Due to their low cost and easy deployment, Bluetooth beacons have emerged as a powerful technology with many applications across different industries.
The construction industry is no exception, as these beacons are especially useful for tracking tools, equipment, and other valuable assets in storage and construction sites.
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the world of Bluetooth beacons, their functionality, and their applications in construction.
In this article...
What Are Bluetooth Beacons
Bluetooth beacons are small, battery-powered devices that transmit signals to nearby mobile devices using Bluetooth technology.
As such, their functionality is directly linked to having Bluetooth-enabled devices like smartphones or tablets that can detect their presence and determine the device’s proximity to the beacon.
Moreover, these mobile devices have an app installed that enables beacon-transmitted data to be processed, stored in the cloud, and interpreted in a user-friendly format, e.g., its location shown on a map.
Here’s how that system works, courtesy of Piping Technology.
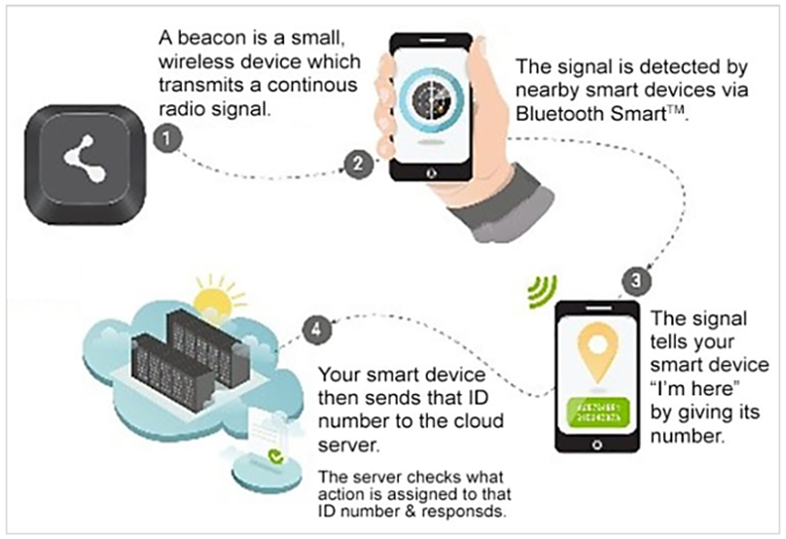
Besides beacons and mobile devices, a Bluetooth-based tracking system can incorporate standalone readers (hubs).
Such stationary devices are specifically designed to detect the presence of beacons in their range.
They are also typically integrated with a cloud-based app, providing extended coverage and seamless data synchronization within the entire system.
Therefore, Bluetooth beacons are an essential part of a wider system that enables wireless detection of “beaconed” assets and processes the transmitted data in an easy-to-use format.
What Are Bluetooth Beacons Used For
As mentioned in the intro, Bluetooth beacons are used in various industries, but we’ll focus on their applications in construction.
Generally, construction companies primarily use beacons for real-time tracking of assets (equipment, tools, etc.) and ensuring construction site security and safety.
In fact, Bluetooth beacons offer significant potential for improving asset visibility, theft prevention, and overall operational efficiency.
For example, by attaching Bluetooth beacons to their valuable assets, construction companies can track their location and movements on a jobsite (or warehouse) in real time.
Here’s an example of how beacons can be used in conjunction with active GPS trackers in a comprehensive asset-tracking system.
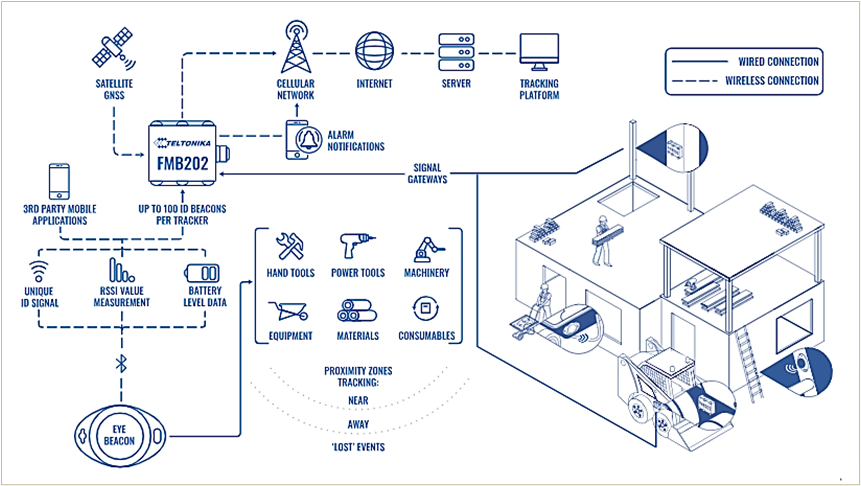
In any system setup, beacons provide complete visibility of assets within the range of the beacon-based tracking system, enabling a construction company to implement theft prevention measures and improve jobsite productivity.
