Bluetooth technology has been around for a while now, serving many different purposes.
Initially, it was mostly employed for personal use, but with the appearance of Bluetooth beacons and then tags, businesses across different industries began to find new and creative ways to utilize this technology.
Soon, such beacons and tags became indispensable in a whole range of sectors, from manufacturing, logistics, and retail, to tourism, healthcare and many other sectors.
Although the terms “beacon” and “tag” are often used interchangeably, there is a difference between the two.
In this article, we explain in which ways they differ from each other and, more importantly, when each of them should be used.
But first, let’s shed some light on what exactly these devices are.
In this article...
What Are Bluetooth Beacons
Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) technology was introduced in 2010, with its primary focus, as the name suggests, on reducing energy consumption, which, in turn, impacted how we use
Bluetooth and significantly broadened the application spectrum of the technology.
It was precisely this BLE technology that made Bluetooth beacons possible. But what exactly are they?
The beacons are small, wireless, and usually fixed devices that periodically transmit signals for other devices to see.
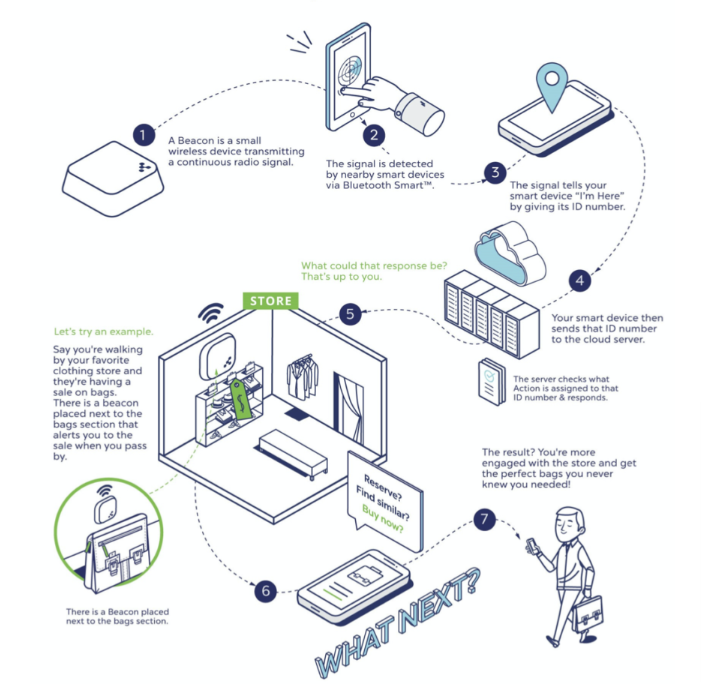
Much like the lighthouses they’re often compared to, which emit light for sailors to see, Bluetooth beacons transmit the radio signal that is then picked up by Bluetooth-enabled devices, such as smartphones.
The signal contains basic information like the device ID and the battery level.
Although beacons do not transmit location data, the receivers can detect their location by calculating it based on the knowledge of where the beacon is located and how far it is from the receiver.
In other words, they are ideal for navigation in large buildings, such as warehouses.
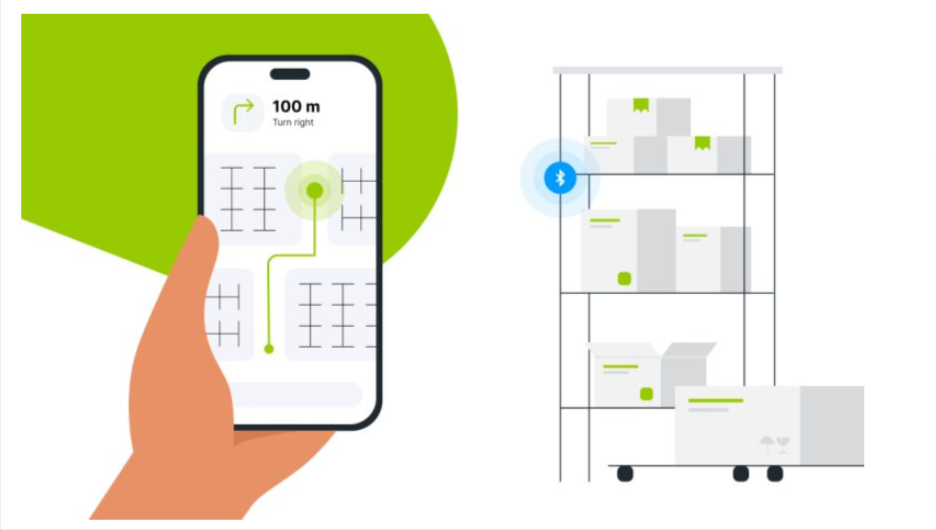
Being so small and practical, Bluetooth beacons find their applications in many different industries and settings.
