Bluetooth beacons are very cost-effective, versatile, and efficient, so it comes as no surprise that many businesses are finding ways to incorporate them into their daily operations.
If you, too, are intrigued by this exciting technology and are considering introducing it to your own company, you’ve come to the right place.
Before diving into many different brands and types of Bluetooth beacons, it’s best to first get a solid understanding of the technology’s fundamentals.
Therefore, consider this article Bluetooth Beacons 101, where we cover all the beacon basics, from their hardware to all the ins and outs of how they operate.
Let’s start with the hardware.
In this article...
What Hardware Are Bluetooth Beacons Made Of
Crack a Bluetooth beacon open, and inside, you won’t see a bunch of wires or gears.
Instead, there will be a radio, a microprocessor, and a small battery, usually a lithium-ion one.
Some beacons may even have built-in accelerometers, temperature sensors, and other various add-ons, but that’s pretty much all there is to the hardware that makes them up.
Thanks to such a simple design, Bluetooth beacons are inexpensive and easily-maintainable solutions.
Consequently, many businesses choose them for asset tracking, indoor navigation, access control, and a plethora of other applications.
While the way they look on the inside remains almost the same from beacon to beacon, their outside appearance is dictated by their particular use case.
For example, if a beacon is used for navigation within, say, a museum, it’ll probably be designed to blend in with the surroundings, with subtle colors and smaller size.
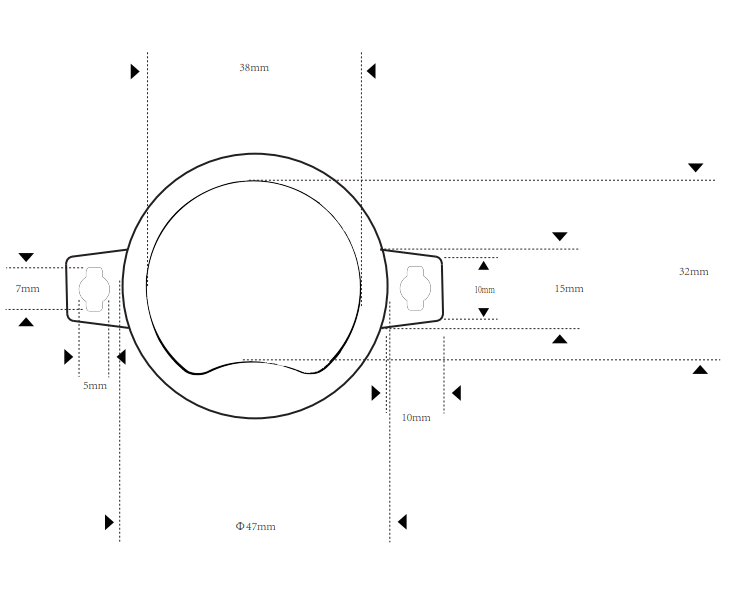
In fact, some vendors even offer customization of their beacons, which is ideal for environments where branding and aesthetics matter, such as retail.
Overall, Bluetooth beacons are simple devices that are made to be compact, rugged, and have a long service life.
That way, they can withstand even the most hectic and demanding of environments, which makes them ideal for any business, from retail and restaurants to healthcare and construction.
But how exactly do they work?
What Do You Need to Work With Bluetooth Beacons
To get started with using beacon technology, you’ll need these three components:
- Bluetooth beacons
- Bluetooth receiver
- Software or app
Here’s how they work.