For instance, the site manager can use their smartphone as the central Bluetooth reader that detects all beacon-tracked assets within its range and will send an alert when any of those assets moves out of the phone’s range.
So, in case of unauthorized movement of an asset (excavator, generator, etc.), the manager can take immediate action to investigate and address the situation.
In addition to jobsite security, beacons can be used to enhance workplace safety, i.e., enforce safety protocols by monitoring personnel movement (with their consent) and identifying restricted jobsite areas or hazardous zones.
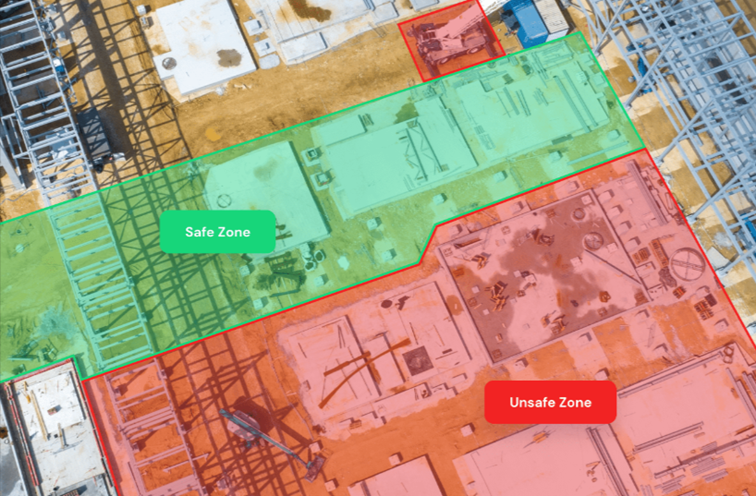
Finally, real-time asset visibility allows workers to use the mobile app to quickly find assets (in storage or on-site) and receive precise instructions on how to get to them.
Concurrently, managers can monitor the movement, usage, and maintenance status of the tracked assets, allowing them to implement different productivity-enhancing measures.
Overall, due to their affordability and ease of use, Bluetooth beacons have various applications in the construction industry, primarily revolving around asset tracking, jobsite security, and workplace safety.
What Hardware Are Bluetooth Beacons Made Of
As said, beacons are small devices (about 2 inches (5 cm) in diameter and 0.6 inches (1.5 cm) in height), usually of simple round design.
The beacon’s enclosure houses its internal components, protecting them from environmental factors such as dust, moisture, and physical impact.

On the outside, each beacon comprises a sturdy, typically plastic enclosure (box), connecting joint, and an identification sticker (explained below).
On the inside, there are several key hardware components, which you can see here courtesy of ELA Innovation.
