Chances are you’ve already scanned numerous QR codes with your smartphone and experienced firsthand how quick and effortless it is to access online information.
This technology is increasingly used across various industries in a multitude of applications, and the construction industry is no exception.
In this guide, we’ll run you through what QR codes are and how they work, why and how construction companies use them to streamline operations and improve productivity, and how you can implement them in your business to do the same.
In this article...
What Are QR Codes
Although some might associate QR codes with marketing, they have their roots in the Japanese automotive industry, where they were invented almost 30 years ago as a way to track parts during the vehicle assembly process.
The idea behind QR codes was to create a more advanced and efficient solution than traditional barcodes, one that’s more easily scanned at any size from any angle, can hold more information, and can be read even when damaged.
Here’s how Encyclopedia Britannica defines and describes Quick Response (QR) codes.

When encoding data (URL, text, contact details, any other information), the free code generator on your phone or internet uses an open-source QR code standard to turn it into a QR code.
Although QR codes often contain only a small piece of data (like a web link), it’s worth noting that they can store—and make available even when scanned without an internet connection—much more information.
Moving on, let’s see how these versatile codes work.
How Do QR Codes Work
Although QR code patterns may appear complex, the way they work is elegantly simple.
In essence, QR codes function as data carriers; when you scan one with a smartphone, tablet, or a dedicated QR code reader, you open a digital door to access the information within.
The sequence of actions is straightforward—scanning, decoding, and action—and the whole process takes only a few seconds.
The first step involves using your device’s camera to capture the image of a QR code, i.e., scan it.
Then, the built-in scanning app on your device deciphers the code’s pattern, transforming it into readable, i.e., decoded data.
Lastly, once the data is extracted, your device takes the appropriate action.
For example, when a BobCat skid steer operator scans a QR code found on the vehicle or the cover of its operation and maintenance manuals, they’ll be instantly taken to a free operator training video.

So, there is the act of you scanning the code, your device’s scanning app decoding data on it, and taking you to the relevant BobCat training video.
Depending on the extracted data, you might be prompted to save contact details, visit a web page, or perform other actions.
Another often-used QR code-based setup with a similar sequence of actions involves having some type of specialized cloud software with its in-app scanner installed on your smartphone or tablet.
In such cases, you launch the dedicated software and activate its scanning app (instead of the one your phone came with), which typically triggers your phone’s camera to perform the QR code scan.
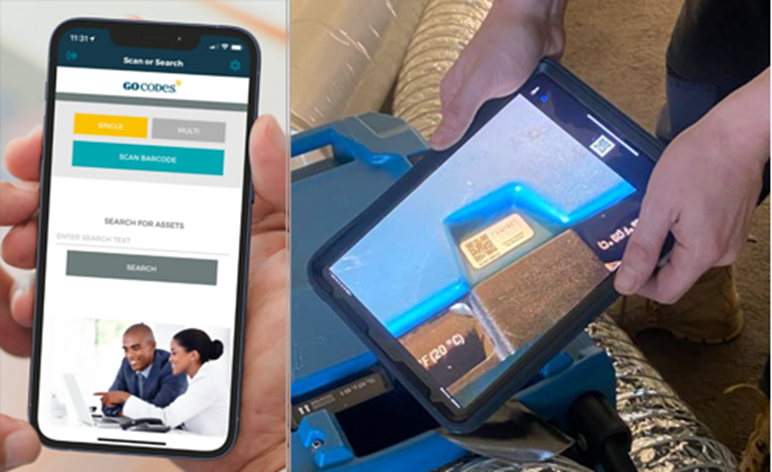
The built-in scanner then decrypts the code’s pattern and sends the extracted data to the cloud software’s database.
The software processes the data and determines the appropriate action to take.
This could involve displaying detailed information, allowing users to update records, triggering notifications, executing specific tasks, and prompting users to confirm an action or provide additional info.
