In today’s world of technological advancements, Bluetooth beacons have emerged as one of the most practical and cost-effective asset-tracking solutions across various industries.
Although beacons have diverse applications beyond tracking assets, such as indoor navigation, employee tracking, and proximity marketing, we’ll focus on exploring asset-tracking use cases in various professional environments.
So, if you’re interested in how Bluetooth beacon asset tracking helps companies in different fields streamline their asset management operations, read on.
In this article...
Construction
Before we delve into how Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) beacons are used to track construction assets like heavy machinery, equipment, and tools, let’s explain how such beacon-based asset-tracking systems generally work.
The first component are the BLE beacons (often called tags) themselves.
They are small, battery-powered devices that frequently emit short-range radio signals within the range of up to 300 feet (100 meters).
When a beacon enters their range, these signals are detected by the second component of a tracking system, Bluetooth-enabled mobile devices (smartphones, tablets), and/or strategically positioned stationary BLE signal receivers.
The third and final component is the asset-tracking software (installed on the above devices, typically cloud-based).
The software processes all the detected signals, calculates the location of assets, presents info in a user-friendly format, and provides other valuable features.
In the image below, light green “tags” are actually beacons, and dark green “anchors” are stationary BLE receivers.
At the same time, the gateway collects and sends the signals to the backend infrastructure, i.e., your tracking software’s cloud database.
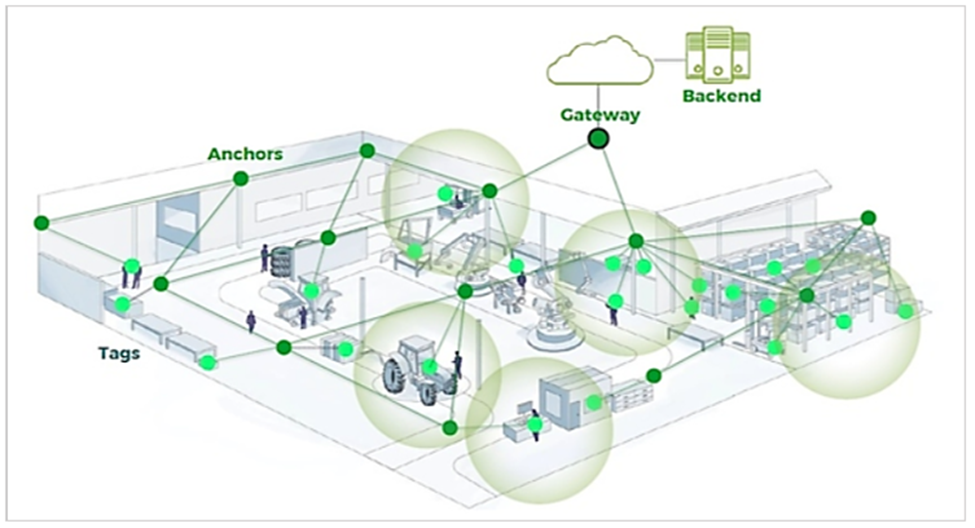
It’s worth noting that fixed BLE signal hubs (anchors) are optional, and the tracking system can work with just one or more mobile devices with Bluetooth turned on and the tracking app installed.
Additionally, beacons can be equipped with different sensors (temperature, acceleration, humidity, etc.).
In any case, the ultimate result of such tracking systems is real-time tracking of assets within a limited area (construction site, warehouse, office, school, hospital, etc.), generating numerous operational advantages for companies utilizing BLE beacons.
As for the construction industry, you can see the top benefits of BLE beacons here.

Note that these advantages of BLE asset-tracking technology are not exclusive to the construction industry, but apply to all fields discussed here.
In construction, beacons have proven to be versatile tools for improving various aspects of asset management and operational efficiency.
They include worker safety, maintenance planning, inventory management, and jobsite workflow optimization, to name a few.
That said, we’ll describe one way Bluetooth beacons are typically used on jobsites: monitoring the real-time location of high-value assets and setting up geofences for theft prevention and site safety purposes.
For instance, you could use Bluetooth beacons provided by our solution, GoCodes Asset Tracking, to tag the most valuable assets on your construction site.
Then, using the GoCodes Asset Tracking Guardian feature, you can turn your phone (or multiple Bluetooth-enabled devices) into a 300-feet security perimeter that will immediately notify you if any beacon-tagged assets leave its range.

