The construction industry uses a wide range of materials for different projects.
Generally, we can sort building materials into two categories: natural and synthetic. Materials like stone and wood are natural, while steel, concrete, or plastics are synthetic (or man-made) materials.
Each material has unique properties which make it ideal for specific uses in construction. But choosing the right ones is not easy when you start a new construction project.
So, here is a list of the most common building materials used in construction to find what you need.
In this article...
Concrete
Concrete is one of the most familiar construction materials. It is a composite material made of a fine and coarse aggregate (crushed stone, gravel, and sand) mixed with a binder like Portland cement and water.
The mixture is later left to harden and cure, so the finished mass is what we usually think of as concrete.
While concrete typically dries after 24 to 48 hours, and you can walk on it without leaving footprints, the entire drying process usually takes 28 days to reach maximum strength.
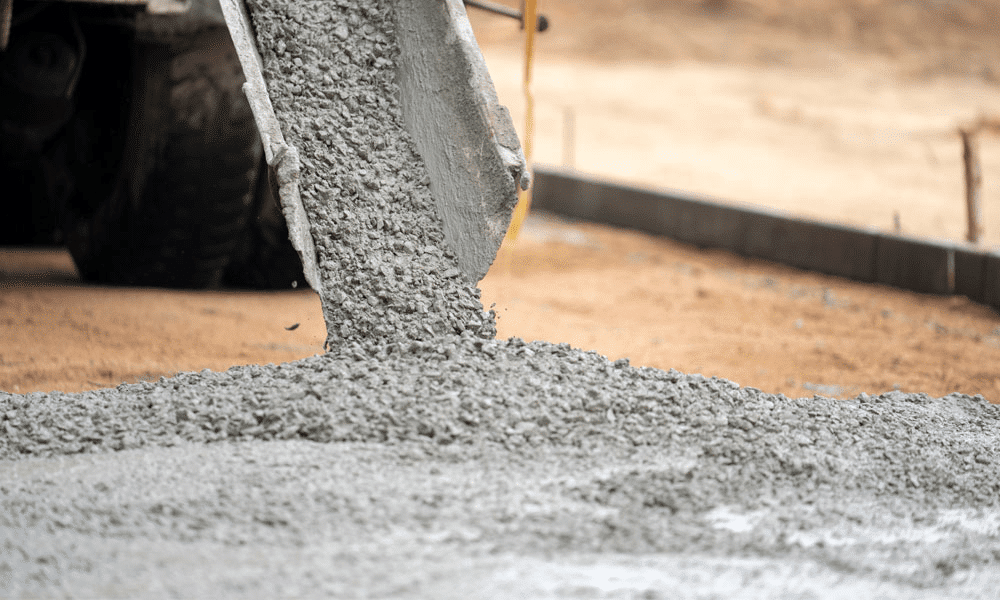

Now, the strength of concrete can vary drastically, depending on the mix, but it’s best used for house foundations because it can carry a heavy load and withstand different environmental forces. In most other cases, you’ll still need extra reinforcement like steel rods or rebar.
This is known as reinforced concrete, and it is applied for large-scale projects such as bridges, dams, and stadiums.
The appeal of this type of concrete is in its resistance to fire, dampness, and weather, as well as its low maintenance costs. In addition to that, it’s more cost-effective when compared to steel structures.
The best thing about concrete is its versatility and adaptability. You can pour it to take any shape a construction project requires, and the hardened material is very durable.
So, in light of the costs and versatility of concrete, it’s no wonder the material is widely used in construction.
Masonry
When we think about masonry, we usually think about structures made of bricks.
But the term masonry can refer to different structures made up of individual building blocks bound together by a type of mortar.
While in most cases these individual units are bricks, you can also find glass, stone, and cement blocks in masonry structures.
Historically, bricks were a popular building material due to their high compression and heat resistance, but their downside is that they are also very brittle and can break if you drop them.
Masonry is mostly used to construct load-bearing walls, and it can support multi-story buildings if reinforced with concrete.
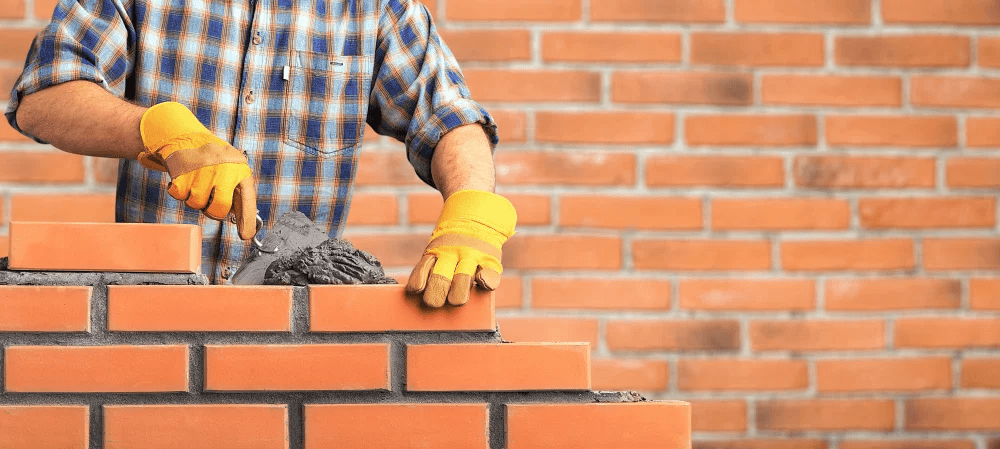