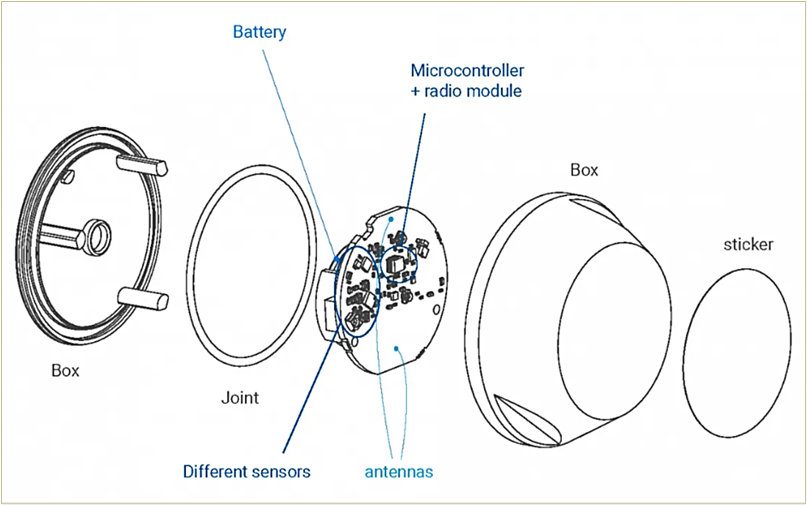
As you can see, the main electronic components of Bluetooth beacons are:
- battery, which acts at the beacon’s power source and is designed to be energy-efficient to ensure longer battery life
- microcontroller unit (MCU), which controls beacon operations, including transmitting signals, managing power consumption, and executing programmed instructions
- radio module or the Bluetooth chipset, which is responsible for establishing communication with mobile devices
- antenna, which facilitates the transmission of Bluetooth signals
As for the sticker, it’s usually a QR code that serves as an additional identification method for the beacon/asset, and users can easily retrieve asset information by scanning it with their smartphone or tablet.
All in all, when coupled with cloud software and mobile devices, these simple devices enable construction companies to, among other things, establish a real-time asset tracking system.
What Sensors Are Common for Bluetooth Beacons
In their basic form, Bluetooth beacons have no sensors.
In other words, they just emit short radio signals that BLE-enabled devices use to determine the beacon’s location.
However, beacons can incorporate various sensors to capture additional data and provide contextual information.
For instance, this beacon is used to monitor temperature fluctuations in its environment.

Some standard sensors used in Bluetooth beacons for construction applications include:
- accelerometer, which measures the acceleration of a beacon-tagged device and can be used to detect (unauthorized) movement or vibrations
- temperature sensor, which monitors ambient temperature and can be used to prevent equipment damage due to extreme temperature variations
- humidity sensor, which monitors moisture levels and can be used to ensure optimal storage conditions for sensitive equipment and materials
Other than these, beacons can be paired with sensors that measure ambient light levels or air quality, while some beacons also have buttons specially designed for emergency and reporting purposes.
In any case, when beacons are integrated with sensors, they can, together with their positioning signal, emit relevant sensor-collected information.
How Do Bluetooth Beacons Communicate
As mentioned, Bluetooth beacons act as small radio transmitters that continuously send signals which are then picked up by Bluetooth-compatible mobile devices.
The communication between a beacon and your phone or tablet is typically one-sided.
This means that the beacon only transmits a small stream of data (covered in the next section), but it does not have the capability to receive data, such as new programming instructions.
Therefore, it’s up to the cloud software (app) on your mobile device to recognize the signal and use it to trigger an action (depending on its use).
For example, an asset-tracking platform like GoCodes Asset Tracking will use the beacon’s signals to identify any tracked assets within the range of the user’s smartphone or tablet and show their location on a map.

As you can see, once it detects the Bluetooth beacon’s signal, this tracking app will also allow users to click on the identified asset to view relevant asset info.
Again, all this means that beacons are still predominantly used as passive broadcasters, where it’s up to different software apps to do all the work.
That said, it’s worth noting that there are already Bluetooth beacons designed for specific use cases where two-way communication is required, meaning they can receive signals from mobile devices and respond with their own signals.
What Data Do Bluetooth Beacons Transmit
Typical Bluetooth beacons used for proximity and location-based applications transmit a string of numbers and letters known as the universally unique identifier (UUID).
This UUID is used by a mobile device to identify and determine its proximity to a specific beacon (asset).
When the beacon is programmed, the UUID (i.e., the beacon frame format) can be customized to indicate a specific country/region/city/facility.