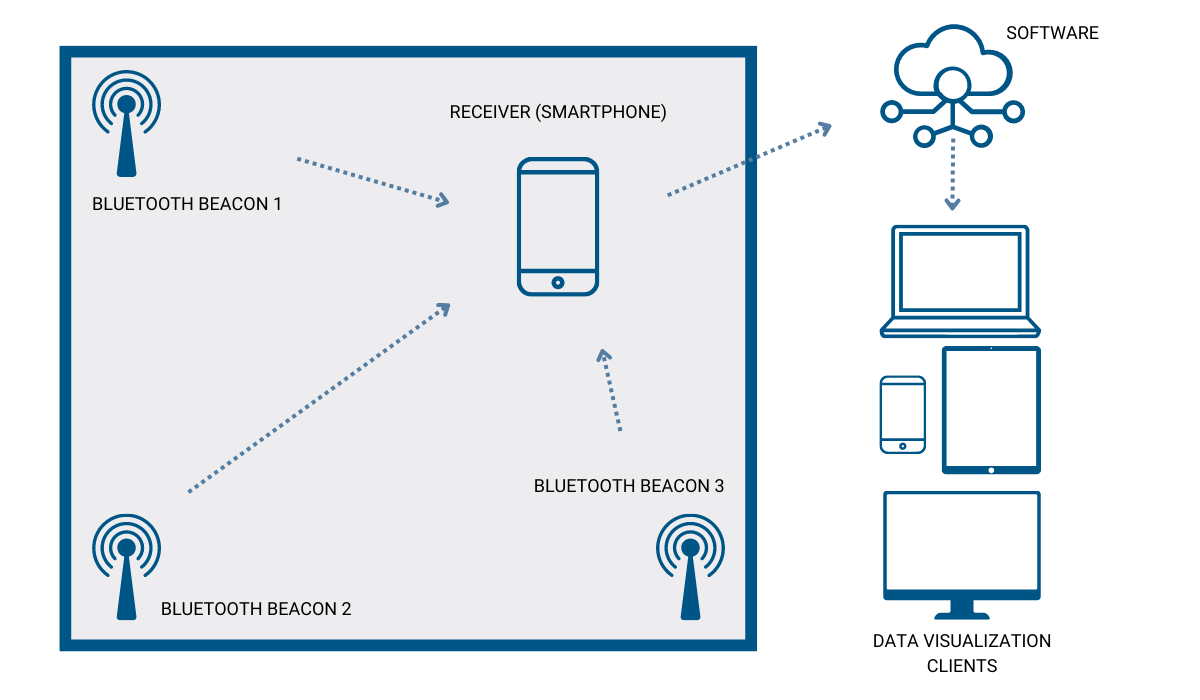
Wireless Bluetooth beacons emit a signal that’s then picked up by a Bluetooth receiver.
The receiver can be any Bluetooth-enabled device, from smartphones and tablets (both Android and iOS) to laptops.
The software or smartphone application identifies the beacons within a specific range and displays information such as the beacons’ presence and/or distance.
GoCodes Asset Tracking’ own Bluetooth beacons rely on a smartphone app to pick up broadcasted data of all beacons within 300 feet.
This data includes:
- Beacon’s/tagged asset’s identity
- Distance between beacon/asset and smartphone
- Different environmental data, such as for example, temperature and acceleration
The GoCodes Asset Tracking app identifies your location on Google Maps, so with every step you take, it can zero in on the Bluetooth beacon, enabling you to find your tagged asset in no time.
What’s more, your assets remain identifiable, even if they’re obscured from sight.
For instance, if there are objects blocking the tagged tools in your warehouse, or even if there’s a wall between you and your assets, you’ll still be able to see them in the app.

Moreover, the GoCodes Asset Tracking Guardian feature, which can be found in the app, monitors all the beacons and notifies you via text message when an asset is removed from within the app’s range, vigilantly protecting your equipment from loss and theft.
What Protocols Do Bluetooth Beacons Use
Beacons, receivers, and software all communicate, but how exactly do they understand one another?
There are, in fact, standards that dictate the language they use, or more specifically, protocols that define the data format Bluetooth beacons broadcast.
A single beacon, however, is sometimes able to broadcast multiple protocols, depending on the configuration and manufacturer.
The three leading Bluetooth beacon protocols today are:
- iBeacon
- Eddystone
- AltBeacon
iBeacon was first introduced in 2013 by Apple at the Apple Worldwide Developers Conference.
This is the first-ever official beacon standard and is still widely accepted by developers and hardware support today.
Officially, the standard is only supported by iOS, but there are available Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) for Android apps to scan for iBeacon signals.
AltBeacon was developed the following year as an, as the name suggests, alternative to iBeacons.
It was created by Radius Networks with the goal of providing a free, open-source beacon standard without favoring any particular vendor.

Finally, in 2015, Google introduced Eddystone, an open-source and cross-platform standard that supports both iOS and Android.
Eddystone added different types of data, i.e., frames, to include more data than the iBeacon protocol, such as for instance, battery voltage, temperature, advertising counts, and more.
However, this protocol was discontinued in 2018.
How Do Bluetooth Beacons Communicate
Now that we covered the languages Bluetooth beacons can use, let’s get into how these languages work.
Of course, there are slight variations from system to system, but in essence, here’s how beacons communicate.
Each beacon has its own ID number that is sent out every second—about ten times per second, to be exact, and a Bluetooth-enabled receiver within range picks up the transmitted data via radio waves.
