Inventory management has come a long way since the time of physical counting.
Today, inventory management systems can run on both SaaS and on-premises systems, integrate with accounting and ERP systems, which makes them suitable for large organizations.
The reason Inventory management was invented was that physical inventories took too much time.
Every time you need to know something, you have to go down to the warehouse, count the stock. There are many SKUs (Stock Keeping Units) that companies had to handle.
Along with SKU’s came problems related to handling those SKU’s, such as spoilage or dead stock.
But what was the solution to these problems? Inventory management software.
Inventory management systems help cut your losses and ensure an even better flow of operations. But even with an inventory management system, you need to understand which metrics to track.
In this article...
1. Gross Margin ROI
This inventory metric is a profitability ratio that defines the average amount the product returns above its cost.
Gross Margin metric answers the question: “For every dollar I invested, how many I got back?”
It is the Gross profit divided by average inventory cost.

This metric is better used when calculating it per item. When used that way, it will reveal product performance and improvements required for that particular stock.
2. Gross Margin Percent
This is the percentage of the difference between sales and cost of goods divided by sales. Or “For every product I have sold, how much is my profit?“

This metric predicts whether you should have more stock in inventory, get more or fewer suppliers, or for an existing supplier how much should the price be.
Gross Margin is different than Contribution margin (selling price per unit minus variable cost per unit).
Here’s how.
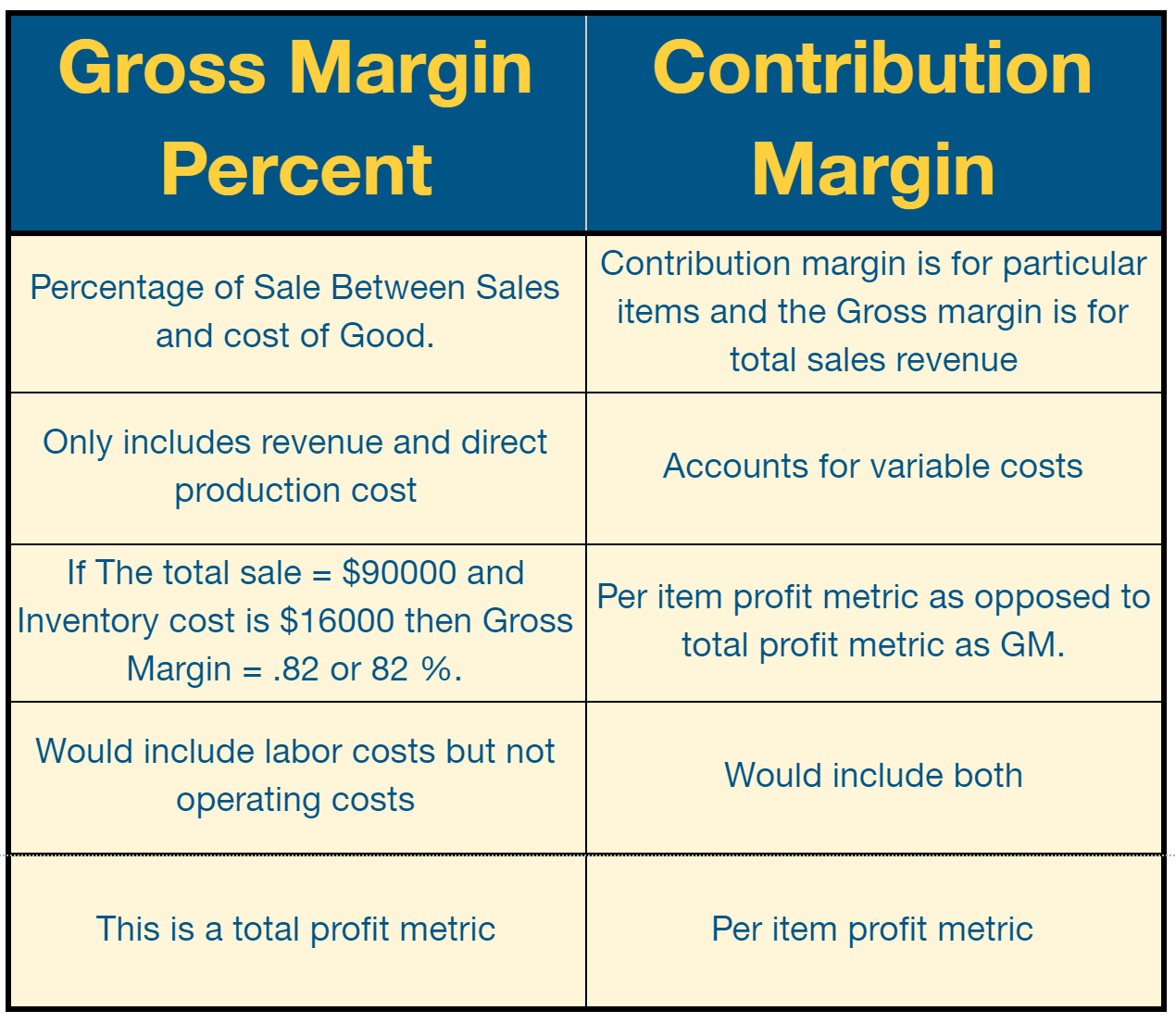
Source: GoCodes
3. Inventory Record Accuracy
This inventory metric determines how close the recorded inventory is to the actual inventory.