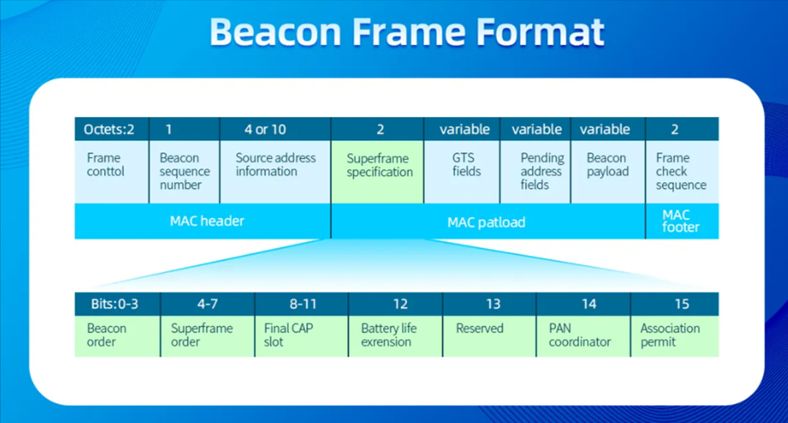
In the context of tracking construction assets, beacons typically transmit only their identifier, enabling asset identification and location tracking.
On the other hand, the beacons with the integrated sensors we mentioned (acceleration, temperature, humidity, etc.) transmit not only their identifier but also the values picked up by the sensors.
Finally, two-way beacons will send different data (messages) depending on the message they receive from the dedicated app on a mobile device.
What Is the Transmission Range of a Beacon
In theory, Bluetooth beacons have a maximum range of up to 300 feet (100 meters), which coincides with the range of most Bluetooth-enabled devices like smartphones and tablets.
However, the actual maximum transmission range of a Bluetooth beacon is closer to 230-260 feet (70-80 meters), depending on various factors such as hardware capability, physical barriers, and battery consumption.
Here’s a general overview of these factors, courtesy of Moko Blue:
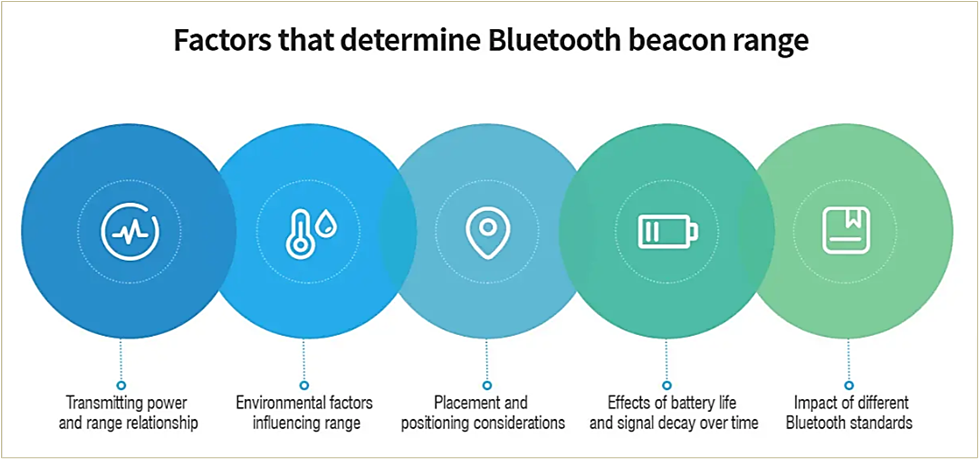
In practical terms, this means that the beacon range is susceptible to many site-specific factors, which will ultimately influence your decision on the optimal transmission range of beacons depending on their use.
For example, in storage applications, it makes sense to prolong the battery life by setting a lower transmission range while relying on mobile devices to do the scanning within their predefined, wider beacon detection range.
This approach allows for efficient asset tracking in confined areas like warehouses while maximizing the beacon’s battery life.
To sum up, the actual transmission range of Bluetooth beacons can be influenced by environmental factors such as obstacles, interference, and signal strength.
These issues can be addressed by strategically positioning portable, standalone Bluetooth signal receivers incorporated alongside BLE-enabled devices.
Do Beacons Use Classic Bluetooth or BLE
Despite their commonly used name, Bluetooth beacons almost exclusively use BLE (Bluetooth Low Energy) technology instead of Bluetooth Classic.
The primary reason for this is lower energy consumption.
Moreover, these two Bluetooth technologies are actually incompatible and used for entirely different purposes.
Here’s an overview of their technical differences, courtesy of Telink.