In any case, QR codes offer a simple and quick means of connecting physical and digital objects with their information stored online, enabling a wide range of applications in various industries, including construction.
Let’s see what they are.
What Are the Applications of QR Codes in Construction
While the number of diverse QR code applications in construction keeps growing, we’ll explore five major aspects of construction operations where QR codes can help streamline processes and improve efficiency.
Project Management
A successful completion of any construction project usually implies that all the other aspects covered here, such as information access and quality control, were efficiently managed, too.
The fact that QR codes can facilitate processes in all of them is a testament to their versatility, simplicity, and affordability.
As for more specific project management tasks, QR codes can help monitor project progress in various ways.
For example, when one part of the construction is completed, the site engineer filing an inspection request can generate a unique QR code, which the quality engineer will use to initiate the relevant inspection process.
You can see that workflow here.
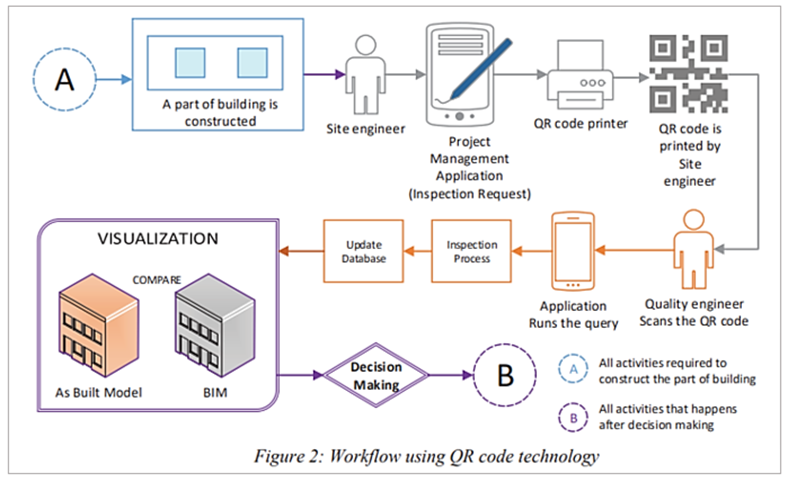
After the inspection, the project management software’s database is updated, and, in this specific example, as-built data is compared to the digital model made using Building Information Modeling (BIM) software.
That way, project managers and construction teams can monitor progress as the project tasks are completed and project milestones reached.
Naturally, there are many other areas of project management where QR codes can streamline processes, and a major one is information access.
Information Access
This is the most extensive area of QR code applications in construction.
QR codes enable quick and convenient access to crucial information, such as project drawings and documents, safety and emergency instructions, and operating manuals, to name a few.
When QR codes are placed on these documents, equipment, or specific locations on a construction site, they allow workers and project stakeholders to effortlessly retrieve essential and sometimes life-saving data, like these emergency lowering guidelines for scissor lifts.

Since QR codes can be printed on any material and affixed to any surface or object (or just shown digitally), there are countless examples of their use for easy information access on construction sites.
For instance, by scanning a QR code on a blueprint, construction teams can access the latest design revisions and construction instructions in seconds, ensuring their work complies with approved project changes.
Again, noting the multitude of existing and emerging ways in which QR codes enable fast and easy access to online information, let’s move to quality control.
Quality Control
Workers’ equipment and tools should be high-quality and well-maintained, the construction materials should fit project specifications and local building codes, and completed construction works should meet stringent quality standards.
QR codes play a significant role in streamlining all these quality control processes by enabling contractors to track, monitor, and conduct essential inspections on equipment, materials, and finished works.

In the above image, the inspection team uses QR codes posted around the site to access digital floor plans during inspections.
Another example involves QR codes on materials, enabling workers to easily verify that the materials delivered on-site meet specific project requirements and quality standards.
As for ensuring that tools and equipment are regularly inspected and well-maintained, we’ll cover how QR codes can help under asset management.