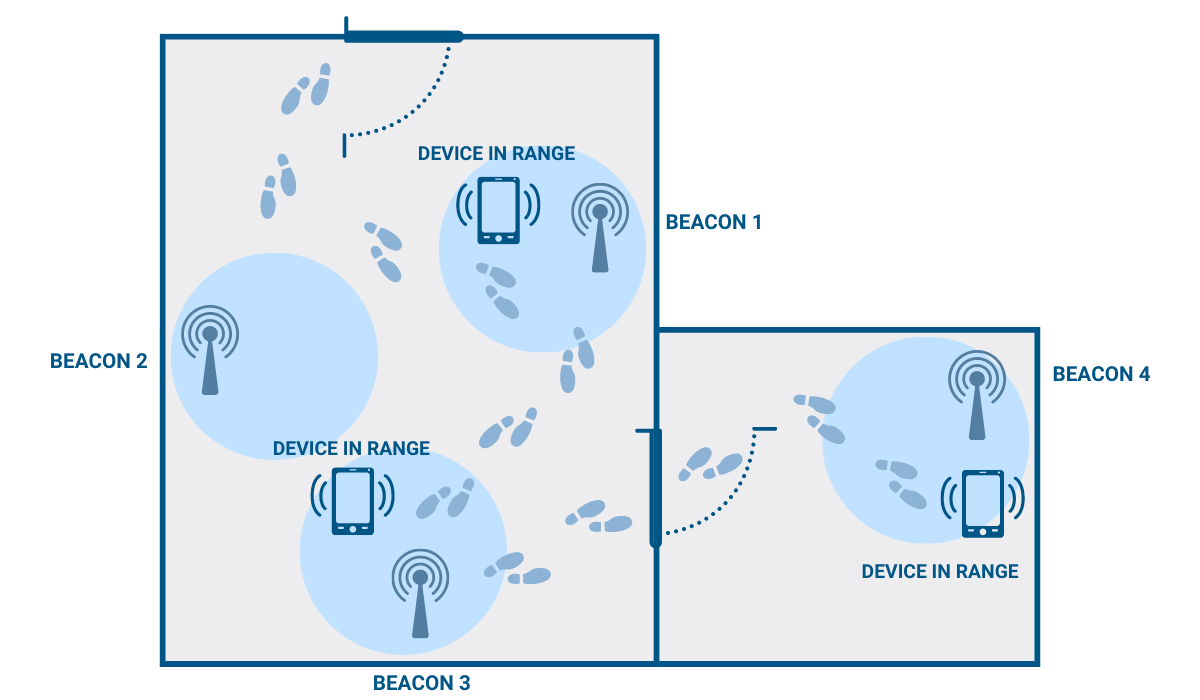
Then, a dedicated app or software recognizes it and either displays it to the user as a self-contained piece of information or it triggers some kind of event on the receiver, like, for example, push notifications, app actions, or prompts.
However, note that the beacon signal only triggers certain actions. The beacons themselves are not the ones who send you these notifications, images—or any meaningful data, for that matter.
What Data Do Bluetooth Beacons Transmit
What they do transmit, though, is a short identifier unique to each beacon that tells the receiver: “Hey, I’m here!”
Let’s once again consider a large warehouse as an example.
Every beacon on every asset in that warehouse would have its own unique ID number registered in the dedicated software, and the software would be able to immediately recognize the identifier and the asset it belongs to.
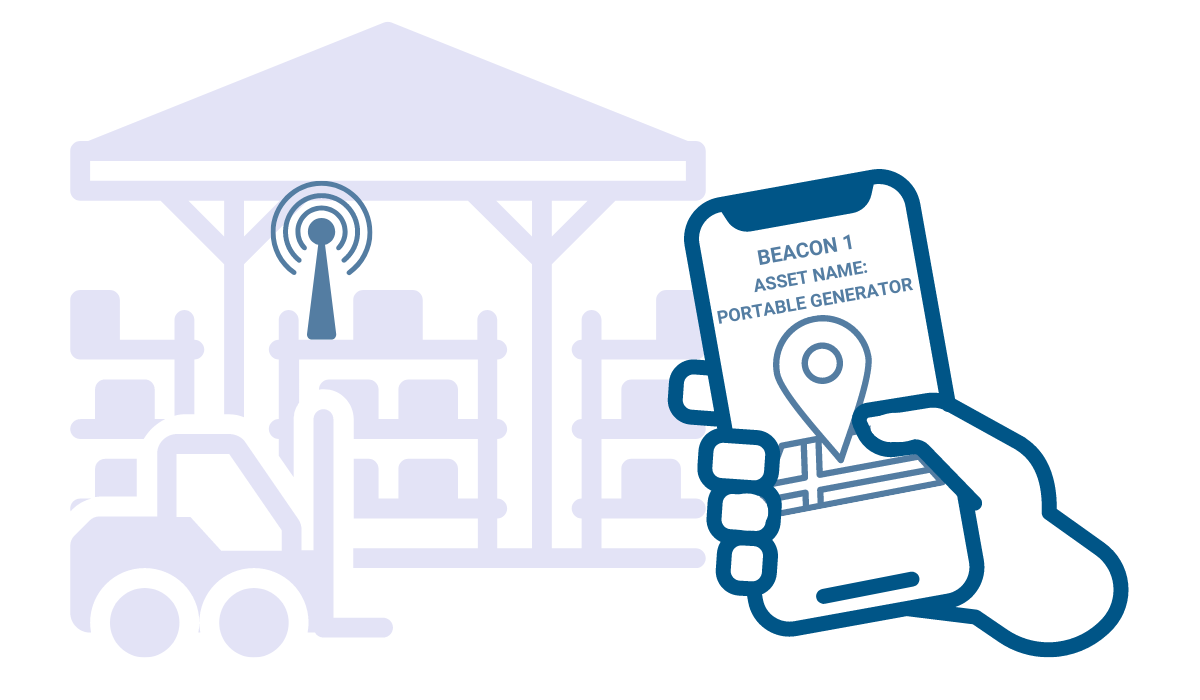
In essence, identifiers transmitted by Bluetooth beacons have very little meaning on their own. It’s the apps and software that do the heavy lifting and make sense of the signals.