For instance, they can be used for automated check-ins of vehicles when they return to the base or for monitoring the air quality in an office building.
In other words, Bluetooth beacons truly are a practical and versatile solution for many businesses.
What Are Bluetooth Tags
It should be noted, though, that the versatility of Bluetooth beacons is somewhat limited by the fact that they are immobile devices. This is where Bluetooth tags come in.
Unlike their predecessors, Bluetooth tags are meant to be used on the go.
These dynamic devices are able to change their operating behavior based on their location, state of motion, and other factors instead of simply broadcasting signals statically.
Their mobility is what changes the game in the application of Bluetooth technology for either personal or commercial and industrial use.
From tagging and tracking your luggage in a busy airport to tracking tools and equipment of all sizes on a construction site, Bluetooth tags prove themselves to be an excellent solution for tracking movable assets.
And although both Bluetooth beacons and Bluetooth tags operate by transmitting signals picked up by Bluetooth-enabled devices, they find their applications in entirely different areas.
The fact that these two types of technology serve different purposes dictates many of their traits.
As you’ll see, this will be a common thread throughout the following sections, in which we cover the main differences between beacons and tags.
Physical Properties
Let’s begin with the most obvious difference: the physical properties of Bluetooth beacons and Bluetooth tags.
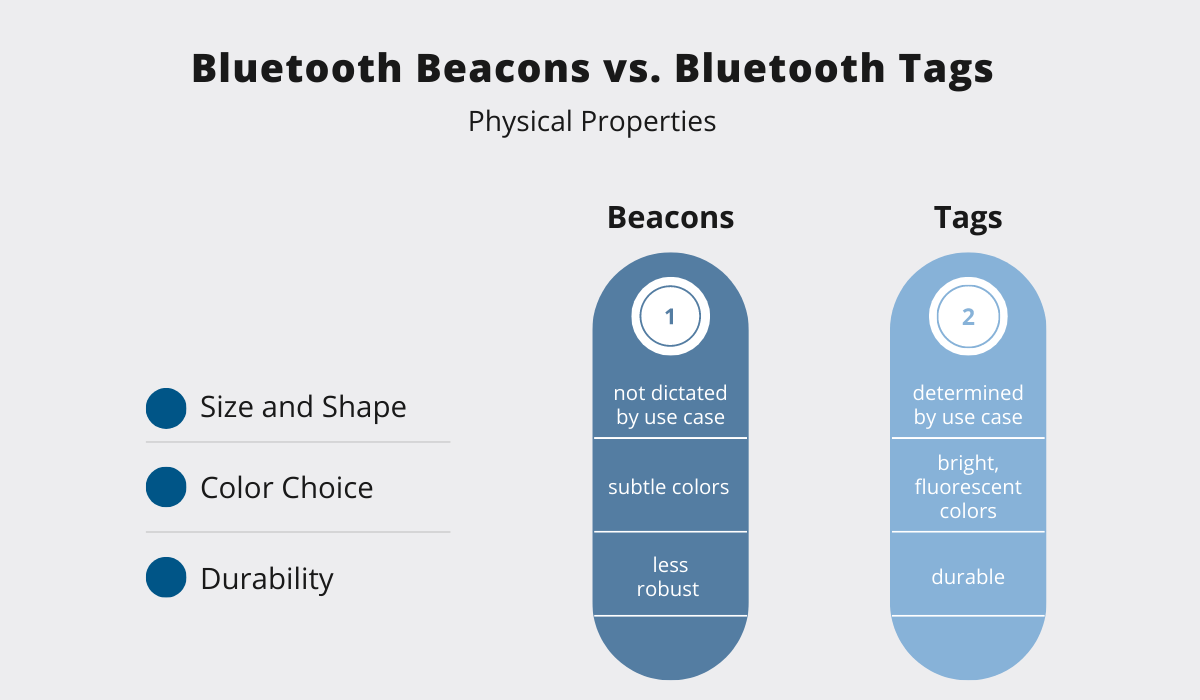
Seeing as beacons are meant to be permanently mounted, their appearance needs to be inconspicuous. This is reflected in their color, which usually blends in with the surroundings.