This is difficult to determine accurately as this means someone has to physically go to the warehouse and count.
But not doing so can cause many problems. You can have a stock out problem (non-availability of product), misplaced/missing inventory.
Also, to maintain a high level of accuracy, you need an extremely accurate record (most software goes for 95% accuracy).
How can you achieve such accuracy?
- Develop a routine to do physical inventory (cycle counting)
- Check your naming conventions to make sure that they align with your SKU’s
- Get a WMS (warehouse management systems) for inventory tracking
- Protect your inventory from threats such as moisture, pests, thieves
4. Sell-through Rate
This metric is the percentage of the number of units sold divided by actual inventory. To calculate it, ask yourself “How much of the total inventory am I actually selling?”

Sell through rate is calculated for particular products. It determines whether you should rebuy this particular stock, how much you should buy etc. It is mostly used to determine product discounts on a particular item.
5. Cost Of Carrying Inventory
The cost of carrying inventory is the cumulative cost of keeping a particular product.
Or “How much money am I spending just to keep this stock\inventory in my warehouse?”

The cost of carrying inventory is the sum of:
- Capital costs: includes inventory purchasing cost, services cost (legal, accounting, etc.) and cost of the improvement (upgrading the product, adding new features).
- Storage cost: consists of fixed and variable costs associated with renting the warehouse. Lighting, air conditioning/heating, rent, etc. are fixed costs. i.e. costs that won’t change irrespective of the volume of the inventory. The number of employees, bonuses, commissions, etc. are variable costs that increase or decrease with changes in inventory.
- Service cost: also called the cost of handling inventory. Insurance, installing hardware and software, taxes, etc are part of service cost. Service cost depends on the volume of inventory in your warehouse (variable cost). Higher volume means more tax, more hardware to keep the inventory and more installation costs.
- Risk cost: storing inventory comes with the risk of deterioration, obsoletion, expiry, etc. But this risk can also be physical damage to the inventory (water damage, theft, vendor fraud). Or it may be an administrative error (shipping error, shrinkage, misplaced item error).
Ideally, the cost of carrying inventory should not be more than 20-30% of the carried inventory.
In this case, the capital cost should be the highest one. Companies should aim to reduce this cost as much as possible.
Some factors can be easily changed, e.g. using cheaper software to track inventory. Others are difficult, e.g. rent of warehouse, equipment, etc. But still, changing the inventory cost can have a huge impact on the profit margin.
6. Inventory Turnover
This metric measures how quickly the entire inventory sell-through during a particular period of time. This is a ratio that looks at how much time a particular stock is kept before selling completely.