Asset Management
Similar to accessing information, when QR codes and cloud software are used for asset management, this opens a wide range of features that enable you to track the location, usage, and maintenance status of your equipment, tools, and other construction assets.
To illustrate, here are just some features enabled when QR codes are attached to assets and linked to the tracking software’s database.
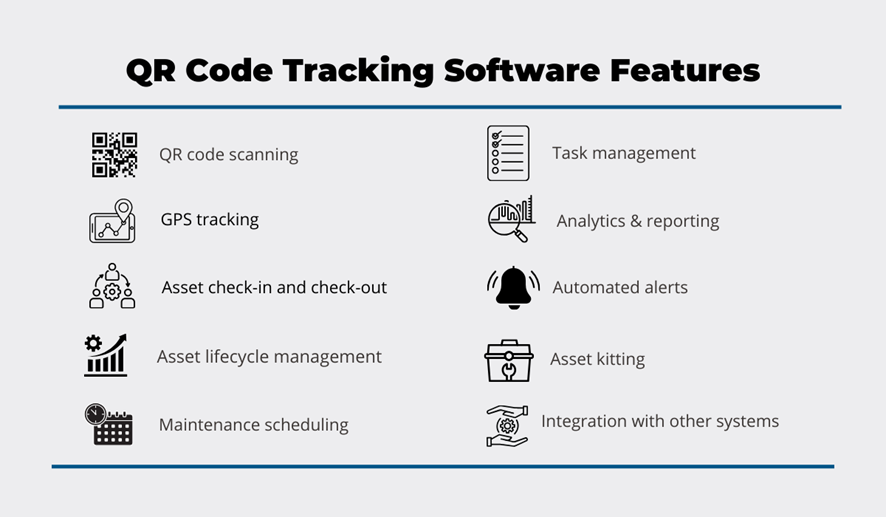
Since there’s no room to explore all of them, we’ll highlight just two QR code-enabled features that allow construction companies to minimize external and internal theft, poor maintenance, and negligent handling of their equipment, tools, and other assets.
Firstly, QR codes enable you to set up an automated check-in/check-out system where workers, by scanning one or more assets, check them out (assume responsibility for them) and check them back in.
Since the software keeps track of asset users—and they know it—this instantly increases worker accountability and reduces cases of loss, theft, negligent operation, and poor maintenance.
Secondly, when a QR code asset tag is scanned with a smartphone or tablet, the tracking software will use the device’s GPS function to automatically capture where the asset is located, which leaves room for improved security measures.
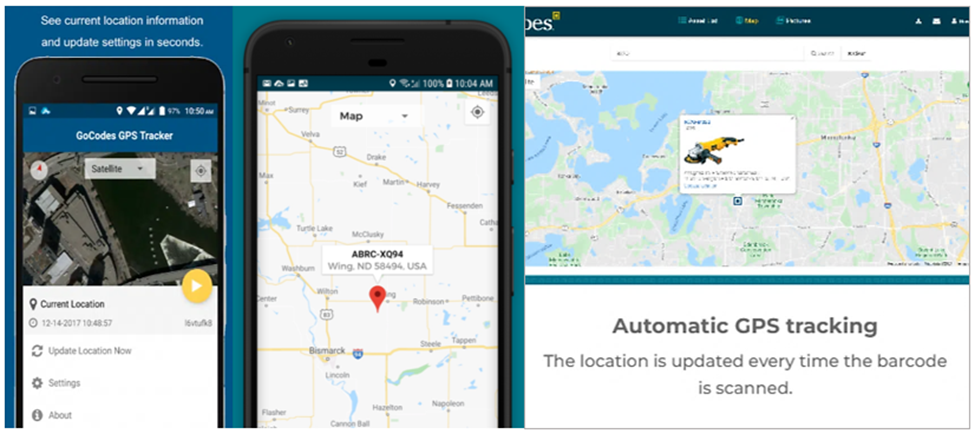
All in all, there is almost no aspect of asset management that can’t be streamlined using a QR code-based asset tracking and management system, which, as we’ll see next, involves keeping track of spare parts and other inventory.
