So, what are you waiting for?