Bricks were widely used from the 1700s to the 1900s because they were fairly cheap to produce, but they weren’t resistant to earthquakes.
In modern times, to prevent brick buildings from falling, architects reinforce them with steel rods.
Masonry most commonly finds its use in foundations, gabion construction, walls, fireplaces, and decorating finishes.
So, just like other low-cost, durable, and versatile materials, masonry will continue to be a popular choice among many contractors.
Stone
We have knowledge about some of the oldest civilizations in the world because of a very simple reason. They used stone to build their cities and buildings.
Stone is one of the longest-lasting building materials in the world. It is incredibly durable, heavy, and has high compressive strength, so it’s not surprising that people have been using it for thousands of years to build structures.

Yet, stone has some drawbacks architects and contractors must consider before building with it.
First, it’s an incredibly dense and heavy material, making it challenging to work with. Also, it’s not an efficient insulator and, therefore, is ineffective for colder climates.
Despite these shortcomings, stone can still be used in other areas in construction.
For example, ordinary stone is cheap and can be used for masonry works for walls, dams, and bridge piers. On the other hand, more expensive types of smoothly finished stone, like marble and granite, can be used for countertops, floors, and support structures.
In a nutshell, stone has many uses in construction, and it’s not going away any time soon.
Steel
When we look at tall modern buildings or large industrial facilities, we notice that they have one thing in common: they are largely built from steel.
Steel is a metal alloy made of iron and other materials, such as carbon, to make it stronger and more resistant. But it is also a lightweight material that’s easy to work with, and it retains its structural properties even when you bend it.
Some other qualities of steel are as follows:
- Easy to install in any environment
- Stainless steel is resistant to corrosion and oxidation
- The level of fire resistance depends on the type of steel
On the other hand, steel has some drawbacks like high cost (in comparison to other metals), high probability of breaking down when exposed to high temperatures, and susceptibility to corrosion if improperly installed.
Despite this, it is still widely used to build skyscrapers, bridges, internal fixtures (rails, stairs), utilities (water, fuel, and gas lines), and as a structural reinforcement.
Steel can also be found as an ingredient in standard construction products such as nails, screws, or bolts.
As you can see, steel has widespread use, and it’s an ideal choice for building large structures.
Aluminum
Aluminum is another popular metal in modern construction.
While pure aluminum isn’t suitable for building because it’s not strong enough, aluminum alloys meet the requirements for construction. The most common aluminum alloys are made with copper, magnesium, and zinc. These alloys can later be cast, forged, or welded easily.
So, because it’s strong, lightweight, and flexible metal, it’s widely used in construction.
For example:
- Window frames, moldings, and exterior wall panels
- Roofs and walls
- Staircases and railings
- Power and chemical plants, paper mills, petroleum refineries (for protection against corrosion)
But the great thing about aluminum is that structures can be easily assembled, disassembled, and transported when needed. The metal also excels in other areas.
For example, it is very durable when exposed to low temperatures, so it is more suitable for colder climates than steel.
Furthermore, aluminum is also resistant to water, corrosion, and UV rays, making structures made from it highly durable.
Even better, they don’t require special maintenance and can easily stand for 25 to 30 years without any intervention.
To sum up, aluminum has become an important construction material due to several beneficial properties. It is also widely available, making it a perfect choice for various construction projects and applications.
Copper
People have been mining copper for thousands of years. And there are good reasons for this.
This naturally occurring metal is corrosion-resistant, durable, and lightweight. It is reddish-brown in color, but it can oxidize to blue-green. Additionally, it is soft and malleable, but it is also stable and sturdy due to its low thermal expansion.

Because of its many beneficial properties, it’s used in construction in the following areas:
- Rainwater and heating systems
- Water pipes
- Roofing
- Cladding
- Oil and gas lines
- Electrical wiring
So, because of its broad use and general versatility, almost 43% of copper produced in the US in 2020 was used in the construction industry. Construction experts work with copper in different ways, mainly by soldering and welding it to create joints.
Due to its great physical properties, such as strength, corrosion resistance, and conductivity, it’s safe to assume that copper will be used in construction for a very long time.
Wood
Just like stone, wood is one of the oldest building materials in the world. But even though it’s not as durable, you can find wooden structures in most climates.