Inventory Management
Remember how QR codes were initially designed for tracking car parts during production?
As examples show, the same principle applies to tracking materials and assets.
This naturally extends to tracking inventory quantities of spare parts, accessories, and other consumable items required for efficient construction operations.
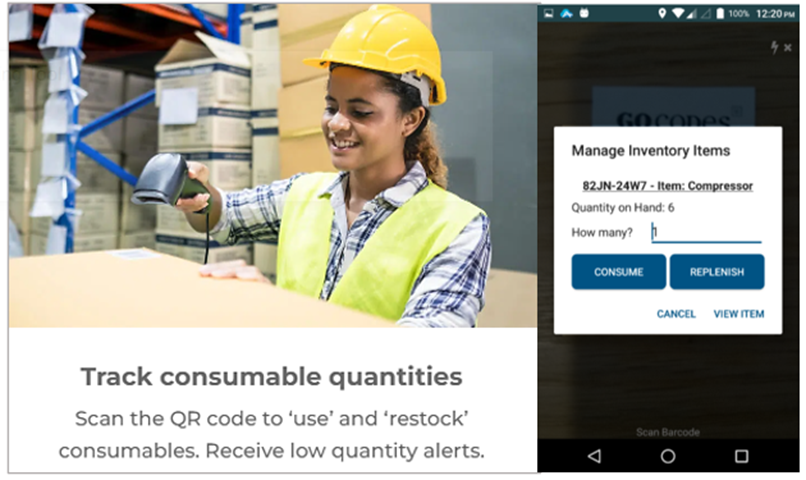
This function then enables further inventory management features, such as receiving automated low-quantity notifications, allowing you to order and restock supplies on time.
Since QR codes can link any physical item to its digital information, one software app can perform numerous functions, acting as an all-in-one solution for tracking assets, maintenance, materials, and inventory.
Let’s see what you need to implement different QR code applications into your company’s processes and jobsites.
How to Implement QR Codes in Construction
Naturally, the method of implementing QR codes will depend on your company’s specific use case.
In some instances, such as linking QR codes to web-based content, only a QR code (digital, printed, label/tag) needs to be generated and associated with the online material.
However, when QR codes are utilized for tracking and managing physical items and when tracking software is employed for additional management features, the implementation of a QR code-based system varies.
Let’s see how the process of QR-coding works in such cases.
Choose a QR Code Asset Tag Supplier
While it’s possible to generate and print QR codes yourself and attach them to assets and inventory, you’ll still need the software to convert them into data-collecting tools and take advantage of its management features.
The best way to do it is to select a tracking software provider that delivers customized QR code asset tags (which you can also print yourself).
That way, you’re ensuring seamless compatibility of all system components (QR codes, software, in-app scanner) while simplifying and lowering the cost of all processes associated with running an efficient tracking system.
For instance, our QR code-based tracking software, GoCodes Asset Tracking, is a one-stop solution for tracking and managing tools, equipment, and consumable inventory.
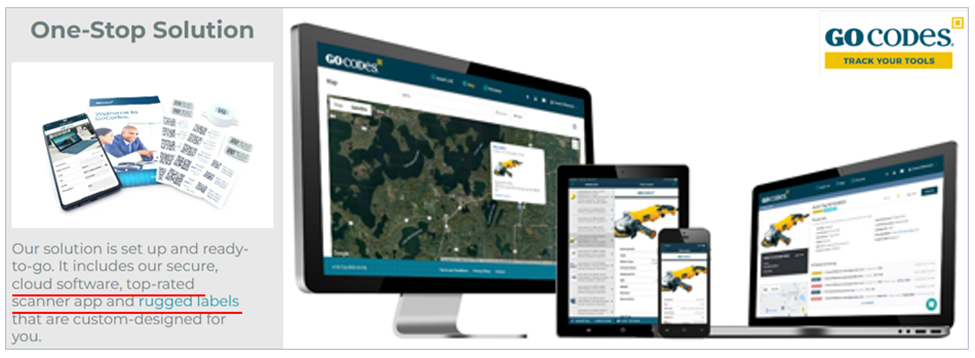
When QR codes are coupled with easy-to-use software, a built-in scanner app, and the powerful features we mentioned—and sourced from a single provider—you end up with a very affordable, easily implemented, and user-friendly system with integrated customer support.