Source: Unsplash.com
This is different from the sell-through rate as it focuses on sales per month.
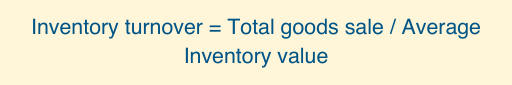
A higher value for inventory turnover is favored as it would mean everything that’s coming into the warehouse is getting sold quickly.
It would also make inventory carrying costs a minimum. Different sectors can have different ratios and different ways to calculate profits depending on how they stock their warehouse.
7. Fill Rate
Fill rate is the number of orders coming to your warehouse and going out on time. It is the answer to the question: “How many orders is my company fulfilling successfully as opposed to the number of orders coming in?”
This metric corresponds to customer service. The better fill rate is, the better the overall experience the customer would have.

Getting regular feedback from customers determines the accuracy of your fill rate. The purpose of a business should not be just to get customers but also to retain them, and fill-rate has a direct impact on that stat.
- The goal should be 100% fill rate, most companies maintain 98%.
- More than a 100% fill rate is also not good. That would mean you have stockouts and you have to backorder.
- Ideally, you should maintain a sweet spot of 95-100%.
To maintain this, invest in a sales management software solution that has an inventory feature. Also, you can keep a standard record or a ledger for the inventory and make sure that everyone who needs it can access it.
8. Operation Productivity
This metric asks “Are my employees happy?” If they are not happy, managing a huge inventory warehouse can be a dreadful challenge.

Source: Unsplash.com
For maximum warehouse productivity, you should implement the following things with your staff:
- Labor and productivity measurement: There may be some tasks that are done repetitively and some tasks are done sparingly. Set up TMU’s (Time measurement units) that break down all the time taken into units and calculate the average time taken per task.
- Set up performance, quality, quantity and organization metrics for your team: Once the staff sees that they have defined metrics on which they will be judged, they will work harder to be on par with the metrics.
- Metrics can also be adjusted so as to customize them to your company’s needs. If you need targeted inventory handling that focuses more on the accuracy of the work than speed, you can focus on quality metrics more than quantity ones.
- Calculate efficiency: Efficiency can easily be calculated for each employee, based on the data collected for the previous metrics. This can also help the staff figure out what they are doing wrong and how to fix it.
- Training: Those who are lacking the skills, provide training so that you may have an upskilled staff.
- Easily implemented software solution: With a software solution (RFID chips or barcodes), measuring inventory and stocking becomes easy. Execute such a solution and train your staff.
Easier solutions will help people get more organized, complete their jobs with more efficiency and productivity will increase.
9. Safety Stock
Safety stock is your backup plan in case of stockout. It is the little extra stock you keep in your warehouse that acts as a buffer for stockout and price fluctuations.
Safety stock answers the question: “How many orders can I still fulfill if I run out of stock?”
Keep this too low and you risk stockout. Keep this too high and you risk losing shelf space and carrying costs.
This should also correlate with inventory securing time and shipment time. (Overlapping of shipment time and inventory securing time so that you get the next shipment as early as possible)
Point to measure are vendor lead time (time in which inventory reaches warehouse), consumption (a requirement for the item), reorder point (the point at which you order for next stock from vendor)
Real-time forecasting can be used to identify buying patterns and sale records so as to forecast the amount of safety stock required. And if some unexpected fluctuations do happen, that’s what safety stock is there for. Use it to minimize damage.
10. Cycle Time
This metric tracks the time from when the order is issued until the time order is fulfilled. Or “How quickly can my customer get an item after ordering?”
Item processing time, packing time, shipping time, etc. are all covered in cycle time.
- This sets an expectation for the customers, as they get a tentative delivery date for the ordered item.
- Make sure that users are getting accurate dates when they order.
- Also, ensure that shipping errors are less and time expectations are real.
Other things to reduce cycle time: deliveries can be optimized for distance so that there is minimum traveling time between the warehouse to address.
Algorithms can be maintained to cluster customers by address for targeted delivery.
Conclusion
Once you understand the metrics, start tweaking and customizing them to your warehouse and type of stock.
For example, if your item is a perishable one, you can assign more value points to cycle time than shelf space. You just have to tweak your metrics as per your points of analysis.
Data-driven, smarter decision making is the new future of warehouse management. Your goal should be adjusting your strategy for maximum profit.
There’s a demand, and there’s a market.
You just need to fulfill it.