In general, it is a lightweight, easily modified, and inexpensive building material, but an interesting thing about wood is that its qualities depend on the type of tree that is used.
So, for example, teak is durable and fire-resistant, so it’s used in house construction, railway carriages, and manufacturing ships. Spruce wood can withstand saltwater, so it’s used for underwater structures.
Basically, specific species are better suited for different uses. The right choice depends on the conditions and project requirements.
But the reason why wood is still widely used, aside from its physical qualities, is that it’s a readily available natural resource, while being environmentally sustainable.
Wood’s versatility, cost-effectiveness, and compatibility with other materials such as steel or aluminum make it a popular choice for construction companies.
Ceramics
Another highly versatile building material is ceramics. But what are ceramics exactly?
By ceramics, we mean objects like tiles or shingles made from a mixture of minerals like silica sand.
These essential raw materials are heated at high temperatures to create a firm material that will retain its properties for years without maintenance.

Some of its other qualities include:
- Heat resistant
- Long-lasting and resistant to scratches
- Good insulators
- Unreactive with other chemicals
But a big disadvantage to ceramics is their fragility. In most cases, if you drop a ceramic tile or suddenly change its temperature, it will shatter. Yet, they are still widely used in indoor or outdoor environments.
So, the most common uses for ceramics are fixtures such as countertops, bathtubs, sinks, or coverings such as tiles used for patios, staircases, or porches.
Ceramic shingles are used in warm climates for insulation and protection against heavy rains.
While we mostly associate ceramics with decoration and design, their physical properties make them one of the hardest and most resilient building materials in construction.
Glass
There is a reason glass is mostly used as a building product for windows, facades, and skylights.
While it is a hard substance made from mixtures of sand, lime, and silicates, it is very brittle. On the other hand, properties such as transparency and weather resistance make it excellent for letting in light but protecting against the natural elements.

Most importantly, special types of glass can resist ultraviolet and infrared transmission. It is also a great insulator against heat, electricity, and electromagnetic radiation.
Here are some other types of glass used in construction:
- Tinted glass
- Float glass
- Shatterproof glass
- Laminated glass
- Glass blocks
- Glass wool
All in all, glass is yet another versatile and common building material widely used in construction.
Plastic
While plastic is considered environmentally unfriendly and poorly suited for consumer goods, it is still widely used in construction.

As a term, plastics covers a range of synthetic materials made from different polymers. In construction, the most popular plastics are acrylic, polycarbonate, polyvinyl chloride (PVC), and polystyrene (PS).
All of them have key properties that are useful in construction, like strength, durability, waterproofing, light weight, and the ability to be molded into various shapes.
Because of this, we can use them for various purposes:
- Flooring (polyvinyl chloride (PVC) and polyethylene)
- Roofing (vinyl and polyurethane foam)
- Insulation (polyurethane spray)
- Pipes
- Windows (vinyl, polycarbonate)
In general, plastics are very adaptable, durable, and inexpensive, ensuring its application in almost all areas of the construction industry.
Fabrics
Fabrics are flexible materials ‘’stretched’’ over a structural framework or cabling system that holds them in position. They can be used in construction to create temporary structures like roofs, tents, and shading.
The great thing about fabric structures is that they can cover large areas without supporting columns in some cases.
They also use less material than other building materials, but they don’t provide good insulation and have a shorter lifespan.
Here are some common types of fabrics used in construction:
- Cotton
- Polyesters
- Vinyl-coated polyester
- Vinyl-laminated polyesters
- Fiberglass
- Woven PTFE
- ETFE foil
- Meshes, netting, and film
- Blackout fabric
Most fabric structures are easily assembled and relocated, and recent innovations in fabric manufacturing produce more durable and environmentally resistant fabrics.
This allows wider application and improved compliance with construction standards.
Paper
Paper is not just useful in a construction company’s office. It can also be a building material.
Building paper is very thick and can provide weather protection and thermal insulation.
It is one of the main ingredients in drywall, but it’s also used as an additional waterproofing layer in roofing or for flood protection in basements.

Some common types of building paper include:
- Sheathing paper
- Floor lining paper
- Tar paper
- Asphalt felt paper
This building material is easy to install and replace. Another great use of building paper is for stucco and masonry application to prevent water from getting into contact with wood and metal.
Some building codes demand using two layers of building paper for this application.
In the end, although it’s not as versatile as other materials, building paper is still a common choice among contractors for building.
Conclusion
Architects and contractors must consider various building materials’ structural abilities and physical properties when planning construction projects.
Each material has different strength, weights, and durability, and not all are suited for the same types of climate either.
Luckily, with a wide variety of building materials available, you can find a suitable material for your project while keeping track of costs and design requirements.