Most importantly, even less tech-savvy workers in your team will be able to use it with minimum training, thus simplifying the system’s deployment and user onboarding.
To recap, the first step in implementing QR codes (for asset tracking) is choosing the right tracking software (provider) that handles the entire process of customizing and delivering rugged QR code asset tags and providing support, training, and updates.
Create a Plan to Onboard Your Team
Establishing a QR code-based system does require a well-thought-out plan for team onboarding.
Start by identifying key personnel (administrators) who will use the system and their specific roles, followed by determining other users and what procedures they should perform.
This should serve as the basis for preparing different templates for documents like inspection reports, maintenance schedules, safety checklists, task assignments, equipment manuals, etc., all of which will be accessed when a QR code asset tag is scanned.
All such documents can be linked and accessed through the asset’s info page within the software’s database, which allows managers to track many specific data points, like the location, usage, and maintenance of assets.
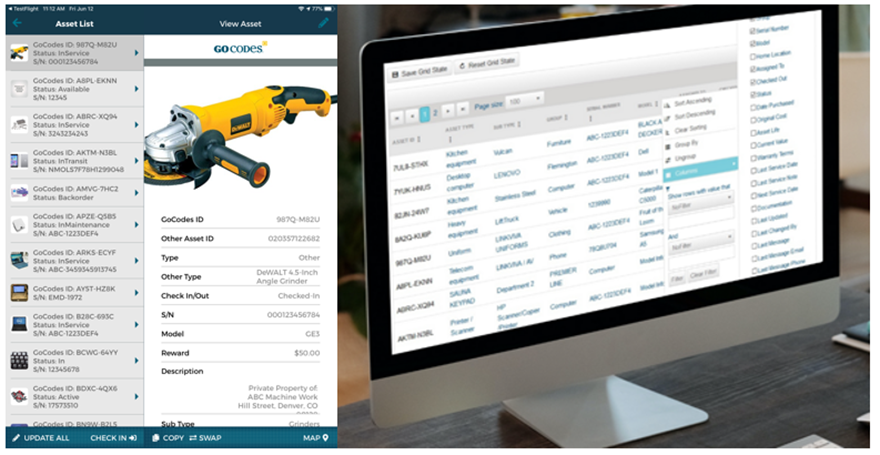
Naturally, some of these documents, guidelines, and instructions can have their own QR codes printed and attached to specific locations, depending on their use.
Once QR codes are attached to tracked items and linked to initial asset data in the software’s database, your team can be onboarded and trained.
Train Your Team on How to Use QR Codes
Since using QR codes is straightforward (scan and access info), training your team involves demonstrating how tracking software works and explaining best-use practices, including proper scanning techniques, data entry, and troubleshooting common issues.
That’s why you should prioritize the software’s simplicity and ease of use, including system setup, deployment, training requirements, and user support.

Of course, your software provider should offer direct and practical support (email, chat, phone), provide any training required, and ensure users have access to a great help center with FAQs, in-depth articles, and video tutorials.
Effective training will empower your workers to embrace the QR tracking technology, making the system’s implementation easier and your operations more efficient and data-driven.
Conclusion
So, we covered the basics and followed them up with some key fields of QR code application in construction, such as information access and asset management.
Then, we explained how to set up different QR code-based systems and what steps you should take to optimize the process.
We hope this article helped you better understand the versatility and simplicity of utilizing QR codes in construction and the benefits your company can enjoy from this easy-to-use and affordable technology.