Simply put, Bluetooth Classic is widely used for transmitting continuous high-data loads (think wireless headphones and speakers).
Conversely, BLE transmits much smaller data loads at regular intervals, which means that it consumes less power, extending the beacon’s battery life.
Moreover, BLE technology offers faster connection establishment, lower latency, and simplified data exchange protocols.
All this makes Bluetooth Low Energy beacons ideal for construction applications like asset tracking, where efficiency (fast connection), practicality, and affordability (long battery life) are essential.
Do Bluetooth Beacons Cause Interference
Bluetooth beacons typically operate on the 2.4 GHz frequency band, which is a globally available spectrum for various wireless devices.
When beacons send their signal, that could potentially cause interference with other devices and networks operating in the same frequency range, such as other Bluetooth devices or Wi-Fi routers.
That said, Bluetooth beacons are designed to minimize interference with other devices by using frequency-hopping spread spectrum (FHSS) technology.
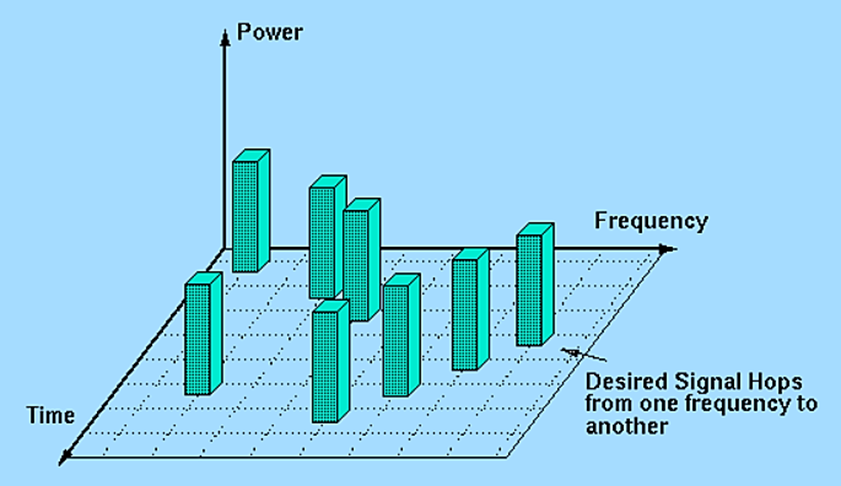
This technology allows beacons to switch frequencies rapidly, reducing the chances of collisions and interference with nearby devices.
For example, interference with widely used Wi-Fi networks is minimized because beacons function at a lower power level and emit only short signals.
Additionally, there is no interference when Wi-Fi routers use other frequency ranges (5 GHz and 6 GHz).
Overall, Bluetooth beacons are designed to minimize or eliminate interference, ensuring their effective operation alongside other wireless devices and networks.
Can Beacons Be Used With All Mobile Devices
Bluetooth beacons can be detected by a wide range of mobile devices, including smartphones and tablets, as long as they support Bluetooth technology.
Both iOS and Android devices have native support for Bluetooth beacons, allowing them to receive beacon signals and interact with associated mobile apps.
Therefore, all you need to use Bluetooth beacons for various construction applications is an internet-connected mobile device with Bluetooth turned on, and a dedicated app installed.
For instance, the GoCodes Asset Tracking Guardian feature is an excellent example of how mobile devices, a cloud-based app, and beacons can work together to protect your valuable assets from disappearing from the jobsite.

In practice, a phone with the Guardian App turned on can be positioned at the center of a smaller construction site (or a zone within a larger one) and instructed to send alerts to the site manager’s phone if any beacon/asset goes out of range.
Naturally, this ability is easily scaled by having more mobile devices (and/or stationary BLE detection hubs), improving asset tracking accuracy and coverage.
Ultimately, the right combination of beacons, cloud software, and mobile devices leads to establishing an effective real-time location tracking system.
Conclusion
Now that we’ve covered a lot about Bluetooth beacons and their possible applications in construction, it’s clear that beacons offer immense potential for companies that want to streamline asset management, prevent theft, and optimize jobsite workflows.
By utilizing these beacons for asset tracking, construction companies can make better-informed decisions, improve operational efficiency, and achieve higher productivity while safeguarding their valuable tools and equipment.