What happens when the signal is received depends solely on what the device was programmed to do.
Will it send a discount code or navigation services—the possibilities are pretty much endless.
That’s why the use of Bluetooth beacons is so widespread. They are highly versatile and adaptable to any business’s needs.
What Is the Transmission Range of a Beacon
Generally speaking, a Bluetooth beacon’s signal can reach up to around 300 feet.
However, this is only in theory. In reality, multiple factors can affect the beacon’s transmission range, causing it to drop.
Some of those factors are:
- Bluetooth beacon’s power
- Obstructions such as blocking objects or walls, especially thick ones made of brick or metal
- Interference from other devices
Additionally, Bluetooth beacon protocols operate using three different ranges of distance: far, near, and immediate.
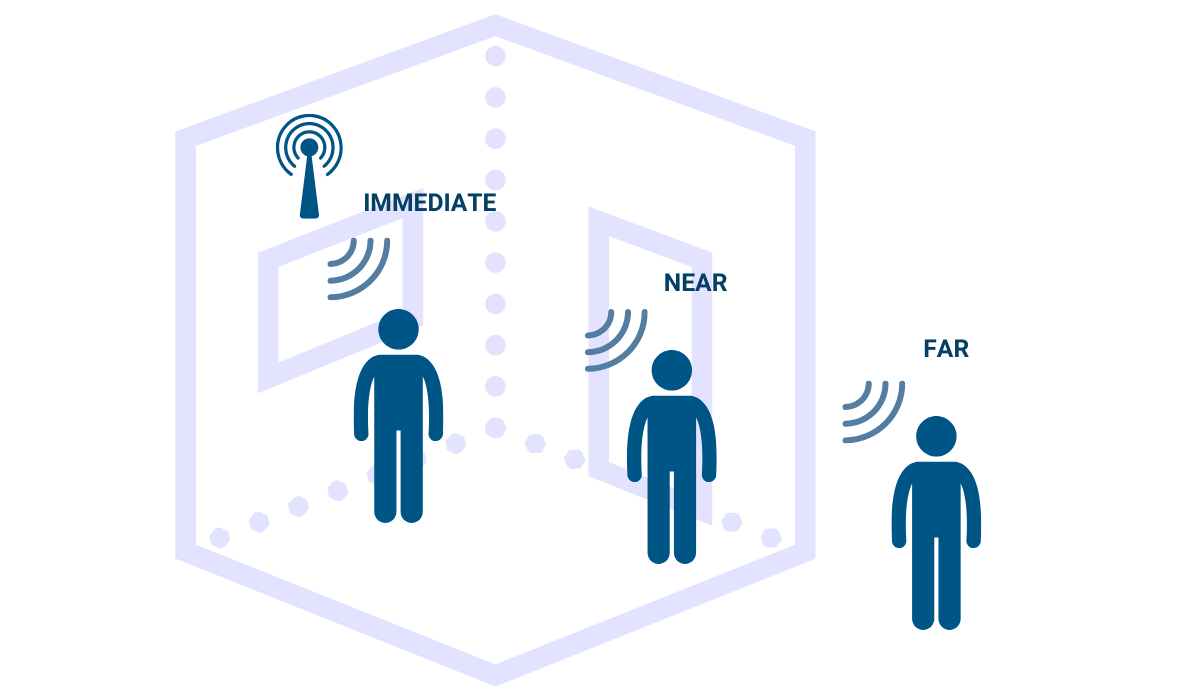
The far signal range is designed to be picked up even if you’re outside the room where the beacon is located, while near range, on the other hand, requires you to be in the same room as the beacon.