That’s why beacons tend to be white, gray, or black.
On the other hand, since tags are usually used for asset tracking, they need to be more easily recognizable, especially if they’ll have to be removed at some point.
For instance, if tags are attached to a product in a warehouse, they should be removed before shipping.

Therefore, bright or even fluorescent colors are more common for tags.
Moreover, unlike tags, the size and shape of the beacons are not determined by their use case.
Since they are fixed in one location, their form is of little relevance.
In contrast, tags are attached to assets of different types and of different uses.
So naturally, a tag on an ID badge will differ greatly in size from, let’s say, an industrial tag attached to a larger piece of equipment.
Moreover, in that same vein, tags are usually required to withstand much more mechanical stress than beacons, which demands greater durability.
In other words, while beacons are installed in a warehouse, where they’ll spend their whole life cycle without being moved or touched, tags are often subjected to continuous motion, high acceleration, and collision, which calls for a more robust design.
Device Mobility
Besides the physical properties, one of the most apparent differences between Bluetooth beacons and tags is their (im)mobility and mounting requirements stemming from it.
Once a beacon is installed, it will no longer be removed, meaning it needs to be appropriately and firmly mounted.
The choice of location, therefore, plays an important role here because once you decide where to put the beacon, it can’t be moved.
In other words, make sure you plan your beacon position carefully and, to ensure you’re doing everything correctly, follow these simple rules.

Now, tags are somewhat trickier, because their mounting requirements vary.
To elaborate, just because they’re mobile doesn’t mean tags don’t need to be firmly secured to an asset.
You don’t want them to detach accidentally, after all. On the other hand, they still do need to remain demountable so they can be removed when required.
As a result, there are different mounting solutions, each accommodating different needs and preferences.
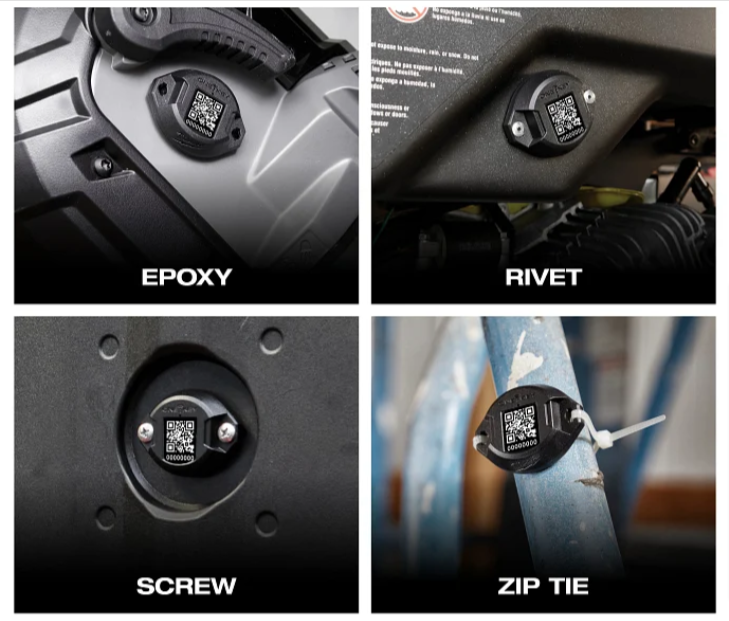

Essentially, anything from zip ties, Velcro, and tape to magnets, epoxy, bolts, and screws can be used for mounting Bluetooth tags.
Deployment Density
The onsite density of Bluetooth beacons is relatively low since usually there’s one device on a grid of 6-9 ft distance.
To illustrate, they can be uniformly allocated through a large factory or warehouse and serve as checkpoints for real-time tracking of security guards.
In other words, beacons are evenly distributed throughout the environment.
On the other hand, the onsite density of tags can be very high, with thousands and thousands of tags per facility.
Moreover, since they’re attached to movable objects, they are not as evenly distributed as Bluetooth beacons. Instead, they can be highly concentrated in particular areas of a facility.
Having so many active devices simultaneously broadcasting signals could potentially very quickly overburden the air interface.
However, tags have the ability to switch states when needed. Therefore, transmission rates can be set based on asset motion, thus reducing air interface load.