This anti-theft feature enables you to take immediate action if one of your assets goes missing from the jobsite, i.e., leaves the geofence established by the app’s Guardian feature.
It’s worth noting that GoCodes Asset Tracking combines its Bluetooth beacons with patented QR code asset tags, also used for tracking, protecting, and managing tools, equipment, and inventory.
Simply put, QR code labels are attached to assets and linked with individual asset data in the tracking software’s database.
Using an in-app scanner, workers can scan QR code tags with smartphones or tablets and access the asset’s info page and the central asset list.
All these components are shown here.

When QR codes and Bluetooth beacons are deployed together, this results in a multi-layered tracking system where low-value assets can be tracked with QR code labels and high-value equipment with BLE beacons.
In other words, this solution combines the advantages of the two most affordable and easy-to-use asset-tracking technologies.
Generally, a beacon-based system is easily scaled to any contractor’s specific needs and budget and can be transferred from site to site (especially if no fixed system components are used).
To recap, the versatility, ease of use, and affordability of Bluetooth beacons make them ideal for asset tracking in construction environments, providing companies with real-time monitoring of asset locations and usage within a specific area.
Corporate
Since we now know how beacon-based asset tracking works, it will be easier to describe and give examples of how beacons are used across different industries and in particular professional environments, starting with the corporate setting.
Generally speaking, corporate environments are full of assets that can be tracked with Bluetooth beacons, starting with IT equipment and office furniture.
Therefore, the scope, design, and functionalities of a corporate asset-tracking system will depend on a company’s specific needs.
For example, beacons can be attached to shared office assets that frequently move around, such as laptops, projectors, printers, and conference room equipment.

In conjunction with mobile or stationary BLE signal receivers and tracking software, this enables real-time tracking of these assets’ locations, ensuring that employees can quickly locate them when needed.
In this case, beacons can also serve as an anti-theft measure, alerting users if these assets leave the building.
Another use case for BLE beacons in office settings refers to maintaining assets like printers, copiers, and dispensers, where an app can analyze usage patterns and trigger service requests when maintenance or refilling is needed.
The same applies to attaching sensor-enabled beacons to the building’s fixed assets, such as HVAC, plumbing, or electrical systems, to monitor their performance and environmental conditions like temperature and humidity.

The sensor-obtained data can be used for triggering emergency alerts (e.g., water leakage, overheating), predictive maintenance, and optimizing the building’s energy consumption.
Additionally—if we count rooms and office areas as assets—beacons can also assist in monitoring the occupancy of meeting rooms or workstations.
They can help employees find available spaces quickly and optimize room allocation.
In both applications, a beacon fixed inside a specific room or at a particular desk/workspace will detect an employee’s smartphone or another Bluetooth-enabled device, and the software app will signal that the room/workstation is occupied.
In summary, Bluetooth beacons offer diverse solutions for asset tracking in corporate settings.
They range from enhanced resource management and anti-theft measures to predictive maintenance and optimized room and workspace allocation.
Education
Educational institutions like schools and universities are large organizations spread out over numerous classrooms, common areas, and storage rooms, often working across multiple buildings.
This means that the equipment they use (laptops, tablets, overhead projectors, lab equipment, etc.) should be tracked for both asset management and security purposes.
Therefore, a beacon-based tracking system can monitor the movement of such equipment used in classrooms, laboratories, and other facilities.
For example, this ensures that valuable tools such as microscopes and other scientific instruments are returned to their designated locations after use, preventing loss/theft and ensuring their availability for other classes.