Immediate range entails getting really close to a beacon, to the point you’re almost touching it.
Naturally, the higher the range of the signal, the higher the battery consumption will be.
Overall, Bluetooth beacons are able to reliably transmit up to around 100 feet, provided there are no signal obstructions, but their typical operating range is 6-16 feet.
As a result, they’re most commonly used for short-range applications.
Do Beacons Use Bluetooth Classic or Low Energy
From asset tracking and access control to fleet management and onsite environmental monitoring—there are so many applications of beacon technology in the construction industry alone.
Each of these tasks, however, requires a long service life. So how do these tiny devices manage to function for so long without draining their batteries?
This is because they rely on Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE).
Unlike its older counterpart—Bluetooth Classic—Bluetooth Low Energy has more limited data capacity and, in turn, uses much less energy.
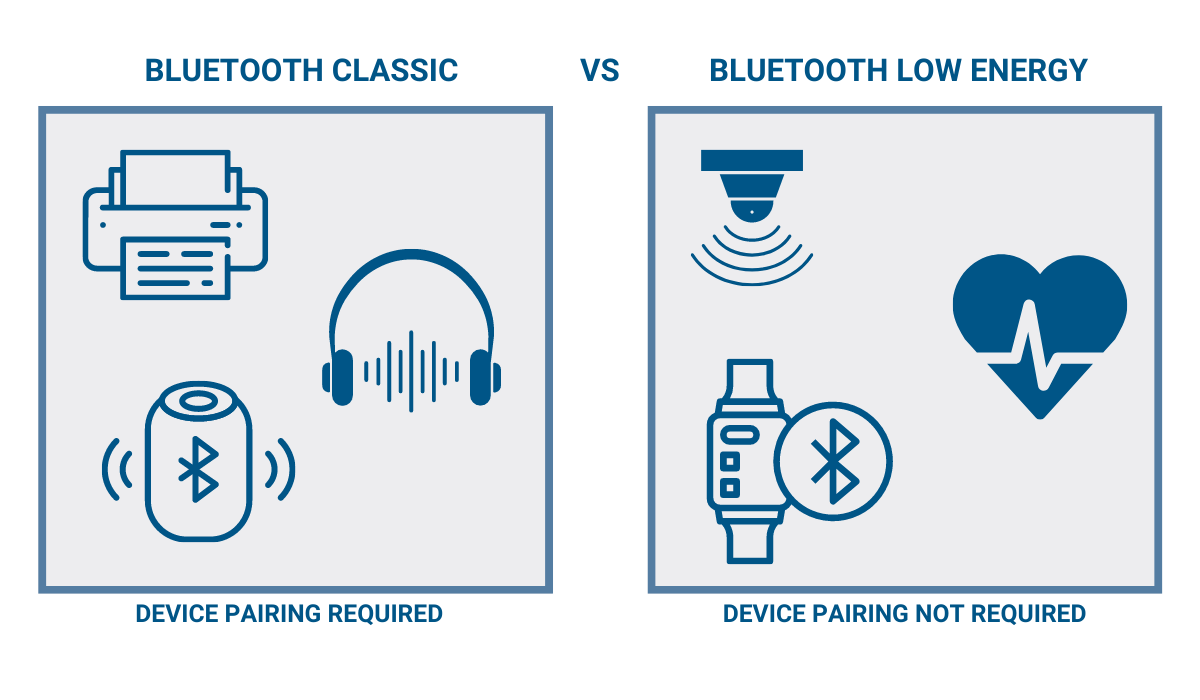
Usually, BLE consumes 1-20% of Bluetooth Classic’s power and has 15-50% of its speed. This balance between performance and battery consumption is crucial for beacons’ longevity.
As a result, the terms Bluetooth beacon and BLE beacon are often used interchangeably. After all, without BLE, the beacons would not be possible, at least not in the way they exist today.
Conclusion
All in all, there’s more to these tiny, battery-powered, and simple-looking devices than it first meets the eye.
Although the beacons’ hardware and how they operate are relatively uncomplicated, they can be a powerful tool for any business out there, provided they’re used strategically.
Therefore, if your own company could benefit from an inexpensive yet efficient solution for better asset or personnel tracking, fleet management, or security, definitely look further into Bluetooth beacons to see how they can take your business to the next level.