After all, not all of your assets are moving simultaneously, so it’s wise to allocate air interface to those that are in motion.
Data Transfer
Another key difference between beacons and tags lies in the way they transfer data between the device and the receiver.
Beacons rely on wireless data transfer because here, transmission is more crucial than how the data moves between a Bluetooth beacon and the Bluetooth-enabled device, i.e., the receiver.
Conversely, tags use radio signal propagation to better estimate the source of the signal since they’re used more frequently for positioning.
What all of this boils down to is that different modes of data transfer require different conditions.
For instance, phenomena such as rich scattering, shadowing, or multipath propagations help with the wireless transfer but interfere with radio signal propagation, so it’s important to minimize them when using Bluetooth tags.
This is also why tags’ antennae need to be carefully designed—they are what ensures the better visibility of a Bluetooth tag.
Transmission Frequency
Bluetooth beacons and Bluetooth tags are also differentiated by their transmission frequency.
Beacons are more predictable in this regard as they’re mounted to a fixed location and transmit a more rapid, constant signal in accordance with a predetermined profile.
In other words, its behavior is simple, making its battery life easier to anticipate.
The dynamic behavior of Bluetooth tags is more advanced, and so their transmission actually depends on different factors, such as their location, whether or not they’re in motion, or commands from the centralized system.
This change of states influences transmission rates and power usage, which in turn extends the battery life of the tags as well.
To elaborate, a tag attached to a piece of equipment can be configured to transmit more frequently while the equipment is being used and then less frequently during downtime, thus regulating power usage and prolonging battery life.
When Should You Use Bluetooth Beacons
To put it in the most simple terms, beacons are used on immobile assets. If you’re looking for a Bluetooth device to attach to your wall or still objects, beacons are the way to go.
Let’s get into some specific examples of beacons being applied in the construction industry.
Firstly, Bluetooth beacons are very useful for access control, i.e., ensuring that there are no unauthorized personnel entering the job site.
Construction sites are hectic and unsafe as is, so you need to do whatever you can to improve the overall safety of your assets and workers. Beacons do a seamless job of protecting your job sites.
Each time a worker with a Bluetooth-enabled device approaches a Bluetooth access reader, their smartphone quickly connects to the access control system and authenticates the employee.
Secondly, many beacons, GoCodes Asset Tracking Bluetooth beacons included, are able to detect environmental information, such as air quality, temperature, humidity, and acceleration, making them perfect for onsite environmental monitoring.
This way, you’re working towards preventing pollution and creating a smart, future-oriented, and environmentally-conscious construction site at the same time.
Finally, GoCodes Asset Tracking’ app is able to automatically detect the presence and proximity of all beacons within a range of up to 300 ft, which makes indoor navigation easier.
This is especially helpful when you’re looking for assets in your warehouse that are not immediately visible.
For instance, with beacons, it’s so much easier to find tools hidden in different boxes.
When Should You Use Bluetooth Tags
On the other hand, Bluetooth tags work better with mobile assets, and just like Bluetooth beacons, they have many applications in the construction industry.
For instance, tags, combined with asset tracking software, are of significant help when it comes to fleet management.
This complex part of construction operations includes different elements, such as route planning, vehicle monitoring, data collection, and reporting—all of which can be improved with Bluetooth tags.
Since they track the locations of vehicles, onsite operation coordination and planning, as well as checking and counting the vehicles, drivers, and cargo, are all much easier and more effective.
Moreover, with tags, you can also track your personnel and tools, enabling better-informed decision-making about their allocation.
This also reduces unplanned downtime and project delays, since it ensures everyone on the team has accurate data about each tool’s whereabouts, especially if there are multiple job sites you need to manage.
Finally, with the help of Bluetooth tags, construction machinery monitoring can be significantly improved.
In other words, tags with different built-in sensors enable you to keep a close eye on various metrics regarding machinery’s utilization and potentially discover what might be slowing you down, i.e., whether some of the machinery is underperforming and why.
Conclusion
All in all, although both are Bluetooth-based location solutions, beacons and tags are not completely the same.
While Bluetooth beacons are mostly stationary and, therefore, best used for indoor navigation, Bluetooth tags are mobile and so they commonly find their application in asset tracking.
Which solution you should choose is completely up to you and your company’s needs, but hopefully, this article has equipped you with all the necessary information to make a decision that makes the most sense for your business.