Naturally, the decision on which assets should and shouldn’t be tracked with BLE beacons is entirely up to the educational institution introducing asset-tracking.
In practice, the price of beacons and their size are the deciding factors.
In other words, just like in other industries, schools and universities can opt to track frequently moved, high-value equipment with beacons and everything else (from textbooks to classroom supplies and other inventory) with barcodes or QR codes for a more cost-effective option.
Of course, when it comes to monitoring and maintenance of their buildings’ systems, sensor-enabled beacons can be utilized.
Wrapping up, educational institutions can deploy beacon-based asset tracking in various applications to improve resource allocation, minimize losses, and create a more efficient environment for students, educators, and staff.
Healthcare
Of course, the versatility of BLE beacons means they have multiple practical asset-tracking applications in healthcare.
In other words, a beacon-based tracking system can be used in healthcare settings to improve asset utilization, minimize response time, increase staff productivity, and enhance hygiene protocols.
For instance, beacons can be affixed to essential medical equipment, such as portable diagnostic machines, IV pumps, and wheelchairs.
This means that a nurse looking for a vacant wheelchair can use a dedicated tracking app on their smartphone to easily locate the nearest one, saving precious time.
Moreover, as discussed in the article below, hospitals can use a beacon-based tracking system to prevent wheelchairs from being misplaced or stolen, which happens to about 25% of their wheelchair inventory.

Another use case for beacons in healthcare refers to monitoring adherence to hygiene protocols and staff efficiency by attaching beacons to cleaning carts used by janitorial staff.
As staff members move the cart throughout different areas of the healthcare facility, the beacon emits signals received by nearby Bluetooth-enabled mobile or stationary devices.
Through the tracking app’s user interface, staff and supervisors can monitor the movement of cleaning carts in real time and see which areas have been cleaned and when, thus bolstering infection control measures.
Overall, beacons and tracking software can ensure seamless coordination and accessibility of vital equipment, reduce staff response times, and ensure adherence to sanitation protocols.
When all of these factors are combined, they ultimately contribute to the delivery of quality patient care.
IT
By now, it’s clear that all professional environments covered in this article typically include a growing number of IT assets like laptops, desktops, tablets, routers, network switches, and the like.
In all these cases, companies will need to decide which valuable and often critical assets should be tracked with beacons and which, due to size and price limitations, with other tracking methods (e.g., QR codes).

That said, there are many more specialized, IT infrastructure-rich facilities that house a multitude of critical equipment, such as data centers, network operation centers, server rooms, and telecommunication hubs.
Such operations, where precision and efficiency are paramount, can use beacons for many specific use cases.
For example, by attaching BLE beacons to portable servers, server racks, network switches, and cable spools, IT personnel can easily locate them when needed (efficiency) and receive alerts if they’re moved from a specific area (security).
Of course, many IT assets are sensitive to temperature fluctuations and environmental conditions, as discussed in the article shown below.

That’s why sensor-equipped beacons are ideal for continuously monitoring temperature and other variables.
In such cases, the tracking app will alert staff if predefined thresholds are breached.
Lastly, we shouldn’t forget that an asset-tracking system will also allow for automated maintenance scheduling for IT assets (tracked with beacons or otherwise), which is critical for IT equipment durability and high performance.
In closing, BLE beacons have many applications in IT infrastructure-heavy settings that companies use to enhance IT asset management, security, and efficiency.
Manufacturing
Various manufacturing plants and facilities are typically filled with a vast array of machinery and equipment spread across a large area.
A single misplaced asset or failed machine can lead to disruption and production delays.
In this sense, manufacturing environments are similar to construction projects and how beacons are used on jobsites.
For instance, manufacturers can use beacons to track the location of different assets (tools, parts, materials) within a production facility to ensure quick retrieval, minimize machine and staff downtime, and optimize maintenance schedules.

In other words, when a specific tool or device is needed on the assembly line, workers can quickly locate it using the beacon’s real-time tracking data.
Likewise, sensor-equipped BLE beacons can monitor machinery parameters like temperature, vibration, and operational status.
For example, if a machine’s vibrations exceed safe levels, the beacon can trigger an alert, which helps prevent costly breakdowns and ensures seamless production.
Therefore, beacon-based asset tracking (with or without sensors) enables manufacturing plants to minimize production floor disruptions, increase productivity, and improve the overall efficiency of their processes.
Conclusion
Having covered just some asset-tracking use cases across different fields, it’s clear that Bluetooth beacons provide companies with real-time asset visibility, streamlined operations, and enhanced security.
These small devices, coupled with the right tracking software, empower businesses to make informed decisions, allocate resources efficiently, and ensure assets are protected and well-maintained.
In short, Bluetooth beacon asset tracking is an easy, efficient, and cost-effective way to take control of asset management and boost overall productivity in various professional environments.